Posted on September 12, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles

In this 2023 article published in the journal
Sensors, Lehmann
et al. of the Mannheim University of Applied Sciences present their efforts towards a research data management (RDM) system for their Center for Mass Spectrometry and Optical Spectroscopy (CeMOS). The proof-of-concept RDM leans on digital twin (DT) technology to answer the challenges posed by RDM of multiple research instruments in their institute, while at the same time addressing the principles of making data more findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR). After introducing the topic and presenting related work as it relates to their efforts, the authors lay out their conceptual architecture and discuss use cases within the context of their spectrometry and spectroscopy work. Then they propose an implementation, proof of concept, and evaluation of the proof of concept within the implementation's framework. After discussing their results, the authors conclude that their efforts contribute to the literature in five different ways, addressing RDM within FAIR, highlighting the value of DTs, developing a top-level knowledge graph, elaborating on reactive vs. proactive DTs, and providing a practical approach to DTs in the RDM at larger research institutes. They also provide caveats and future work that still needs to be done.
Posted on September 5, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
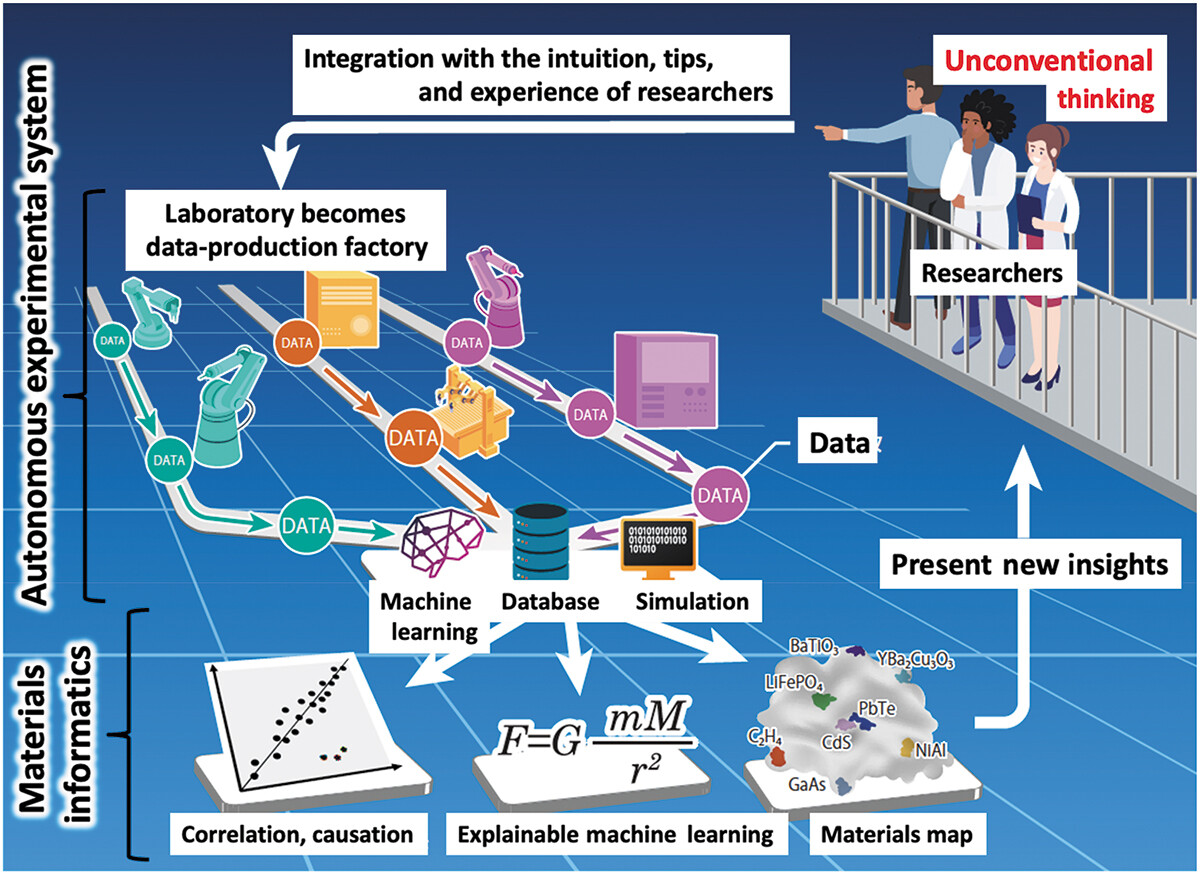
Materials science has been and continues to be an important study, particularly as we strive to overcome challenges such as climate change, pollution, and world hunger. And like many other sciences, the expanding paradigm of autonomous systems, machine learning (ML), and even artificial intelligence (AI) stands to leave a positive mark on how we conduct research on materials of all types. Ishizuki
et al. of the Tokyo Institute of Technology and The University of Tokyo echo this sentiment in their 2023 paper published in the journal
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials: Methods, which discusses the state of the art of autonomous experimental systems (AESs) and their benefits to material science laboratories. After introducing the topic, the authors explore the state of the art through other researchers' efforts, drawing conclusions based upon how AESs can be put to use in the field. After characterizing AESs' use and addressing sociocultural factors such as inventorship and authorship with AI and autonomous systems, the authors conclude that while AES will provide strong value to materials science labs, "human researchers will always be the main players," and this hybrid automation-human approach "will exponentially accelerate creative research and development, contributing to the future development of science, technology, and industry."
Posted on August 31, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
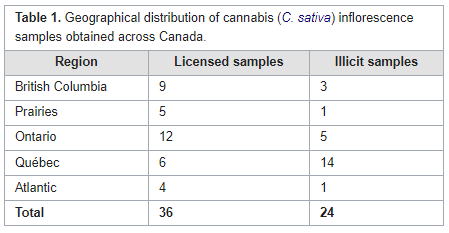
In this brief paper published in
Journal of Cannabis Research, Gagnon
et al. present the results of applying a new analytical technique to quantifying hundreds of pesticides at the same time in cannabis samples. Using a combination of gas chromatography—triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC–MS/MS) and liquid chromatography—triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS), the authors tested not only cannabis samples from licensed retailers in Canada but also illicit cannabis samples acquired from Health Canada Cannabis Laboratory. Their methodology was fully able to manage the search for hundreds of pesticides, discovering only a handful of semi-unregulated pesticides in legal Canadian cannabis, but a surprising amount of pesticides in illicit samples. The authors conclude that their methodology, as demonstrated, has practical uses going forward towards a wider regulatory approach to ensuring Canadian cannabis is as pesticide-free as possible.
Posted on August 21, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
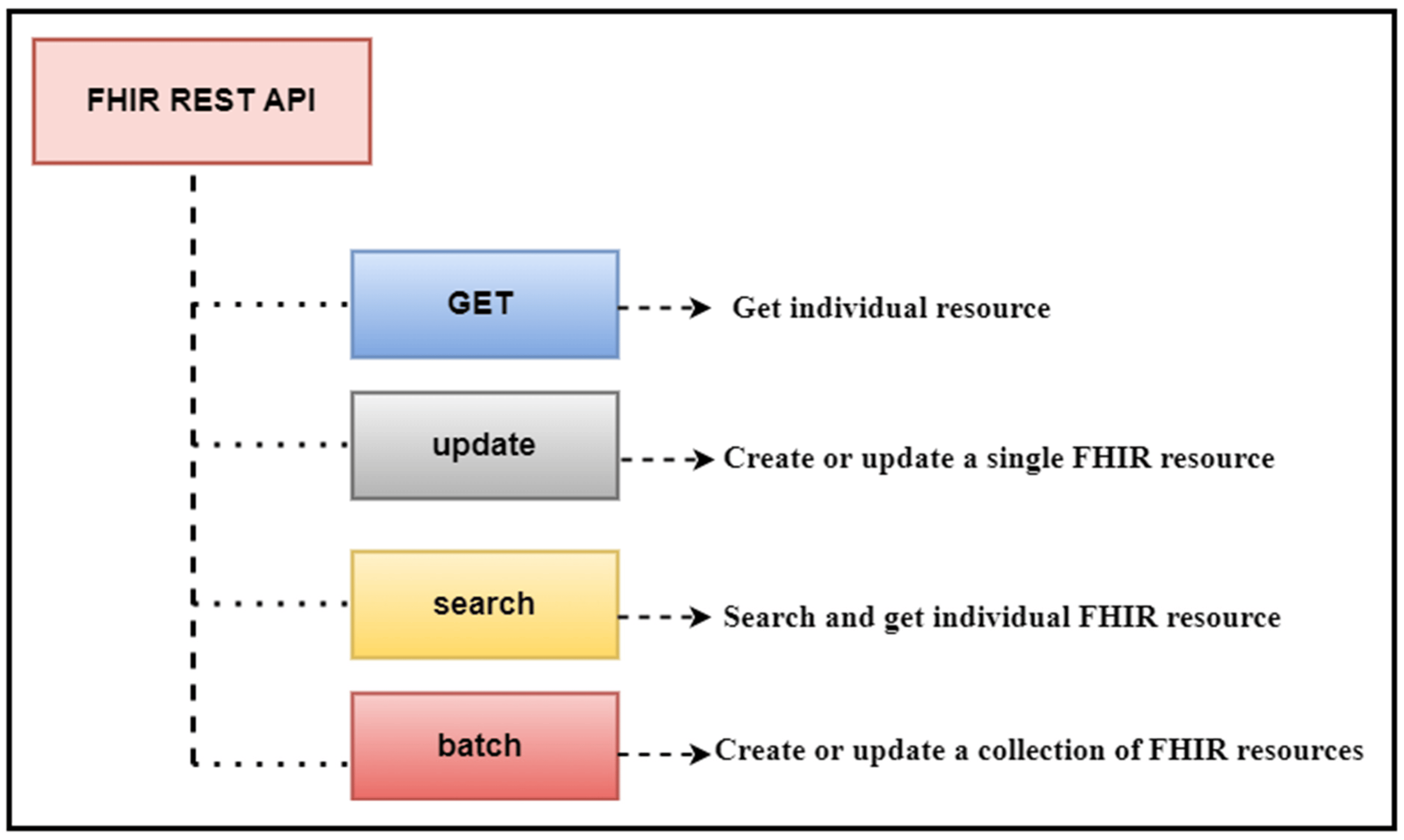
In this 2023 journal article published in
Healthcare, Ayaz
et al. present their work on a "data analytic framework that supports clinical statistics and analysis by leveraging ... Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR)." After providing significant background on the topic, as well as a review of the literature on the topic, the authors discuss the initial preparations that went into developing their framework, followed by the results of their implementation. The authors also present a two-part example with use cases that puts the framework to a test. After discussing the limitations and results of their framework, the authors conclude that it effectively "empowers healthcare users (patients, practitioners, healthcare providers, etc.) to perform advanced data analysis on patient data used in healthcare settings and represented in the FHIR-based standard."
