LIMSwiki
| Part of | West Africa |
|---|---|
| Year dem found am | 2 October 1958 |
| Name in native language | République de Guinée |
| Official name | Guinée, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, République de Guinée, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߬ ߞߊ߲ߓߍ߲ |
| Native label | République de Guinée |
| Short name | 🇬🇳 |
| Official language | French |
| Anthem | Liberté |
| Culture | culture of Guinea |
| Motto | Work, Justice, Solidarity |
| Motto text | Travail, Justice, Solidarité, Work, Justice, Solidarity, Труд, справедливост, солидарност, ߓߊ߯ߙߊ ߸ߕߋߟߋ߲ ߸ߢߐ߲߯ߘߍߡߍ߲, Gwaith, Cyfiawnder, Undod |
| Continent | Africa |
| Country | Guinea |
| Capital | Conakry |
| Located in time zone | UTC±00:00, Africa/Conakry |
| Located in or next to body of water | Atlantic Ocean |
| Located in/on physical feature | West Africa |
| Coordinate location | 10°0′0″N 11°0′0″W |
| Coordinates of easternmost point | 8°22′40″N 7°38′16″W |
| Coordinates of northernmost point | 12°40′12″N 13°42′0″W |
| Coordinates of southernmost point | 7°11′26″N 9°6′29″W |
| Coordinates of westernmost point | 10°37′0″N 15°21′55″W |
| Highest point | Mount Richard-Molard |
| Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean |
| Government ein basic form | republic |
| Office held by head of state | President of Guinea |
| State ein head | Mamady Doumbouya |
| Office head of government hold | Prime Minister of Guinea |
| Government ein head | Bah Oury |
| Legislative body | National Assembly |
| Central bank | Central Bank of the Republic of Guinea |
| Currency | Guinean franc |
| Driving side | right |
| Electrical plug type | Europlug, Schuko, Type K |
| Dey follow | People's Revolutionary Republic of Guinea |
| Dey replace | French West Africa |
| Dema official website | http://www.presidence.gov.gn/ |
| Hashtag | Guinea |
| Top-level Internet domain | .gn |
| Flag | flag of Guinea |
| Coat of arms | coat of arms of Guinea |
| Geography of topic | geography of Guinea |
| Get characteristic | partly free country |
| History of topic | history of Guinea |
| Economy of topic | economy of Guinea |
| Demographics of topic | demographics of Guinea |
| Mobile country code | 611 |
| Country calling code | +224 |
| Emergency phone number | 117, 18, 442-020 |
| Licence plate code | RG |
| Maritime identification digits | 632 |
| Unicode character | 🇬🇳 |
| Category for maps or plans | Category:Maps of Guinea |

Guinea (/ˈɡɪni/ (listen) GHIN-ee),[1] alias Republic of Guinea (French: République de Guinée), be sam coastal country for West Africa. Edey share border plus Atlantic Ocean go de west, Guinea-Bissau go de northwest, Senegal go de north, Mali go de northeast, Cote d'Ivoire go de southeast, den Sierra Leone den Liberia go de south. Samtyms dem refer am as Guinea-Conakry after ein capital Conakry, so say e go distinguish am from oda territories for de eponymous region insyd lyk Guinea-Bissau den Equatorial Guinea.[2][3][4][5] Guinea get population of 13.5 million den area of 245,857 square kilometres (94,926 sq mi).[6]
Formerly French Guinea, e achieve independence for 1958 insyd.[7] Guinea get history of military coups d'état.[8][9][10] After decades of authoritarian rule, for 2010 insyd e hold ein first democratic election.[10][11][12] As e continue make e hold multi-party elections, de country continue dey face ethnic conflicts, corruption, den abuses by military den police.[12][13] For 2011 insyd, de United States government claim say torture by security forces den abuse of women den kiddies (wey dey include female genital mutilation) be human rights issues wey dey go on.[14] For 2021 insyd, military faction overthrow presido Alpha Condé wey dem suspend de constitution.[8][9][10]
Muslims dey represent 85% of de population.[2][15][16] Dem divide de country go four geographic regions: Maritime Guinea for de Atlantic coast, de Fouta Djallon anaa Middle Guinea highlands, de Upper Guinea savanna region for de northeast, den de Guinée forestière region of tropical forests. French, de official language of Guinea, be language of communication for schools, government administration, den de media. Dem dey speak more than 24 indigenous languages wey de largest be Susu, Pular, den Maninka, wey dey dominate respectively for Maritime Guinea, Fouta Djallon, den Upper Guinea insyd, while Guinée forestière be ethnolinguistically diverse. Guinea ein economy dey mostly dependent for agriculture den mineral production top.[17] Ebe de world ein second largest producer of bauxite, wey e get deposits of diamonds den gold.[18] Na de country be de core for de 2014 Ebola outbreak.
Name
History
West African empires den kingdoms
Colony
Post-colonial