Posted on August 14, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
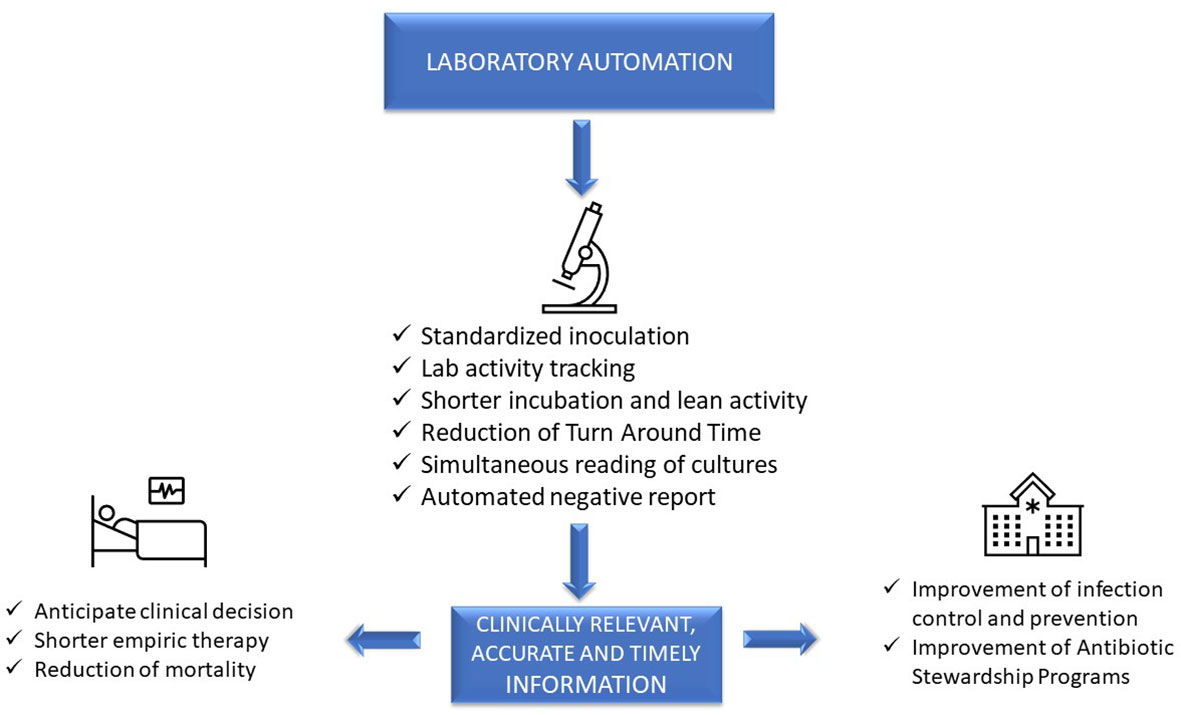
In this 2023 journal article published in
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, Mencacci
et al. examine laboratory automation requirements and demands within the context of clinical microbiology laboratories. Using concepts from “total laboratory automation” (TLA), artificial intelligence (AI), and clinical laboratory informatics, the authors address not only the impact of these technologies on laboratory management and workflows but also on patients and hospital systems. Discussion of the state of the art leads the authors to note that the "implementation of laboratory automation and laboratory informatics can support integration into routine practice monitoring specimens’ quality, isolation of specific pathogens, alert reports for infection control practitioners, and real-time collection of lab trend data, all essential for the prevention and control of infections and epidemiological studies." The authors conclude that "prioritizing laboratory practices in a patient-oriented approach can be used to optimize technology advances for improved patient care."
Posted on August 7, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
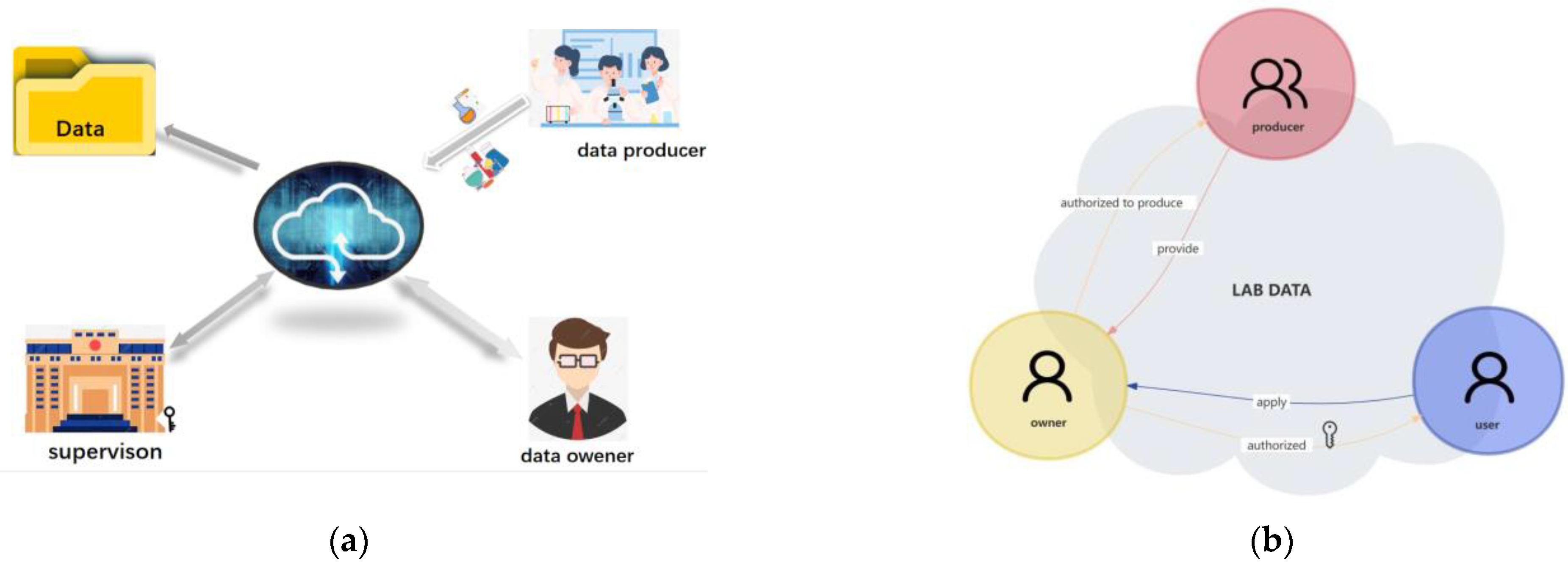
"Islands" of information and data that are dispersed across an organization irregularly can lead to inefficiencies in workflows and missed opportunities to improve or expand the organization. This statement also holds true for college and university laboratories, who equally must face down issues with untimely data, lackadaisical data security, and ownership-related issues. Zheng
et al. tackle this issue with their data-ownership-based security architecture, presented in this journal article published in
Electronics. After providing an introduction and related work, the authors provide in-depth details of the methodology used to develop their secure lab data management architecture, followed by example cases using four different algorithms to find the most suitable solution for authorized encryption and decryption of shared data across the proposed system., which allows "relevant units, universities, and laboratories to encrypt data with public keys and upload them to the data register center to form a data directory." They conclude "that the proposed strategy is secure and efficient for lab data sharing across [multiple] domains."
Posted on July 31, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
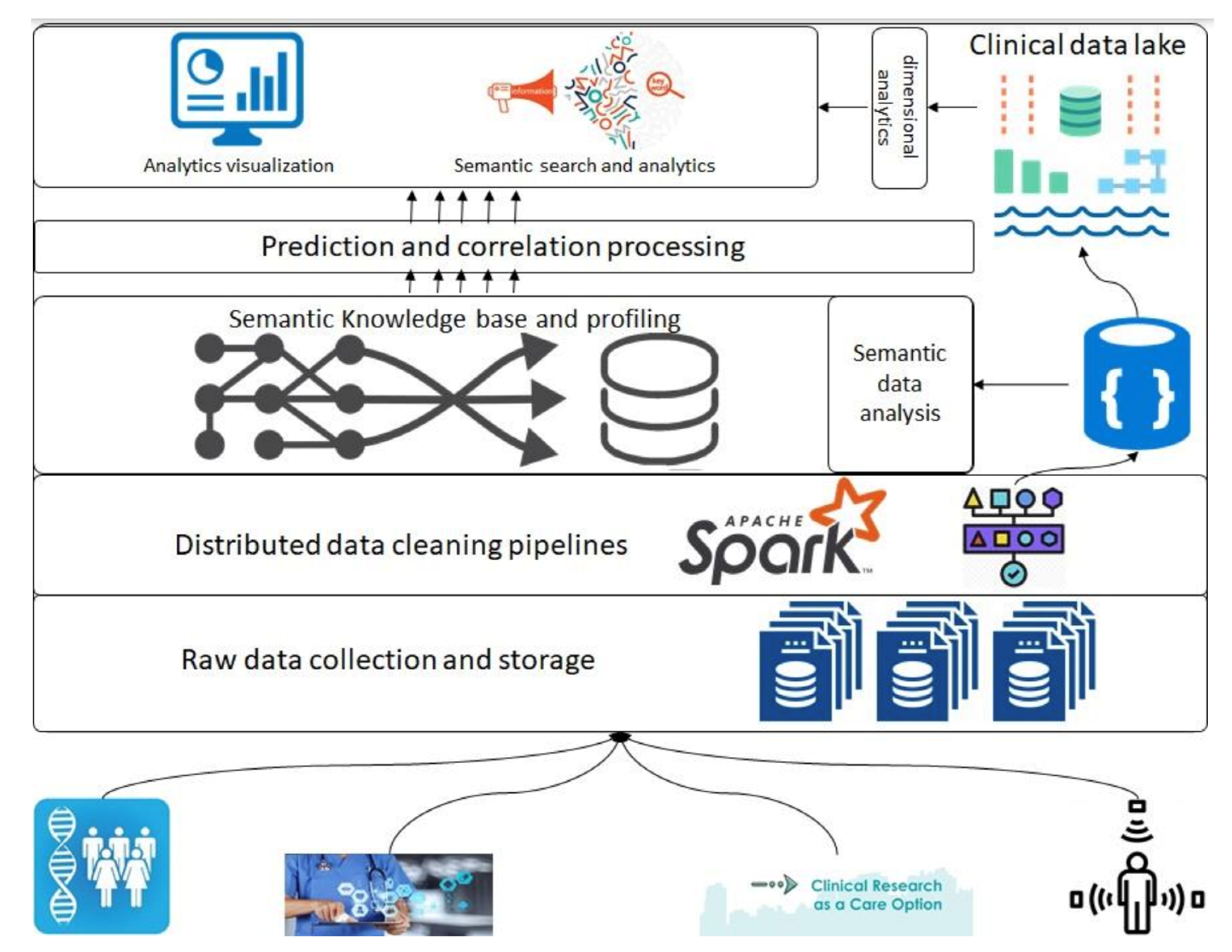
In this 2023 article published in the journal
Healthcare, Siddiqi
et al. propose a "health informatics framework that supports data acquisition from various sources in real-time, correlates these data from various sources among each other and to the domain-specific terminologies, and supports querying and analyses." After providing background information about the need for such a framework, as well as discussing the state of the art, the authors describe their methodology in detail, followed by a experimental use case demonstrating the framework's use. The authors conclude that the "framework is extendable, encapsulates the abilities to include other domains, provides support for semantic querying at the governance level (i.e., at the data assets and type assets level), and is designed towards a data and computation economic model," while at the same time supporting "evidence-based decision tracking ... which follows the FAIR principles."
Posted on July 24, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
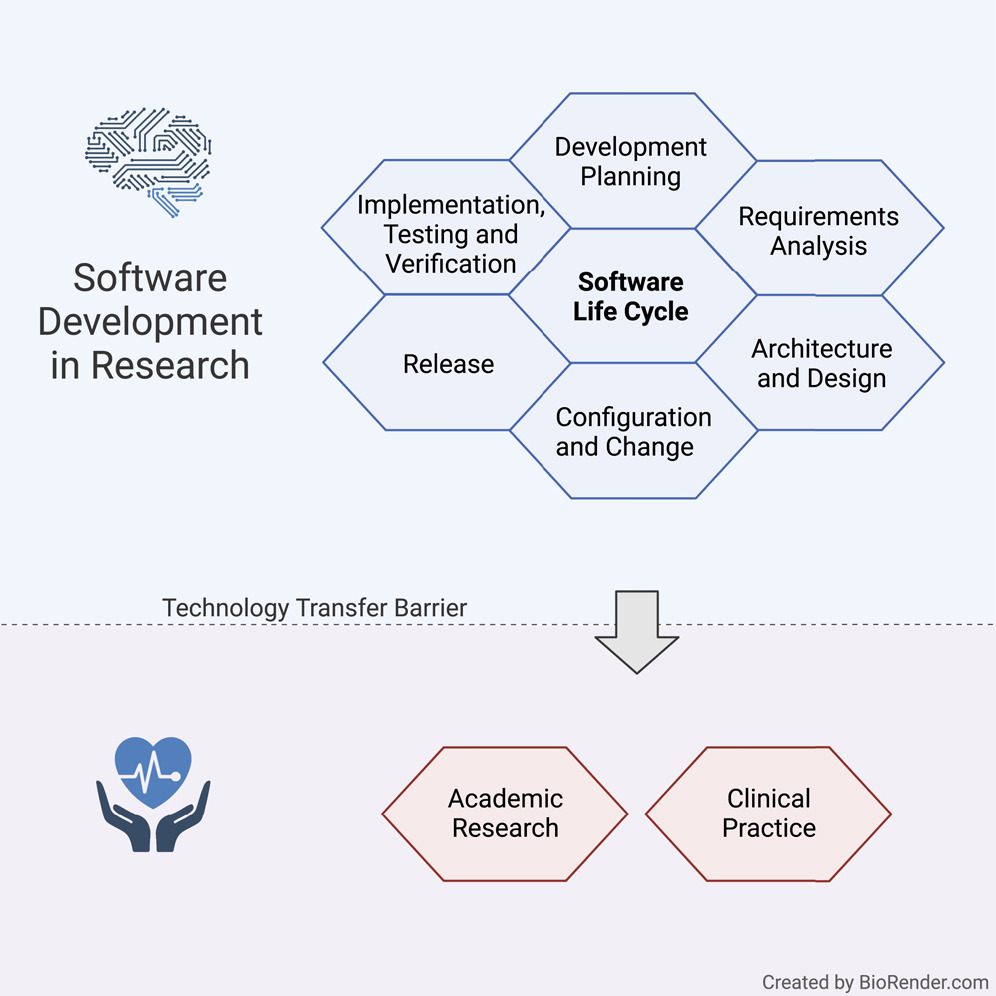
In this 2022 journal article published in
iScience, Hauschild
et al. present a set of guidelines for practicing the academic software life cycle (SLC) within medical labs and research institutes, where commercial industry SLC standards are less applicable. As part of their guidelines, the authors "propose a subset of elements that we are convinced will provide a significant benefit to research settings while keeping the development effort within a feasible range." After a solid introduction, the authors get into the details of their guidelines, addressing all the various stages within the SLC and how they are best applied in the medical academic settings. They close with a brief discussion, concluding that their guideline "lowers the barriers to a potential technology transfer toward the medical industry," while providing "a comprehensive checklist for a successful SLC."
Posted on July 17, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
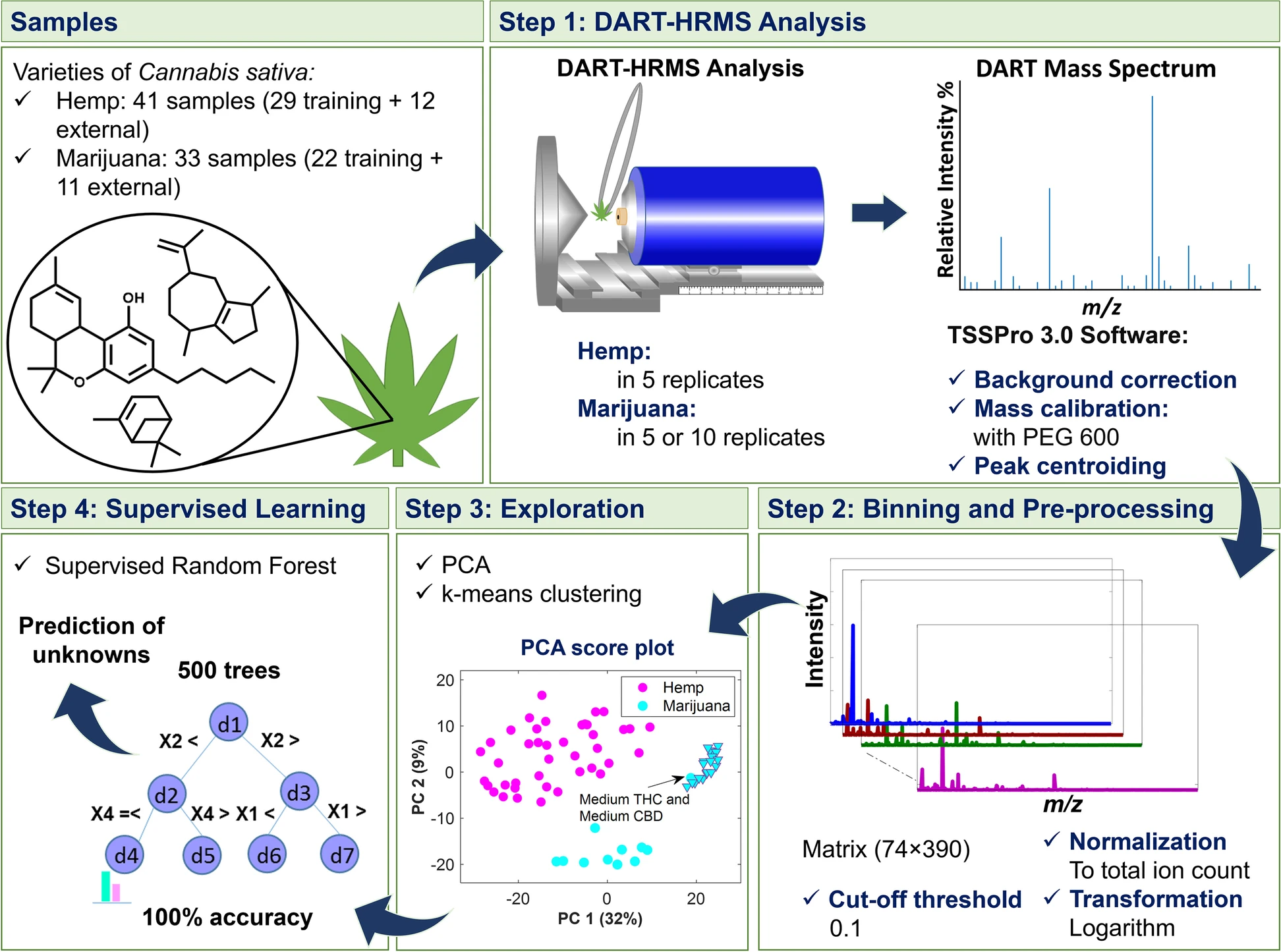
In this 2023 article published in the journal
Journal of Cannabis Research, Chambers
et al. of State University of New York present an analytical method for "the analysis and differentiation of
C. sativa plant materials" that, on paper, represent a major boost over more traditional chromatographic methods. After providing some background on those traditional types of analyses, the authors then present their method of using direct analysis in real time high-resolution mass spectrometry (DART-HRMS) with advanced chemometrics, including results associated with use of their method in a controlled laboratory environment. After some discussion, the authors conclude that their developed method "was successfully used to create a prediction model that facilitated rapid high-accuracy differentiation of
C. sativa hemp and marijuana plant materials obtained from multiple sources (i.e., commercial, DEA-registered, recreational)," while also noting that "100% accuracy in prediction was observed," making it an important potential future method "for the optimal differentiation of hemp and marijuana."
Posted on July 10, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
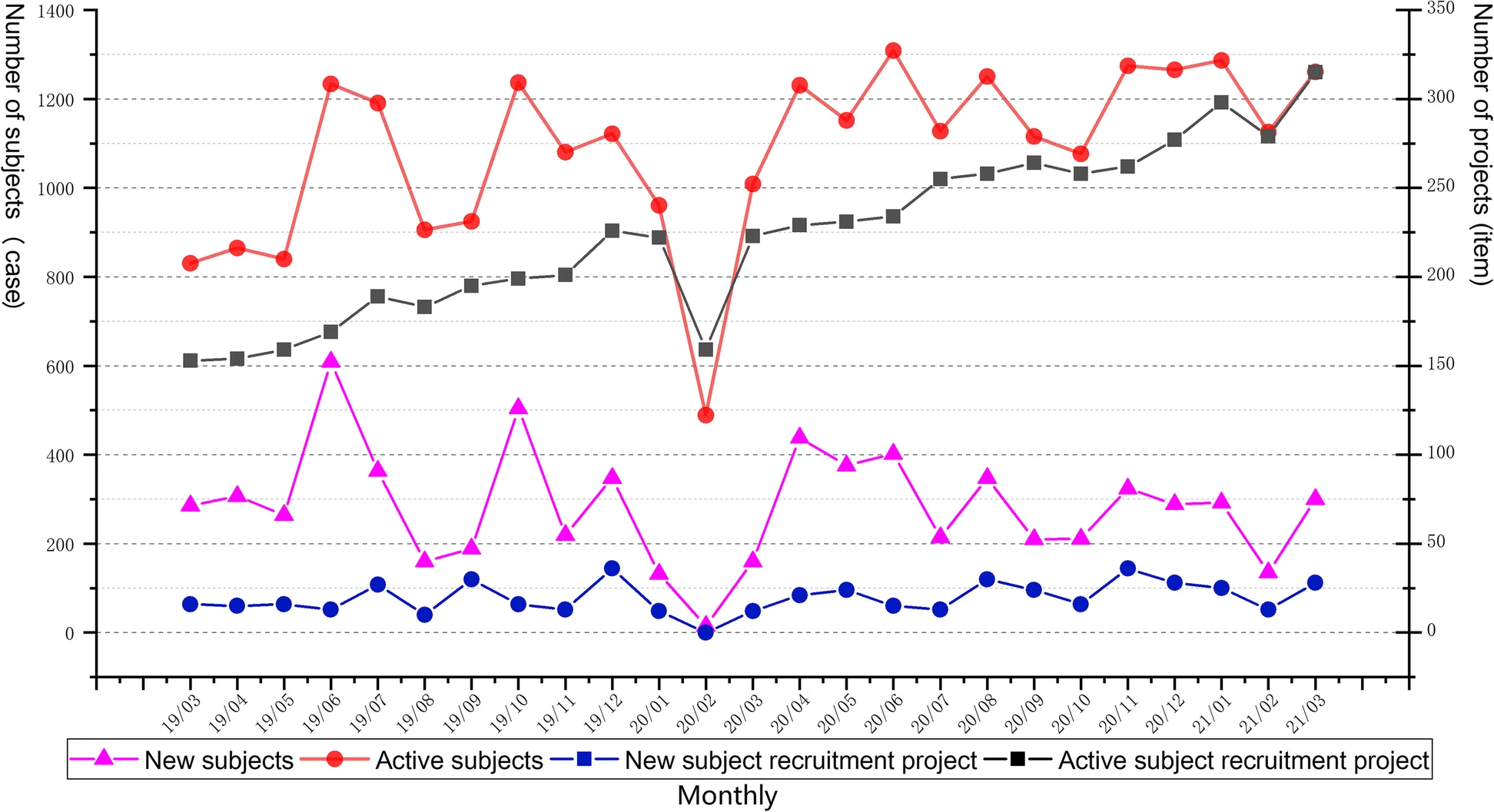
Just as laboratories of all types managing complex workflows and large amounts of test data can benefit from laboratory information management systems (LIMS), similarly do clinical research groups conducting clinical trials benefit from software-based data and workflow management solutions, including the clinical trial management system (CTMS). From more standardized results and documents to more efficient workflows, such clinical systems are a boon to hospitals and research organizations looking to streamline process management for clinical trials. Highlighting this benefit, Shen
et al. present their custom CTMS for the First Affiliated Hospital at Zhejiang University School of Medicine (FAHZU) in this 2023 article published in
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making. After a thorough explanation of their system development and implementation, as well as discussion concerning its use, the authors conclude that the FAHZU CTMS "fully realizes the whole-process data management of clinical trials from project approval and review management to operational management," while providing "a variety of access methods to complete efficient data integration with [other] clinical business systems."