Geography


Guinea be home to 5 ecoregions: Guinean montane forests, Western Guinean lowland forests, Guinean forest-savanna mosaic, West Sudanian savanna, den Guinean mangroves.[19] E get 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 4.9/10, wey dey rank am 114th globally out of 172 countries.[20]
Wildlife

Species found insyd Guinea dey include de following:
- Amphibians : Hemisus guineensis, Phrynobatrachus guineensis
- Reptiles : Acanthodactylus guineensis, Mochlus guineensis
- Arachnids: Malloneta guineensis, Dictyna guineensis
- Insects : Zorotypus guineensis, Euchromia guineensis
- Birds: Melaniparus guineensis
Regions den prefectures
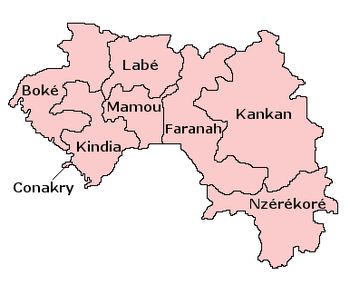
De Republic of Guinea dey cover 245,857 square kilometres (94,926 sq mi) of West Africa, about 10 degrees north of de equator. Dem divide am into 4 natural regions plus distinct human, geographic, den climatic characteristics:
- Maritime Guinea (La Guinée Maritime) dey cover 18% of de country.
- Middle Guinea (La Moyenne-Guinée) dey cover 20% of de country.
- Upper Guinea (La Haute-Guinée) dey cover 38% of de country.
- Forested Guinea (Guinée forestière) dey cover 23% of de country, wey ebe both forested den mountainous.

Dem divide Guinea into 8 administrative regions wich na dem subdivide am into 33 prefectures. De capital Conakry plus population of 1,675,069 ranks as special zone.
| Region | Capital | Population (2014 census by National Institute of Statistics) |
|---|---|---|
| Conakry Region | Conakry | 1,675,069 |
| Nzérékoré Region | Nzérékoré | 1,591,716 |
| Kindia Region | Kindia | 1,573,690 |
| Boké Region | Boké | 1,092,291 |
| Labé Region | Labé | 1,001,392 |
| Mamou Region | Mamou | 737,062 |
| Kankan Region | Kankan | 1,979,038 |
| Faranah Region | Faranah | 949,589 |
Politics
Foreign relations