Posted on July 3, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
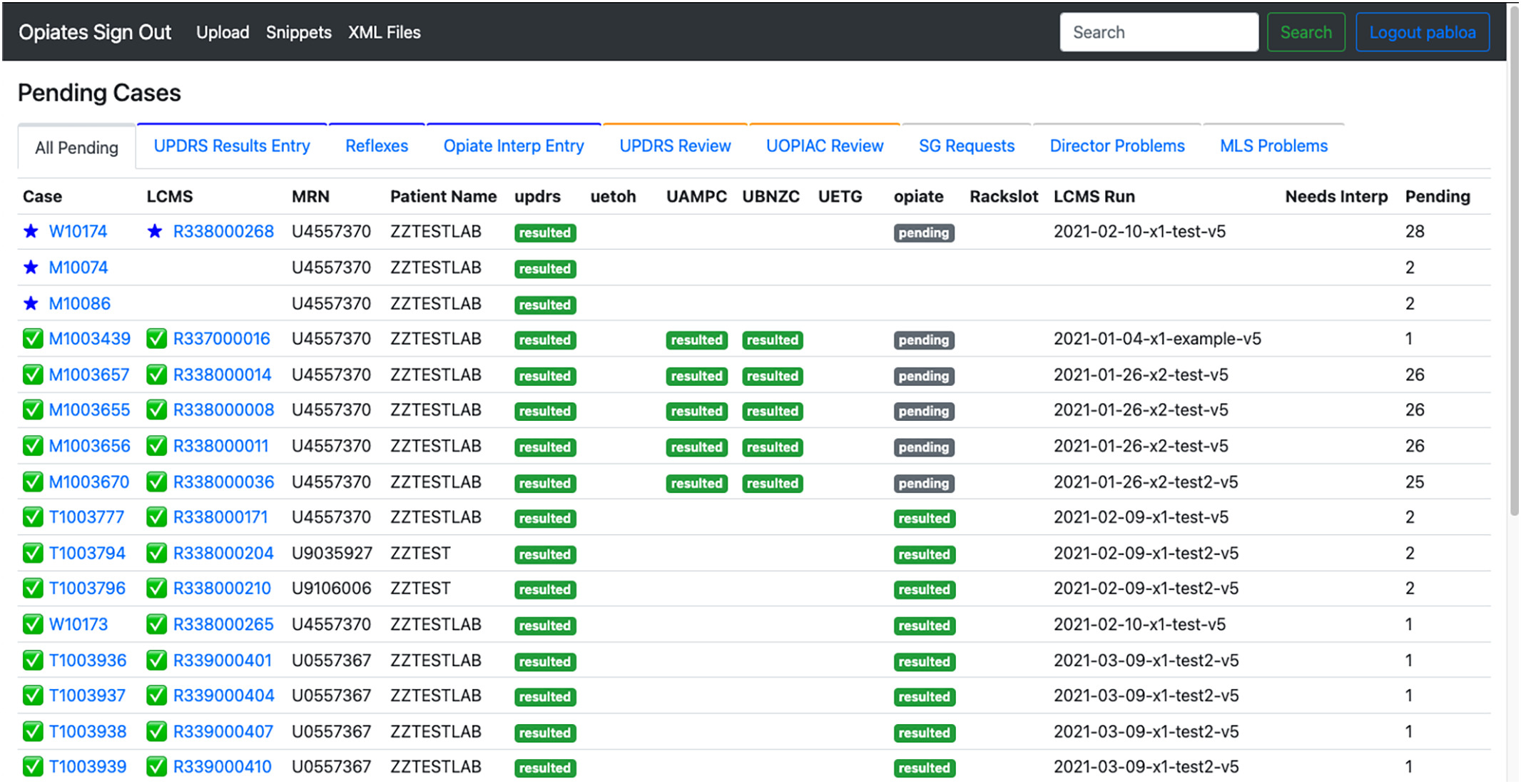
In this 2023 article published in the
Journal of Pathology Informatics, Pablo
et al. of the University of Washington School of Medicine present their work on developing a web-based application for better supporting the complex workflows of labs conducting pain-management-related toxicology and pathology testing. Noting a lack of support of these workflows among traditional laboratory information systems (LISs), the authors describe their approach to developing a system to meet their needs. After providing background and discussing the development approach, the authors present the results of their system implementation and performance analysis. After some discussion, the authors conclude that the "implementation of a purpose-built application to support reflex and interpretation workflows in a clinical pathology practice has led to a significant improvement in laboratory efficiency," adding that their custom, purpose-built application is able to "reduce staff burnout, reduce transcription errors, and allow staff to focus on more critical issues around quality."
Posted on June 26, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
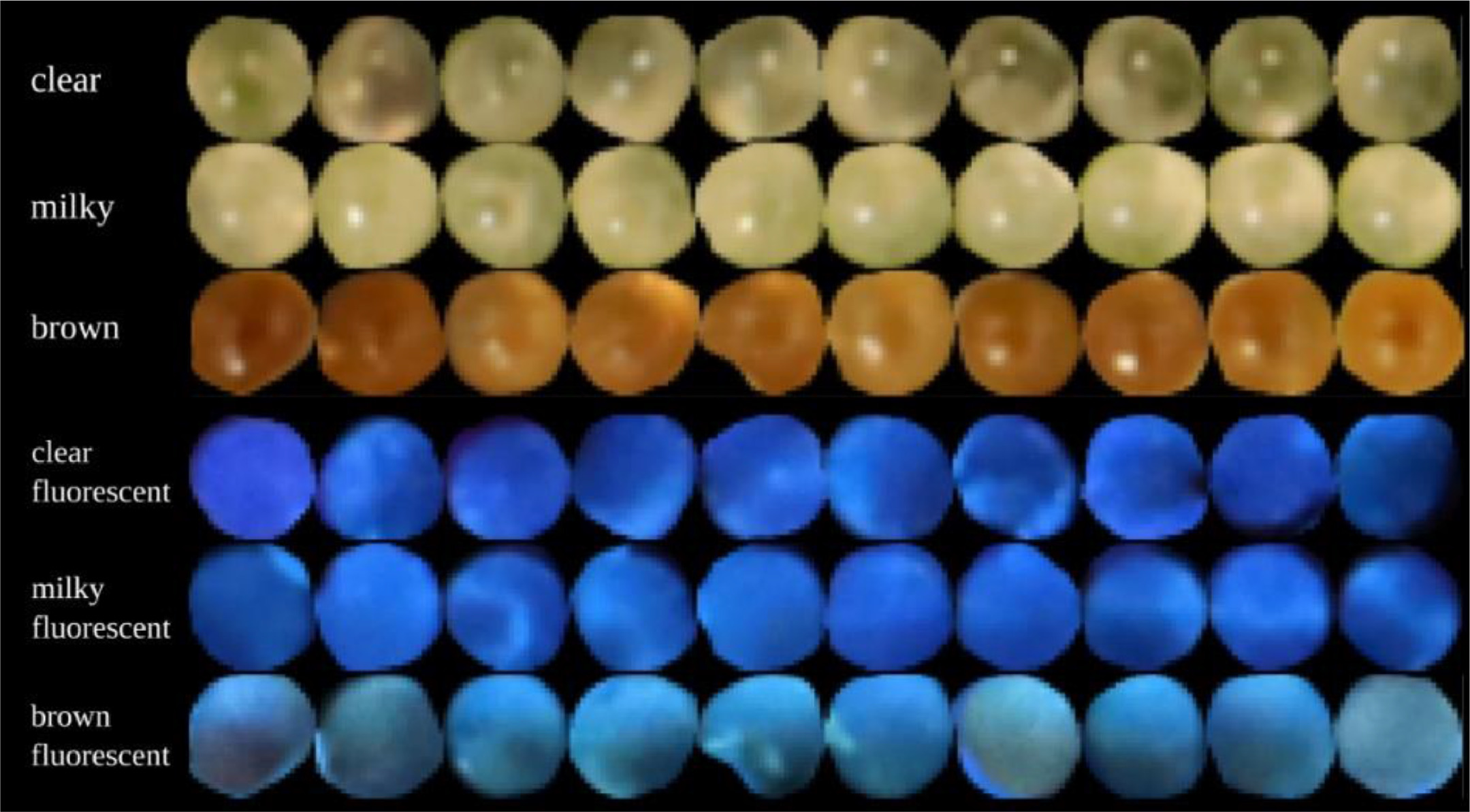
In this 2023 article published in the journal
Smart Agricultural Technology, Sutton
et al. propose an automated method for analyzing the trichomes of the
Cannabis inflorescences for their cultivation maturity. Noting "no scientifically based methods to predict maturation of inflorescences" in the literature, the authors sought out a computational method able to " extract trichome phenotype and morphology metrics during
Cannabis flower development from macroscopic photographs." After providing a brief introduction and a discussion of related work, the researchers discuss their materials, analytical methods, and data collection approach, followed by a lengthy explanation of their experimental results. The authors conclude that through their methods, "the observed relationship between trichome gland head diameter and morphological metrics indicates the feasibility of automatic quality assurance software that can determine how flower maturation is proceeding and if strain-specific potential may be attained." They add that further expansion on their work may produce real practical solutions for cultivators gauging the harvest-readiness of their
Cannabis plants.
Posted on June 20, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
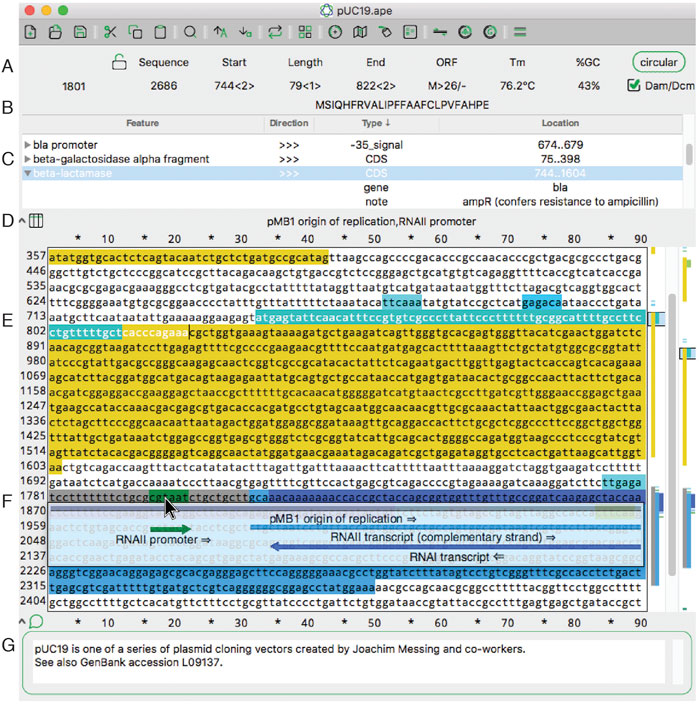
In this 2022 journal article published in
Frontiers in Bioinformatics, Davis and Jorgensen of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and School of Biological Sciences at University of Utah discuss their free, multi-platform software for visualizing, designing, and presenting DNA materials and sequences. Noting that many such applications are out of reach of the small academic or teaching laboratory, the authors have developed and maintained A Plasmid Editor (ApE) for over 17 years, becoming a robust and versatile tool for molecular biologists. After introducing the software in the context of other such software, both free and commercial, they discuss their approach to developing the software over the years, followed by an extensive review of its features and functions. The authors conclude that ApE continues to be a solid " platform for creating visually appealing linear and circular plasmid maps," as well as simulate molecular techniques, adding "that many of its features and user interfaces have been inspired by input from users requesting new or modified functionality" over the years.
Posted on June 12, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
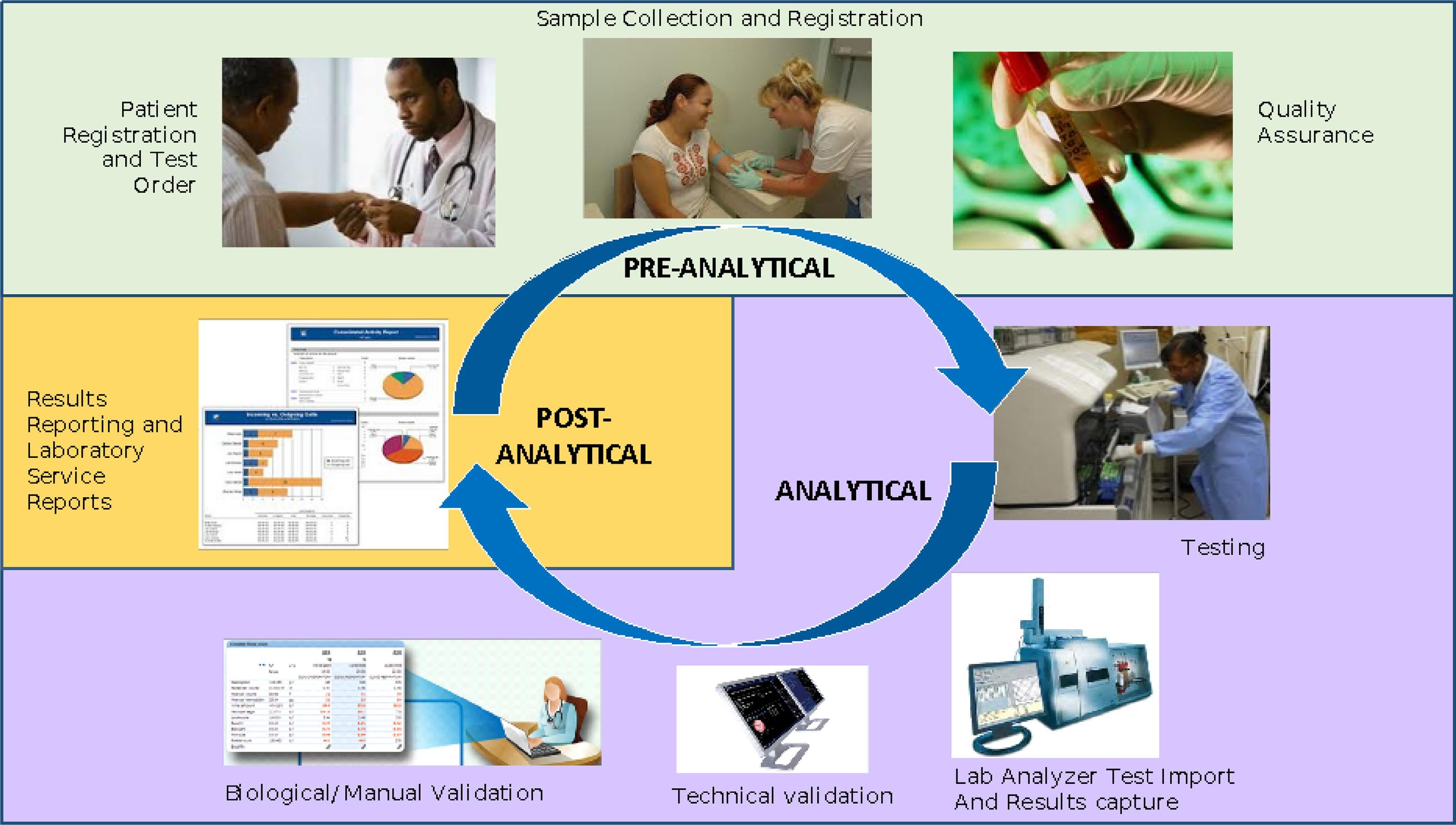
OpenELIS, a free open-source laboratory information system (LIS) for public health laboratories, has been around since 2012 and continue to garner new adopters. But what of the software more than a decade later? Is it still relevant and updated, and has the software demonstrated elements of sustainability for those who have installed it? In this 2023 paper published in the
International Journal of Medical Informatics, He
et al. examine these questions and others in a descriptive case study concerning the software's development, adoption, and use in Côte d'Ivoire. After a full introduction, the authors briefly describe their qualitative methods "to describe the implementation and collaboration around OpenELIS and its supporting activities," followed by discussion of the study results and their implications. The authors conclude that through many different efforts, OpenELIS remains relevant more than a decade later. However, those "planning to adapt and nationally scale [such a] LIS may [need to] consider the importance of HIS workforce development, financial sustainability, and institutionalization of government ownership and technical leadership" through their implementation.
Posted on June 5, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
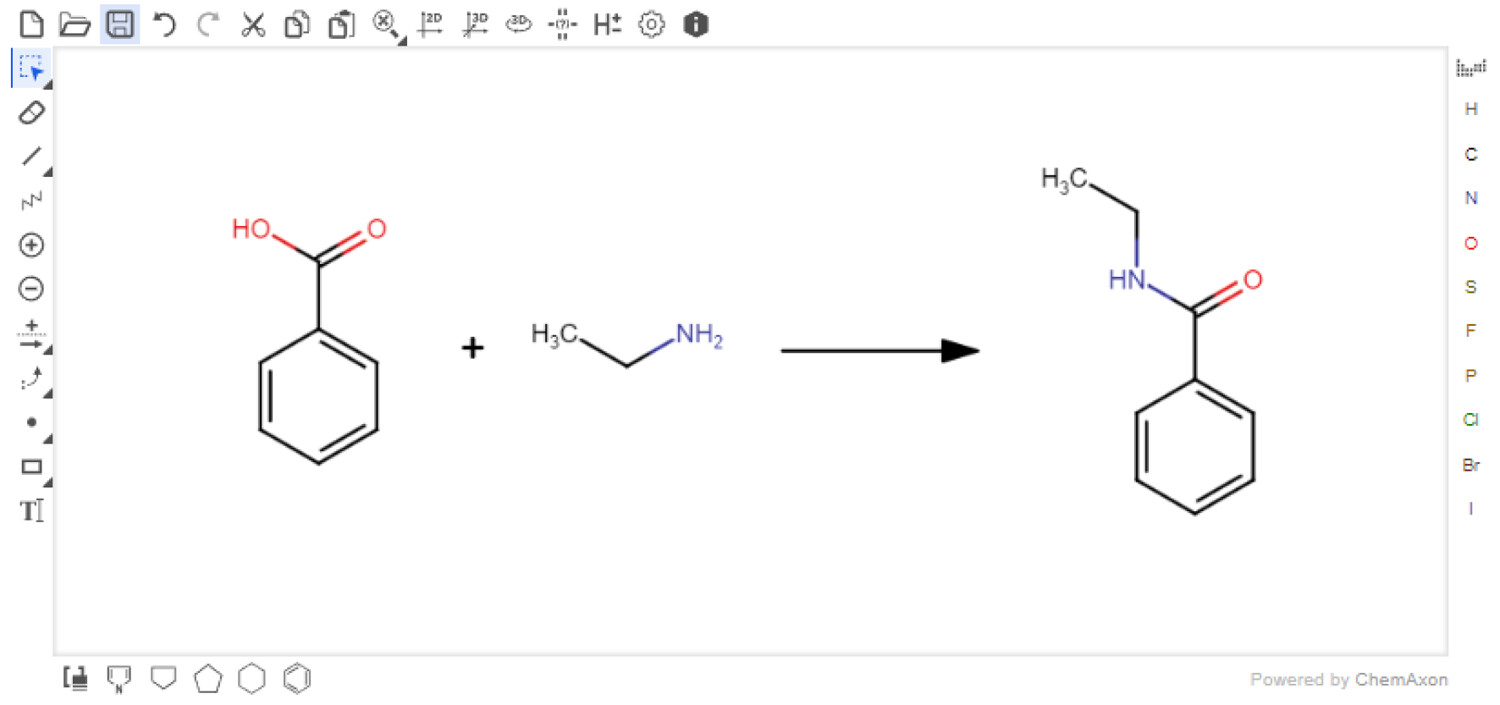
In this 2023 journal article published in the
Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, Boobier
et al. of University of Nottingham discuss their free, open-source electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) for green and sustainable chemistry practice, AI4Green. The authors state their ELN also "automatically presents the hazards and sustainability of an inputted reaction by calculating sustainability metrics and a color-coded assessment of solvents and reaction conditions." After briefly discussing how it's implemented, the authors discuss the various functions of AI4Green, including its support for workgroups, workbooks, user roles, reaction building, reaction sketching, reaction analysis, exporting, and add-on functionality, such as the Solvent Guide. The authors also discuss how feedback was used during application development. They conclude that AI4Green "combines the practical benefits of an ELN alongside a framework for encouraging green and sustainable chemistry," though more work is to be done to extend its functionality. Regardless, even as-is, "AI4Green provides an exciting initial framework to unite an ELN with sustainable chemistry."
Posted on May 30, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
In this 2023 article published in the Indonesian journal
Matrix: Jurnal Manajemen Teknologi Dan Informatika, Ifriza
et al. present their approach to developing a laboratory-based information system for monitoring the condition and maintenance of instruments at the laboratories of the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, State University of Semarang (FMIPA UNNES). After providing a brief introduction, the authors discuss their methodology to developing such a software system, as well as the results, which are explained in terms of the five enterprise architecture planning (EAP) steps used to develop it. The authors conclude that "[b]ased on the results of the study, it can be concluded that the use of laboratory systems for monitoring and maintenance in laboratory management has proven to be very valid."
Posted on May 24, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
In this 2022 paper published in the journal
Complementary Therapies in Medicine, Ennis
et al. discuss the development of a practice-based research network in order to improve the state of understanding of
Cannabis science in the state of Florida, as well as promote future clinical research related to the plant. The authors developed this research network after noting a dearth of such medical marijuana-focused research networks in the state. After providing an introduction, they walk through the steps that led to their Complementary Care Practice-Based Research Network (CC-PBRN), including the methods used in producing usable, de-identified data for research. The authors then summarize the results and address three major challenges in negotiating the "differing foci of academic and business organizations" in developing the network. After noting the strengths and limitations of their network, they conclude that "[t]he data generated by the CC-PBRN can be used to inform and guide patient-centered care, clinical decision-making, and health policy decisions" for medical marijuana patients in Florida.
Posted on May 16, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
In this 2023 paper published in the journal
Accreditation and Quality Assurance, Tziakou
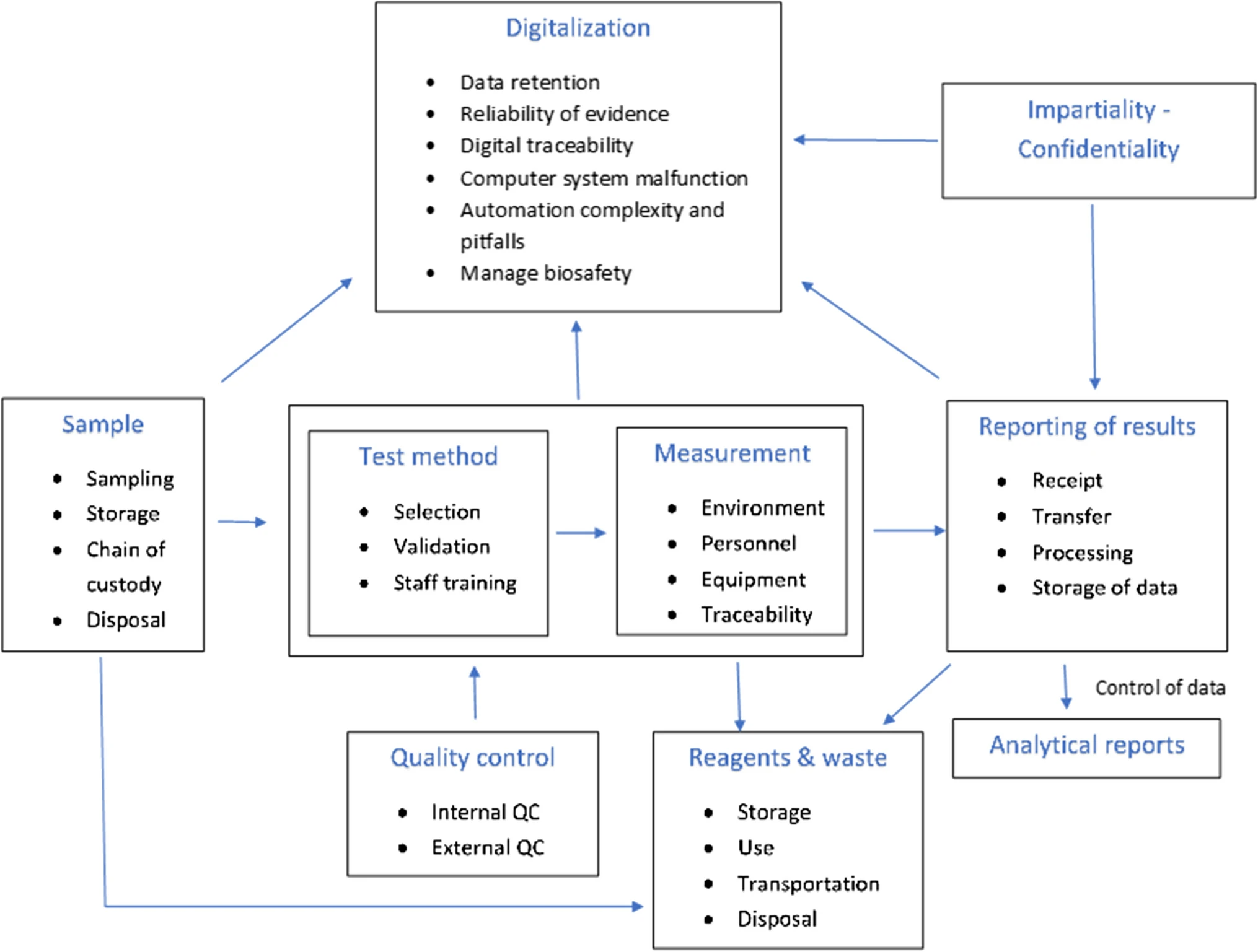
et al. examine the state of risk management as it applies to the modern laboratory environment, tapping into numerous International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards and a review of the literature on the subject. After a brief introduction, the authors discuss the risk management process and risk assessment techniques for organizations of all types. They then take a deep dive into how those techniques apply to the laboratory environment at every step of the lab's workflow, from sample and reagent management to reporting and digitalization of results. They conclude that given the major sources of risk they identified in the lab, "the laboratory can reduce the risks to a tolerable level when clear procedures, continuous supervision, inspections, timely training and continuous education of its staff, and upgrades of its equipment with systems automation are maintained." They add that "the implementation of risk-based thinking can positively affect the outcome of regular assessments in order to explore opportunities for increasing the effectiveness of the [quality management system] and preventing further negative effects."