Military
Human rights
Economy


Agriculture
Natural resources
Guinea get 25% anaa more of de world ein known bauxite reserves. E get diamonds, gold, den oda metals. Bauxite den alumina be de most major exports.
Mining
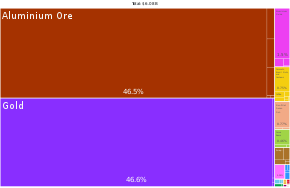
Oil
Tourism
-
De "Voile de la Mariée" (Bride's Veil) waterfall insyd Kindia
-
Chimpanzé de Bossou
-
Plage sur les Ile de Loos
Sciences den technology
Na dem rank Guinea 128th out of 132 insyd de Global Innovation Index insyd 2023.[21]
Transport
Demography
| Largest cities anaa towns insyd Guinea
According to de 2014 Census[22] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Region | Pop. | ||||||
| Conakry
Nzérékoré |
1 | Conakry | Conakry | 1,660,973 | |||||
| 2 | Nzérékoré | Nzérékoré | 195,027 | ||||||
| 3 | Kankan | Kankan | 190,722 | ||||||
| 4 | Manéah | Kindia | 167,354 | ||||||
| 5 | Dubréka | Kindia | 157,017 | ||||||
| 6 | Kindia | Kindia | 138,695 | ||||||
| 7 | Siguiri | Kankan | 127,492 | ||||||
| 8 | Kissidougou | Faranah | 99,931 | ||||||
| 9 | Labé | Labé | 92,654 | ||||||
| 10 | Kamsar | Boké | 83,428 | ||||||
Many languages are spoken in Guinea.
| Population insyd Guinea[23][24] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Million | ||
| 1950 | 3.0 | ||
| 2000 | 8.8 | ||
| 2021 | 13.5 | ||
Religion
Education

Health
Ebola
Maternal den child healthcare
HIV/AIDS
Malnutrition
Malaria
COVID-19 pandemic
Culture