Posted on May 9, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
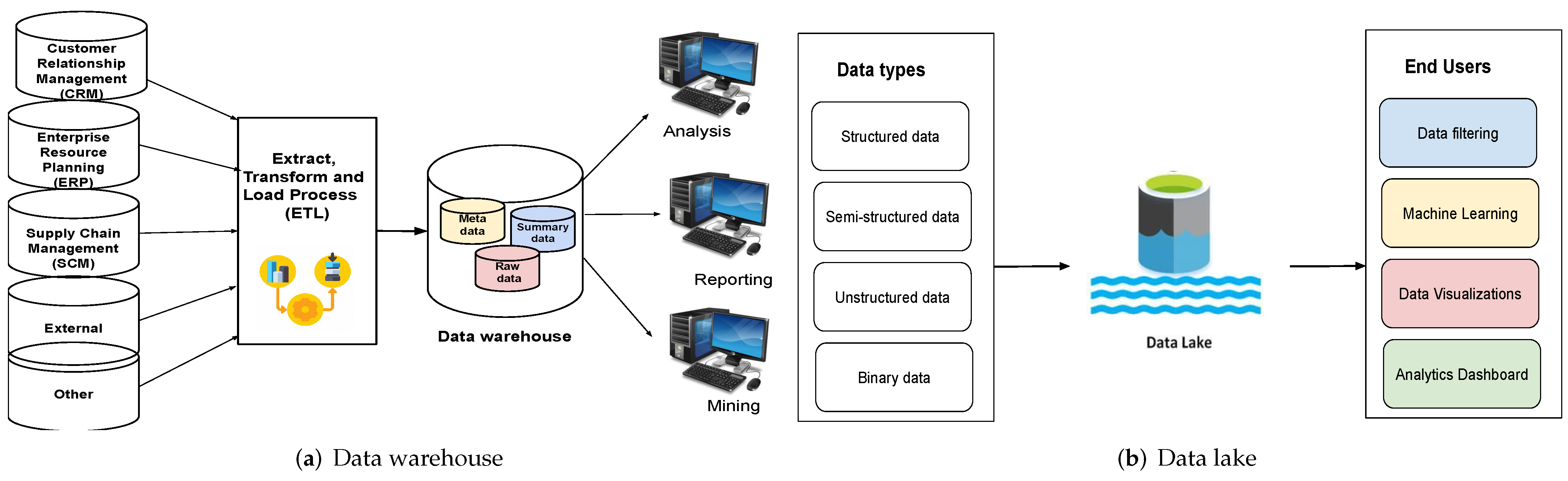
Noting only one known work comparing data warehouses (DWs) with data lakes (DLs), with that article failing to fully address "a comprehensive analysis of both data management schemes by addressing various aspects" in detail, Nambiar and Mundra take to that task in this 2022 article published in
Big Data and Cognitive Computing. After an introduction to the state of DWs and DLs, the authors then discuss the finer points of both data management schemes, while also conducting a literature review on the topic. They then discuss the specifics of architecture regarding DWs and DLs, as well as the data management aspects and useful tools that enhance them. After discussing various challenges and opportunities for the two schemes, the authors conclude that "[d]espite being used interchangeably, they are two distinct storage forms with unique characteristics that serve different purposes."
Posted on May 1, 2023
By LabLynx
Journal articles
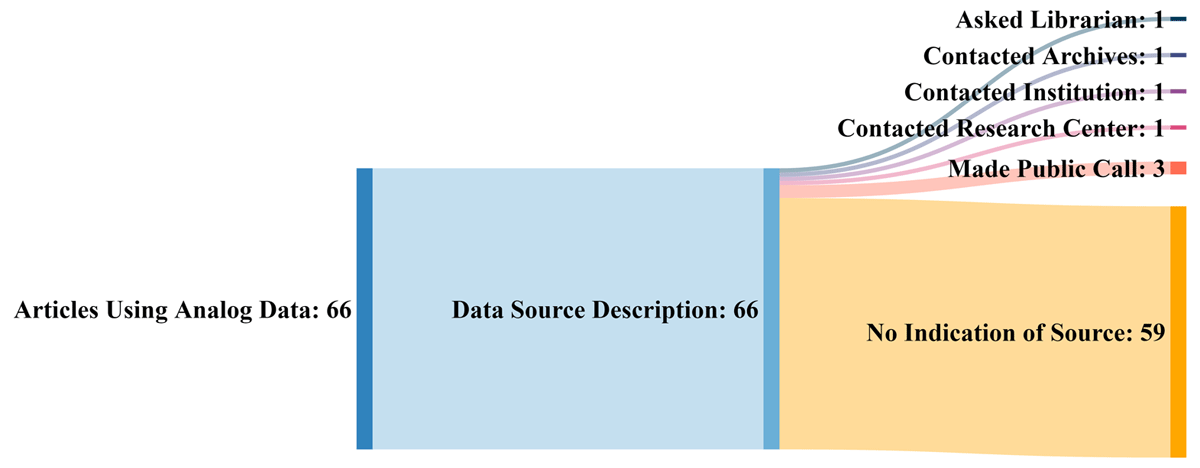
While the management of digitally created data and information is largely in the scope of regulators, standards organizations, and company management these days, the non-trivial surplus of analog data and information (e.g., printed tables, field notebooks, photographs, drawings, maps, etc.) and what to do with it still weighs upon on the research community. Older data has long had uses in retrospective and current research, yet few large-scale solutions for making this analog data and information more FAIR (findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable) have been developed. Kelly
et al. emphasize this in their 2022 research published in the
Data Science Journal and address what they consider should be a set of best practices to managing historic analog data and information. After proving background history on the concerns surrounding older analog data, the authors discuss ways that older analog data is currently and can be used, and they highlight the challenges that come with attempting to reuse such data. They then provide some possible paths forward with a best practice approach, before concluding that "[b]est practices (including selection of metadata schema, developing a data dictionary, describing data collection methods) and policies developed to govern the preservation and dissemination of digital data could serve as an example for developments concerning analog data."
 In this 2023 article published in the journal Sensors, Lehmann et al. of the Mannheim University of Applied Sciences present their efforts towards a research data management (RDM) system for their Center for Mass Spectrometry and Optical Spectroscopy (CeMOS). The proof-of-concept RDM leans on digital twin (DT) technology to answer the challenges posed by RDM of multiple research instruments in their institute, while at the same time addressing the principles of making data more findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR). After introducing the topic and presenting related work as it relates to their efforts, the authors lay out their conceptual architecture and discuss use cases within the context of their spectrometry and spectroscopy work. Then they propose an implementation, proof of concept, and evaluation of the proof of concept within the implementation's framework. After discussing their results, the authors conclude that their efforts contribute to the literature in five different ways, addressing RDM within FAIR, highlighting the value of DTs, developing a top-level knowledge graph, elaborating on reactive vs. proactive DTs, and providing a practical approach to DTs in the RDM at larger research institutes. They also provide caveats and future work that still needs to be done.
In this 2023 article published in the journal Sensors, Lehmann et al. of the Mannheim University of Applied Sciences present their efforts towards a research data management (RDM) system for their Center for Mass Spectrometry and Optical Spectroscopy (CeMOS). The proof-of-concept RDM leans on digital twin (DT) technology to answer the challenges posed by RDM of multiple research instruments in their institute, while at the same time addressing the principles of making data more findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR). After introducing the topic and presenting related work as it relates to their efforts, the authors lay out their conceptual architecture and discuss use cases within the context of their spectrometry and spectroscopy work. Then they propose an implementation, proof of concept, and evaluation of the proof of concept within the implementation's framework. After discussing their results, the authors conclude that their efforts contribute to the literature in five different ways, addressing RDM within FAIR, highlighting the value of DTs, developing a top-level knowledge graph, elaborating on reactive vs. proactive DTs, and providing a practical approach to DTs in the RDM at larger research institutes. They also provide caveats and future work that still needs to be done.
 Materials science has been and continues to be an important study, particularly as we strive to overcome challenges such as climate change, pollution, and world hunger. And like many other sciences, the expanding paradigm of autonomous systems, machine learning (ML), and even artificial intelligence (AI) stands to leave a positive mark on how we conduct research on materials of all types. Ishizuki et al. of the Tokyo Institute of Technology and The University of Tokyo echo this sentiment in their 2023 paper published in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials: Methods, which discusses the state of the art of autonomous experimental systems (AESs) and their benefits to material science laboratories. After introducing the topic, the authors explore the state of the art through other researchers' efforts, drawing conclusions based upon how AESs can be put to use in the field. After characterizing AESs' use and addressing sociocultural factors such as inventorship and authorship with AI and autonomous systems, the authors conclude that while AES will provide strong value to materials science labs, "human researchers will always be the main players," and this hybrid automation-human approach "will exponentially accelerate creative research and development, contributing to the future development of science, technology, and industry."
Materials science has been and continues to be an important study, particularly as we strive to overcome challenges such as climate change, pollution, and world hunger. And like many other sciences, the expanding paradigm of autonomous systems, machine learning (ML), and even artificial intelligence (AI) stands to leave a positive mark on how we conduct research on materials of all types. Ishizuki et al. of the Tokyo Institute of Technology and The University of Tokyo echo this sentiment in their 2023 paper published in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials: Methods, which discusses the state of the art of autonomous experimental systems (AESs) and their benefits to material science laboratories. After introducing the topic, the authors explore the state of the art through other researchers' efforts, drawing conclusions based upon how AESs can be put to use in the field. After characterizing AESs' use and addressing sociocultural factors such as inventorship and authorship with AI and autonomous systems, the authors conclude that while AES will provide strong value to materials science labs, "human researchers will always be the main players," and this hybrid automation-human approach "will exponentially accelerate creative research and development, contributing to the future development of science, technology, and industry."
 In this brief paper published in Journal of Cannabis Research, Gagnon et al. present the results of applying a new analytical technique to quantifying hundreds of pesticides at the same time in cannabis samples. Using a combination of gas chromatography—triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC–MS/MS) and liquid chromatography—triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS), the authors tested not only cannabis samples from licensed retailers in Canada but also illicit cannabis samples acquired from Health Canada Cannabis Laboratory. Their methodology was fully able to manage the search for hundreds of pesticides, discovering only a handful of semi-unregulated pesticides in legal Canadian cannabis, but a surprising amount of pesticides in illicit samples. The authors conclude that their methodology, as demonstrated, has practical uses going forward towards a wider regulatory approach to ensuring Canadian cannabis is as pesticide-free as possible.
In this brief paper published in Journal of Cannabis Research, Gagnon et al. present the results of applying a new analytical technique to quantifying hundreds of pesticides at the same time in cannabis samples. Using a combination of gas chromatography—triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC–MS/MS) and liquid chromatography—triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS), the authors tested not only cannabis samples from licensed retailers in Canada but also illicit cannabis samples acquired from Health Canada Cannabis Laboratory. Their methodology was fully able to manage the search for hundreds of pesticides, discovering only a handful of semi-unregulated pesticides in legal Canadian cannabis, but a surprising amount of pesticides in illicit samples. The authors conclude that their methodology, as demonstrated, has practical uses going forward towards a wider regulatory approach to ensuring Canadian cannabis is as pesticide-free as possible.
 In this 2023 journal article published in Healthcare, Ayaz et al. present their work on a "data analytic framework that supports clinical statistics and analysis by leveraging ... Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR)." After providing significant background on the topic, as well as a review of the literature on the topic, the authors discuss the initial preparations that went into developing their framework, followed by the results of their implementation. The authors also present a two-part example with use cases that puts the framework to a test. After discussing the limitations and results of their framework, the authors conclude that it effectively "empowers healthcare users (patients, practitioners, healthcare providers, etc.) to perform advanced data analysis on patient data used in healthcare settings and represented in the FHIR-based standard."
In this 2023 journal article published in Healthcare, Ayaz et al. present their work on a "data analytic framework that supports clinical statistics and analysis by leveraging ... Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR)." After providing significant background on the topic, as well as a review of the literature on the topic, the authors discuss the initial preparations that went into developing their framework, followed by the results of their implementation. The authors also present a two-part example with use cases that puts the framework to a test. After discussing the limitations and results of their framework, the authors conclude that it effectively "empowers healthcare users (patients, practitioners, healthcare providers, etc.) to perform advanced data analysis on patient data used in healthcare settings and represented in the FHIR-based standard."
 In this 2023 journal article published in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, Mencacci et al. examine laboratory automation requirements and demands within the context of clinical microbiology laboratories. Using concepts from “total laboratory automation” (TLA), artificial intelligence (AI), and clinical laboratory informatics, the authors address not only the impact of these technologies on laboratory management and workflows but also on patients and hospital systems. Discussion of the state of the art leads the authors to note that the "implementation of laboratory automation and laboratory informatics can support integration into routine practice monitoring specimens’ quality, isolation of specific pathogens, alert reports for infection control practitioners, and real-time collection of lab trend data, all essential for the prevention and control of infections and epidemiological studies." The authors conclude that "prioritizing laboratory practices in a patient-oriented approach can be used to optimize technology advances for improved patient care."
In this 2023 journal article published in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, Mencacci et al. examine laboratory automation requirements and demands within the context of clinical microbiology laboratories. Using concepts from “total laboratory automation” (TLA), artificial intelligence (AI), and clinical laboratory informatics, the authors address not only the impact of these technologies on laboratory management and workflows but also on patients and hospital systems. Discussion of the state of the art leads the authors to note that the "implementation of laboratory automation and laboratory informatics can support integration into routine practice monitoring specimens’ quality, isolation of specific pathogens, alert reports for infection control practitioners, and real-time collection of lab trend data, all essential for the prevention and control of infections and epidemiological studies." The authors conclude that "prioritizing laboratory practices in a patient-oriented approach can be used to optimize technology advances for improved patient care."
 "Islands" of information and data that are dispersed across an organization irregularly can lead to inefficiencies in workflows and missed opportunities to improve or expand the organization. This statement also holds true for college and university laboratories, who equally must face down issues with untimely data, lackadaisical data security, and ownership-related issues. Zheng et al. tackle this issue with their data-ownership-based security architecture, presented in this journal article published in Electronics. After providing an introduction and related work, the authors provide in-depth details of the methodology used to develop their secure lab data management architecture, followed by example cases using four different algorithms to find the most suitable solution for authorized encryption and decryption of shared data across the proposed system., which allows "relevant units, universities, and laboratories to encrypt data with public keys and upload them to the data register center to form a data directory." They conclude "that the proposed strategy is secure and efficient for lab data sharing across [multiple] domains."
"Islands" of information and data that are dispersed across an organization irregularly can lead to inefficiencies in workflows and missed opportunities to improve or expand the organization. This statement also holds true for college and university laboratories, who equally must face down issues with untimely data, lackadaisical data security, and ownership-related issues. Zheng et al. tackle this issue with their data-ownership-based security architecture, presented in this journal article published in Electronics. After providing an introduction and related work, the authors provide in-depth details of the methodology used to develop their secure lab data management architecture, followed by example cases using four different algorithms to find the most suitable solution for authorized encryption and decryption of shared data across the proposed system., which allows "relevant units, universities, and laboratories to encrypt data with public keys and upload them to the data register center to form a data directory." They conclude "that the proposed strategy is secure and efficient for lab data sharing across [multiple] domains."
 In this 2023 article published in the journal Healthcare, Siddiqi et al. propose a "health informatics framework that supports data acquisition from various sources in real-time, correlates these data from various sources among each other and to the domain-specific terminologies, and supports querying and analyses." After providing background information about the need for such a framework, as well as discussing the state of the art, the authors describe their methodology in detail, followed by a experimental use case demonstrating the framework's use. The authors conclude that the "framework is extendable, encapsulates the abilities to include other domains, provides support for semantic querying at the governance level (i.e., at the data assets and type assets level), and is designed towards a data and computation economic model," while at the same time supporting "evidence-based decision tracking ... which follows the FAIR principles."
In this 2023 article published in the journal Healthcare, Siddiqi et al. propose a "health informatics framework that supports data acquisition from various sources in real-time, correlates these data from various sources among each other and to the domain-specific terminologies, and supports querying and analyses." After providing background information about the need for such a framework, as well as discussing the state of the art, the authors describe their methodology in detail, followed by a experimental use case demonstrating the framework's use. The authors conclude that the "framework is extendable, encapsulates the abilities to include other domains, provides support for semantic querying at the governance level (i.e., at the data assets and type assets level), and is designed towards a data and computation economic model," while at the same time supporting "evidence-based decision tracking ... which follows the FAIR principles."
 In this 2022 journal article published in iScience, Hauschild et al. present a set of guidelines for practicing the academic software life cycle (SLC) within medical labs and research institutes, where commercial industry SLC standards are less applicable. As part of their guidelines, the authors "propose a subset of elements that we are convinced will provide a significant benefit to research settings while keeping the development effort within a feasible range." After a solid introduction, the authors get into the details of their guidelines, addressing all the various stages within the SLC and how they are best applied in the medical academic settings. They close with a brief discussion, concluding that their guideline "lowers the barriers to a potential technology transfer toward the medical industry," while providing "a comprehensive checklist for a successful SLC."
In this 2022 journal article published in iScience, Hauschild et al. present a set of guidelines for practicing the academic software life cycle (SLC) within medical labs and research institutes, where commercial industry SLC standards are less applicable. As part of their guidelines, the authors "propose a subset of elements that we are convinced will provide a significant benefit to research settings while keeping the development effort within a feasible range." After a solid introduction, the authors get into the details of their guidelines, addressing all the various stages within the SLC and how they are best applied in the medical academic settings. They close with a brief discussion, concluding that their guideline "lowers the barriers to a potential technology transfer toward the medical industry," while providing "a comprehensive checklist for a successful SLC."
 In this 2023 article published in the journal Journal of Cannabis Research, Chambers et al. of State University of New York present an analytical method for "the analysis and differentiation of C. sativa plant materials" that, on paper, represent a major boost over more traditional chromatographic methods. After providing some background on those traditional types of analyses, the authors then present their method of using direct analysis in real time high-resolution mass spectrometry (DART-HRMS) with advanced chemometrics, including results associated with use of their method in a controlled laboratory environment. After some discussion, the authors conclude that their developed method "was successfully used to create a prediction model that facilitated rapid high-accuracy differentiation of C. sativa hemp and marijuana plant materials obtained from multiple sources (i.e., commercial, DEA-registered, recreational)," while also noting that "100% accuracy in prediction was observed," making it an important potential future method "for the optimal differentiation of hemp and marijuana."
In this 2023 article published in the journal Journal of Cannabis Research, Chambers et al. of State University of New York present an analytical method for "the analysis and differentiation of C. sativa plant materials" that, on paper, represent a major boost over more traditional chromatographic methods. After providing some background on those traditional types of analyses, the authors then present their method of using direct analysis in real time high-resolution mass spectrometry (DART-HRMS) with advanced chemometrics, including results associated with use of their method in a controlled laboratory environment. After some discussion, the authors conclude that their developed method "was successfully used to create a prediction model that facilitated rapid high-accuracy differentiation of C. sativa hemp and marijuana plant materials obtained from multiple sources (i.e., commercial, DEA-registered, recreational)," while also noting that "100% accuracy in prediction was observed," making it an important potential future method "for the optimal differentiation of hemp and marijuana."
 Just as laboratories of all types managing complex workflows and large amounts of test data can benefit from laboratory information management systems (LIMS), similarly do clinical research groups conducting clinical trials benefit from software-based data and workflow management solutions, including the clinical trial management system (CTMS). From more standardized results and documents to more efficient workflows, such clinical systems are a boon to hospitals and research organizations looking to streamline process management for clinical trials. Highlighting this benefit, Shen et al. present their custom CTMS for the First Affiliated Hospital at Zhejiang University School of Medicine (FAHZU) in this 2023 article published in BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making. After a thorough explanation of their system development and implementation, as well as discussion concerning its use, the authors conclude that the FAHZU CTMS "fully realizes the whole-process data management of clinical trials from project approval and review management to operational management," while providing "a variety of access methods to complete efficient data integration with [other] clinical business systems."
Just as laboratories of all types managing complex workflows and large amounts of test data can benefit from laboratory information management systems (LIMS), similarly do clinical research groups conducting clinical trials benefit from software-based data and workflow management solutions, including the clinical trial management system (CTMS). From more standardized results and documents to more efficient workflows, such clinical systems are a boon to hospitals and research organizations looking to streamline process management for clinical trials. Highlighting this benefit, Shen et al. present their custom CTMS for the First Affiliated Hospital at Zhejiang University School of Medicine (FAHZU) in this 2023 article published in BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making. After a thorough explanation of their system development and implementation, as well as discussion concerning its use, the authors conclude that the FAHZU CTMS "fully realizes the whole-process data management of clinical trials from project approval and review management to operational management," while providing "a variety of access methods to complete efficient data integration with [other] clinical business systems."
 In this 2023 article published in the Journal of Pathology Informatics, Pablo et al. of the University of Washington School of Medicine present their work on developing a web-based application for better supporting the complex workflows of labs conducting pain-management-related toxicology and pathology testing. Noting a lack of support of these workflows among traditional laboratory information systems (LISs), the authors describe their approach to developing a system to meet their needs. After providing background and discussing the development approach, the authors present the results of their system implementation and performance analysis. After some discussion, the authors conclude that the "implementation of a purpose-built application to support reflex and interpretation workflows in a clinical pathology practice has led to a significant improvement in laboratory efficiency," adding that their custom, purpose-built application is able to "reduce staff burnout, reduce transcription errors, and allow staff to focus on more critical issues around quality."
In this 2023 article published in the Journal of Pathology Informatics, Pablo et al. of the University of Washington School of Medicine present their work on developing a web-based application for better supporting the complex workflows of labs conducting pain-management-related toxicology and pathology testing. Noting a lack of support of these workflows among traditional laboratory information systems (LISs), the authors describe their approach to developing a system to meet their needs. After providing background and discussing the development approach, the authors present the results of their system implementation and performance analysis. After some discussion, the authors conclude that the "implementation of a purpose-built application to support reflex and interpretation workflows in a clinical pathology practice has led to a significant improvement in laboratory efficiency," adding that their custom, purpose-built application is able to "reduce staff burnout, reduce transcription errors, and allow staff to focus on more critical issues around quality."
 In this 2023 article published in the journal Smart Agricultural Technology, Sutton et al. propose an automated method for analyzing the trichomes of the Cannabis inflorescences for their cultivation maturity. Noting "no scientifically based methods to predict maturation of inflorescences" in the literature, the authors sought out a computational method able to " extract trichome phenotype and morphology metrics during Cannabis flower development from macroscopic photographs." After providing a brief introduction and a discussion of related work, the researchers discuss their materials, analytical methods, and data collection approach, followed by a lengthy explanation of their experimental results. The authors conclude that through their methods, "the observed relationship between trichome gland head diameter and morphological metrics indicates the feasibility of automatic quality assurance software that can determine how flower maturation is proceeding and if strain-specific potential may be attained." They add that further expansion on their work may produce real practical solutions for cultivators gauging the harvest-readiness of their Cannabis plants.
In this 2023 article published in the journal Smart Agricultural Technology, Sutton et al. propose an automated method for analyzing the trichomes of the Cannabis inflorescences for their cultivation maturity. Noting "no scientifically based methods to predict maturation of inflorescences" in the literature, the authors sought out a computational method able to " extract trichome phenotype and morphology metrics during Cannabis flower development from macroscopic photographs." After providing a brief introduction and a discussion of related work, the researchers discuss their materials, analytical methods, and data collection approach, followed by a lengthy explanation of their experimental results. The authors conclude that through their methods, "the observed relationship between trichome gland head diameter and morphological metrics indicates the feasibility of automatic quality assurance software that can determine how flower maturation is proceeding and if strain-specific potential may be attained." They add that further expansion on their work may produce real practical solutions for cultivators gauging the harvest-readiness of their Cannabis plants.