Media
Sports
Polygamy
Polygamy be generally prohibited by law insyd Guinea, buh der be exceptions.[25] Insyd 2020, na dem estimate say about 26% of marriages be polygamous (29% Muslim den 10% Christian).[26]
Cuisine
Guinean cuisine dey vary by region plus rice as staple. Dem dey consume cassava.[27] Part of West African cuisine, de chows of Guinea dey include yétissé, peanut sauce, okra sauce den tapalapa bread. Insyd rural areas, dem dey chop chow from "large serving dish" wey dem dey chop by hand outsyd of homes.[28]
Music
Visual art
References
- ↑ French: Guinée, Pular: 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, romanized: Gine, Wolof: Gine, N'Ko: ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, Bambara: Gine
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Guinea-Conakry". Archived from the original on 5 February 2009. Retrieved 11 February 2009.
- ↑ "Music Videos of Guinea Conakry". Archived from the original on 21 February 2007. Retrieved 12 April 2018.
- ↑ "The Anglican Diocese of Ghana". Netministries.org. Archived from the original on 7 January 2009. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- ↑ "CFI – Africa – Guinea Conakry". Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 11 February 2009.
- ↑ "Nations Online: Guinea – Republic of Guinea – West Africa". Nations Online. Archived from the original on 3 May 2003. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ↑ West Africa economic bloc suspends Guinea after military coup, Deutsche Welle (8 September 2021).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Nicholas Bariyo & Benoit Faucon, Military Faction Stages Coup in Mineral-Rich Guinea, Wall Street Journal (5 September 2021).
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Krista Larson, EXPLAINER: Why is history repeating itself in Guinea's coup?, Associated Press (7 September 2021).
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Danielle Paquett, Here's what we know about the unfolding coup in Guinea, Washington Post (6 September 2021).
- ↑ Abdourahmane Diallo and Adam Nossiter, Guinea Votes in Its First Democratic Presidential Election, New York Times (7 November 2010).
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Guinea, Freedom in the World, Freedom House, 2021.
- ↑ Saliou Samb, Guinea President Conde vows to tackle corruption during third term, Reuters (15 December 2020).
- ↑ Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor (2012). "Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2011: Guinea". United States Department of State. Retrieved 27 August 2012.
- ↑ "Religion in Guinea". Visual Geography. Archived from the original on 14 September 2013. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- ↑ "The Pan African Bank". Ecobank. Archived from the original on 19 March 2012. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- ↑ "Guinea Conakry: Major Imports, Exports, Industries & Business Opportunities in Guinea Conakry, Africa". Archived from the original on 5 November 2010. Retrieved 15 October 2014.
- ↑ "Guinea Conakry Support – Guinee Conakry Trade and Support. (GCTS)". Archived from the original on 5 January 2015. Retrieved 15 October 2014.
- ↑ Dinerstein, Eric; Olson, David; Joshi, Anup; Vynne, Carly; Burgess, Neil D.; Wikramanayake, Eric; Hahn, Nathan; Palminteri, Suzanne; Hedao, Prashant; Noss, Reed; Hansen, Matt; Locke, Harvey; Ellis, Erle C; Jones, Benjamin; Barber, Charles Victor; Hayes, Randy; Kormos, Cyril; Martin, Vance; Crist, Eileen; Sechrest, Wes; Price, Lori; Baillie, Jonathan E. M.; Weeden, Don; Suckling, Kierán; Davis, Crystal; Sizer, Nigel; Moore, Rebecca; Thau, David; Birch, Tanya; Potapov, Peter; Turubanova, Svetlana; Tyukavina, Alexandra; de Souza, Nadia; Pintea, Lilian; Brito, José C.; Llewellyn, Othman A.; Miller, Anthony G.; Patzelt, Annette; Ghazanfar, Shahina A.; Timberlake, Jonathan; Klöser, Heinz; Shennan-Farpón, Yara; Kindt, Roeland; Lillesø, Jens-Peter Barnekow; van Breugel, Paulo; Graudal, Lars; Voge, Maianna; Al-Shammari, Khalaf F.; Saleem, Muhammad (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ↑ Grantham, H. S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T. D.; Jones, K. R.; Beyer, H. L.; Schuster, R.; Walston, J.; Ray, J. C.; Robinson, J. G.; Callow, M.; Clements, T.; Costa, H. M.; DeGemmis, A.; Elsen, P. R.; Ervin, J.; Franco, P.; Goldman, E.; Goetz, S.; Hansen, A.; Hofsvang, E.; Jantz, P.; Jupiter, S.; Kang, A.; Langhammer, P.; Laurance, W. F.; Lieberman, S.; Linkie, M.; Malhi, Y.; Maxwell, S.; Mendez, M.; Mittermeier, R.; Murray, N. J.; Possingham, H.; Radachowsky, J.; Saatchi, S.; Samper, C.; Silverman, J.; Shapiro, A.; Strassburg, B.; Stevens, T.; Stokes, E.; Taylor, R.; Tear, T.; Tizard, R.; Venter, O.; Visconti, P.; Wang, S.; Watson, J. E. M. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ↑ WIPO (2022). Global Innovation Index 2023, 15th Edition. World Intellectual Property Organization. doi:10.34667/tind.46596. ISBN 978-92-805-3432-0. Retrieved 29 October 2023.
- ↑ "Cities and Regions". Citypopulation.de. Retrieved 23 July 2021.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ↑ Articles 315–319 Archived 21 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Civil Code of the Republic of Guinea (Code Civil de la Republique de Guinee)
- ↑ "Polygamy is rare around the world and mostly confined to a few regions". 7 December 2020.
- ↑ "Recipes & Cookbooks". Friends of Guinea. Archived from the original on 3 February 2014. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- ↑ "Eating in the Embassy: Guinean Embassy Brings West African Food To Washington". WAMU. Archived from the original on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
External links
Guinea at Wikipedia ein sister projects
- Definitions from Wiktionary
- Media from Commons
- News from Wikinews
- Quotations from Wikiquote
- Texts from Wikisource
- Textbooks from Wikibooks
- Resources from Wikiversity
- Travel information from Wikivoyage
- Official website (insyd French)
- Guinea. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Guinea from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Guinea profile from de BBC News
- Wikimedia Atlas of Guinea
- Geographic data wey relate to Guinea at OpenStreetMap
- Guinea 2008 Summary Trade Statistics