 In this 2022 journal article published in Frontiers in Bioinformatics, Davis and Jorgensen of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and School of Biological Sciences at University of Utah discuss their free, multi-platform software for visualizing, designing, and presenting DNA materials and sequences. Noting that many such applications are out of reach of the small academic or teaching laboratory, the authors have developed and maintained A Plasmid Editor (ApE) for over 17 years, becoming a robust and versatile tool for molecular biologists. After introducing the software in the context of other such software, both free and commercial, they discuss their approach to developing the software over the years, followed by an extensive review of its features and functions. The authors conclude that ApE continues to be a solid " platform for creating visually appealing linear and circular plasmid maps," as well as simulate molecular techniques, adding "that many of its features and user interfaces have been inspired by input from users requesting new or modified functionality" over the years.
In this 2022 journal article published in Frontiers in Bioinformatics, Davis and Jorgensen of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and School of Biological Sciences at University of Utah discuss their free, multi-platform software for visualizing, designing, and presenting DNA materials and sequences. Noting that many such applications are out of reach of the small academic or teaching laboratory, the authors have developed and maintained A Plasmid Editor (ApE) for over 17 years, becoming a robust and versatile tool for molecular biologists. After introducing the software in the context of other such software, both free and commercial, they discuss their approach to developing the software over the years, followed by an extensive review of its features and functions. The authors conclude that ApE continues to be a solid " platform for creating visually appealing linear and circular plasmid maps," as well as simulate molecular techniques, adding "that many of its features and user interfaces have been inspired by input from users requesting new or modified functionality" over the years.
 OpenELIS, a free open-source laboratory information system (LIS) for public health laboratories, has been around since 2012 and continue to garner new adopters. But what of the software more than a decade later? Is it still relevant and updated, and has the software demonstrated elements of sustainability for those who have installed it? In this 2023 paper published in the International Journal of Medical Informatics, He et al. examine these questions and others in a descriptive case study concerning the software's development, adoption, and use in Côte d'Ivoire. After a full introduction, the authors briefly describe their qualitative methods "to describe the implementation and collaboration around OpenELIS and its supporting activities," followed by discussion of the study results and their implications. The authors conclude that through many different efforts, OpenELIS remains relevant more than a decade later. However, those "planning to adapt and nationally scale [such a] LIS may [need to] consider the importance of HIS workforce development, financial sustainability, and institutionalization of government ownership and technical leadership" through their implementation.
OpenELIS, a free open-source laboratory information system (LIS) for public health laboratories, has been around since 2012 and continue to garner new adopters. But what of the software more than a decade later? Is it still relevant and updated, and has the software demonstrated elements of sustainability for those who have installed it? In this 2023 paper published in the International Journal of Medical Informatics, He et al. examine these questions and others in a descriptive case study concerning the software's development, adoption, and use in Côte d'Ivoire. After a full introduction, the authors briefly describe their qualitative methods "to describe the implementation and collaboration around OpenELIS and its supporting activities," followed by discussion of the study results and their implications. The authors conclude that through many different efforts, OpenELIS remains relevant more than a decade later. However, those "planning to adapt and nationally scale [such a] LIS may [need to] consider the importance of HIS workforce development, financial sustainability, and institutionalization of government ownership and technical leadership" through their implementation.
 In this 2023 journal article published in the Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, Boobier et al. of University of Nottingham discuss their free, open-source electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) for green and sustainable chemistry practice, AI4Green. The authors state their ELN also "automatically presents the hazards and sustainability of an inputted reaction by calculating sustainability metrics and a color-coded assessment of solvents and reaction conditions." After briefly discussing how it's implemented, the authors discuss the various functions of AI4Green, including its support for workgroups, workbooks, user roles, reaction building, reaction sketching, reaction analysis, exporting, and add-on functionality, such as the Solvent Guide. The authors also discuss how feedback was used during application development. They conclude that AI4Green "combines the practical benefits of an ELN alongside a framework for encouraging green and sustainable chemistry," though more work is to be done to extend its functionality. Regardless, even as-is, "AI4Green provides an exciting initial framework to unite an ELN with sustainable chemistry."
In this 2023 journal article published in the Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, Boobier et al. of University of Nottingham discuss their free, open-source electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) for green and sustainable chemistry practice, AI4Green. The authors state their ELN also "automatically presents the hazards and sustainability of an inputted reaction by calculating sustainability metrics and a color-coded assessment of solvents and reaction conditions." After briefly discussing how it's implemented, the authors discuss the various functions of AI4Green, including its support for workgroups, workbooks, user roles, reaction building, reaction sketching, reaction analysis, exporting, and add-on functionality, such as the Solvent Guide. The authors also discuss how feedback was used during application development. They conclude that AI4Green "combines the practical benefits of an ELN alongside a framework for encouraging green and sustainable chemistry," though more work is to be done to extend its functionality. Regardless, even as-is, "AI4Green provides an exciting initial framework to unite an ELN with sustainable chemistry."
 In this 2023 article published in the Indonesian journal Matrix: Jurnal Manajemen Teknologi Dan Informatika, Ifriza et al. present their approach to developing a laboratory-based information system for monitoring the condition and maintenance of instruments at the laboratories of the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, State University of Semarang (FMIPA UNNES). After providing a brief introduction, the authors discuss their methodology to developing such a software system, as well as the results, which are explained in terms of the five enterprise architecture planning (EAP) steps used to develop it. The authors conclude that "[b]ased on the results of the study, it can be concluded that the use of laboratory systems for monitoring and maintenance in laboratory management has proven to be very valid."
In this 2023 article published in the Indonesian journal Matrix: Jurnal Manajemen Teknologi Dan Informatika, Ifriza et al. present their approach to developing a laboratory-based information system for monitoring the condition and maintenance of instruments at the laboratories of the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, State University of Semarang (FMIPA UNNES). After providing a brief introduction, the authors discuss their methodology to developing such a software system, as well as the results, which are explained in terms of the five enterprise architecture planning (EAP) steps used to develop it. The authors conclude that "[b]ased on the results of the study, it can be concluded that the use of laboratory systems for monitoring and maintenance in laboratory management has proven to be very valid."
 In this 2022 paper published in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine, Ennis et al. discuss the development of a practice-based research network in order to improve the state of understanding of Cannabis science in the state of Florida, as well as promote future clinical research related to the plant. The authors developed this research network after noting a dearth of such medical marijuana-focused research networks in the state. After providing an introduction, they walk through the steps that led to their Complementary Care Practice-Based Research Network (CC-PBRN), including the methods used in producing usable, de-identified data for research. The authors then summarize the results and address three major challenges in negotiating the "differing foci of academic and business organizations" in developing the network. After noting the strengths and limitations of their network, they conclude that "[t]he data generated by the CC-PBRN can be used to inform and guide patient-centered care, clinical decision-making, and health policy decisions" for medical marijuana patients in Florida.
In this 2022 paper published in the journal Complementary Therapies in Medicine, Ennis et al. discuss the development of a practice-based research network in order to improve the state of understanding of Cannabis science in the state of Florida, as well as promote future clinical research related to the plant. The authors developed this research network after noting a dearth of such medical marijuana-focused research networks in the state. After providing an introduction, they walk through the steps that led to their Complementary Care Practice-Based Research Network (CC-PBRN), including the methods used in producing usable, de-identified data for research. The authors then summarize the results and address three major challenges in negotiating the "differing foci of academic and business organizations" in developing the network. After noting the strengths and limitations of their network, they conclude that "[t]he data generated by the CC-PBRN can be used to inform and guide patient-centered care, clinical decision-making, and health policy decisions" for medical marijuana patients in Florida.
 In this 2023 paper published in the journal Accreditation and Quality Assurance, Tziakou et al. examine the state of risk management as it applies to the modern laboratory environment, tapping into numerous International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards and a review of the literature on the subject. After a brief introduction, the authors discuss the risk management process and risk assessment techniques for organizations of all types. They then take a deep dive into how those techniques apply to the laboratory environment at every step of the lab's workflow, from sample and reagent management to reporting and digitalization of results. They conclude that given the major sources of risk they identified in the lab, "the laboratory can reduce the risks to a tolerable level when clear procedures, continuous supervision, inspections, timely training and continuous education of its staff, and upgrades of its equipment with systems automation are maintained." They add that "the implementation of risk-based thinking can positively affect the outcome of regular assessments in order to explore opportunities for increasing the effectiveness of the [quality management system] and preventing further negative effects."
In this 2023 paper published in the journal Accreditation and Quality Assurance, Tziakou et al. examine the state of risk management as it applies to the modern laboratory environment, tapping into numerous International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards and a review of the literature on the subject. After a brief introduction, the authors discuss the risk management process and risk assessment techniques for organizations of all types. They then take a deep dive into how those techniques apply to the laboratory environment at every step of the lab's workflow, from sample and reagent management to reporting and digitalization of results. They conclude that given the major sources of risk they identified in the lab, "the laboratory can reduce the risks to a tolerable level when clear procedures, continuous supervision, inspections, timely training and continuous education of its staff, and upgrades of its equipment with systems automation are maintained." They add that "the implementation of risk-based thinking can positively affect the outcome of regular assessments in order to explore opportunities for increasing the effectiveness of the [quality management system] and preventing further negative effects."
 Noting only one known work comparing data warehouses (DWs) with data lakes (DLs), with that article failing to fully address "a comprehensive analysis of both data management schemes by addressing various aspects" in detail, Nambiar and Mundra take to that task in this 2022 article published in Big Data and Cognitive Computing. After an introduction to the state of DWs and DLs, the authors then discuss the finer points of both data management schemes, while also conducting a literature review on the topic. They then discuss the specifics of architecture regarding DWs and DLs, as well as the data management aspects and useful tools that enhance them. After discussing various challenges and opportunities for the two schemes, the authors conclude that "[d]espite being used interchangeably, they are two distinct storage forms with unique characteristics that serve different purposes."
Noting only one known work comparing data warehouses (DWs) with data lakes (DLs), with that article failing to fully address "a comprehensive analysis of both data management schemes by addressing various aspects" in detail, Nambiar and Mundra take to that task in this 2022 article published in Big Data and Cognitive Computing. After an introduction to the state of DWs and DLs, the authors then discuss the finer points of both data management schemes, while also conducting a literature review on the topic. They then discuss the specifics of architecture regarding DWs and DLs, as well as the data management aspects and useful tools that enhance them. After discussing various challenges and opportunities for the two schemes, the authors conclude that "[d]espite being used interchangeably, they are two distinct storage forms with unique characteristics that serve different purposes."
 While the management of digitally created data and information is largely in the scope of regulators, standards organizations, and company management these days, the non-trivial surplus of analog data and information (e.g., printed tables, field notebooks, photographs, drawings, maps, etc.) and what to do with it still weighs upon on the research community. Older data has long had uses in retrospective and current research, yet few large-scale solutions for making this analog data and information more FAIR (findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable) have been developed. Kelly et al. emphasize this in their 2022 research published in the Data Science Journal and address what they consider should be a set of best practices to managing historic analog data and information. After proving background history on the concerns surrounding older analog data, the authors discuss ways that older analog data is currently and can be used, and they highlight the challenges that come with attempting to reuse such data. They then provide some possible paths forward with a best practice approach, before concluding that "[b]est practices (including selection of metadata schema, developing a data dictionary, describing data collection methods) and policies developed to govern the preservation and dissemination of digital data could serve as an example for developments concerning analog data."
While the management of digitally created data and information is largely in the scope of regulators, standards organizations, and company management these days, the non-trivial surplus of analog data and information (e.g., printed tables, field notebooks, photographs, drawings, maps, etc.) and what to do with it still weighs upon on the research community. Older data has long had uses in retrospective and current research, yet few large-scale solutions for making this analog data and information more FAIR (findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable) have been developed. Kelly et al. emphasize this in their 2022 research published in the Data Science Journal and address what they consider should be a set of best practices to managing historic analog data and information. After proving background history on the concerns surrounding older analog data, the authors discuss ways that older analog data is currently and can be used, and they highlight the challenges that come with attempting to reuse such data. They then provide some possible paths forward with a best practice approach, before concluding that "[b]est practices (including selection of metadata schema, developing a data dictionary, describing data collection methods) and policies developed to govern the preservation and dissemination of digital data could serve as an example for developments concerning analog data."