LIMSwiki
 | |
 Headquarters in Sant'Agata Bolognese, Italy | |
| Company type | Subsidiary |
|---|---|
| Industry | Automotive |
| Founded | 1963 |
| Founder | Ferruccio Lamborghini |
| Headquarters | , Italy |
Number of locations | 135 dealerships |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people | Stephan Winkelmann (CEO)[1] |
Production output | |
| Revenue | |
| Total equity | |
Number of employees | 1,779 (December 2020)[4] |
| Parent | Audi AG |
| Subsidiaries | Ducati Motor Holding S.p.A. Italdesign Giugiaro |
| Website | lamborghini.com |
Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A., usually referred to as Lamborghini or colloquially Lambo, (Italian: [autoˈmɔːbili lamborˈɡiːni]) is an Italian manufacturer of luxury sports cars and SUVs based in Sant'Agata Bolognese. The company is owned by the Volkswagen Group through its subsidiary Audi.
Ferruccio Lamborghini (1916–1993), an Italian manufacturing magnate, founded Automobili Ferruccio Lamborghini S.p.A. in 1963 to compete with Ferrari. The company was noted for using a rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive layout. Lamborghini grew rapidly during its first decade, but sales plunged in the wake of the 1973 worldwide financial downturn and the oil crisis. The firm's ownership changed three times after 1973, including a bankruptcy in 1978. American Chrysler Corporation took control of Lamborghini in 1987 and sold it to Malaysian investment group Mycom Setdco and Indonesian group V'Power Corporation in 1994. In 1998, Mycom Setdco and V'Power sold Lamborghini to the Volkswagen Group where it was placed under the control of the group's Audi division.
New products and model lines were introduced to the brand's portfolio and brought to the market and saw an increased productivity for the brand. In the late 2000s, during the Great Recession, Lamborghini's sales dropped nearly 50%.
Lamborghini currently produces the V10-powered Huracán, the Urus SUV powered by a twin-turbo V8 engine, and the Revuelto, a V12/electric hybrid, as of 2024. In addition, the company produces V12 engines for offshore powerboat racing.
Lamborghini Trattori, founded in 1948 by Ferruccio Lamborghini, is headquartered in Pieve di Cento, Italy, and continues to produce tractors. Since 1973, Lamborghini Trattori has been a separate entity from the Lamborghini's automobile division.
History

Manufacturing magnate Italian Ferruccio Lamborghini founded the company in 1963 with the objective of producing a refined grand touring car to compete with offerings from established marques such as Ferrari. The company's first models, such as the 350 GT, were released in the mid-1960s. Lamborghini was noted for the 1966 Miura sports coupé, which used a rear mid-engine, rear-wheel drive layout.
In 1963, Ferruccio Lamborghini, already an established industrialist who manufactured tractors, boilers, and air conditioners, founded Lamborghini Automobili on May 7, 1963.[5]
The company was headquartered in a purpose-built facility in Sant'Agata Bolognese. He surrounded himself with highly capable engineers and technicians: Giotto Bizzarrini designed the engine, Gian Paolo Dallara and Paolo Stanzani developed the chassis, and Franco Scaglione designed the bodywork. The first model, the 350 GTV, was not a success due to its futuristic style and remained a one-off prototype. The project was then handed over to the Milanese coachbuilder Touring, which created a more classic and sober design. The new car, named the 350 GT, was a fast and elegant two-seater grand tourer (according to Ferruccio's standards) and was the first series-produced car by Lamborghini. It achieved moderate sales success and was followed by the 400 GT (which benefited from an increased engine capacity) and the 400 GT 2+2, both presented in 1966.
Lamborghini grew rapidly during its first ten years, but sales fell in the wake of the 1973 worldwide financial downturn and the oil crisis. Ferruccio Lamborghini sold the company to Georges-Henri Rossetti and René Leimer and retired in 1974. The company went bankrupt in 1978, and was placed in the receivership of brothers Jean-Claude and Patrick Mimran in 1980. The Mimrans purchased the company out of receivership by 1984 and invested heavily in its expansion. Under the Mimrans' management, Lamborghini's model line was expanded from the Countach to include the Jalpa sports car and the LM002 high-performance off-road vehicle.
The Mimrans sold Lamborghini to the Chrysler Corporation in 1987. After replacing the Countach with the Diablo and discontinuing the Jalpa and the LM002, Chrysler sold Lamborghini to Malaysian investment group Mycom Setdco and Indonesian group V'Power Corporation in 1994. In 1998, Mycom Setdco and V'Power sold Lamborghini to the Volkswagen Group where it was placed under the control of the group's Audi division. New products and model lines were introduced to the brand's portfolio and brought to the market and saw an increased productivity for the brand Lamborghini. In the late 2000s, during the Great Recession, Lamborghini's sales dropped nearly 50%.
In 2021, the CEO of Lamborghini said that by 2024 all its models will be hybrid.[6]
| Years | Owner |
|---|---|
| 1963–1972 | Ferruccio Lamborghini |
| 1972–1977 | Georges-Henri Rossetti and René Leimer |
| 1977–1984 | Receivership |
| 1984–1987 | Patrick Mimran |
| 1987–1994 | Chrysler Corporation |
| 1994–1995 | MegaTech |
| 1995–1998 | V'Power and Mycom Sedtco |
| 1998–present | Audi AG |
Products
Automobiles
As of the 2018 model year, Lamborghini's automobile product range consists of three model lines, two of which are mid-engine two-seat sports cars while the third one is a front engined, all-wheel drive SUV.[7]
Models in production
- Revuelto

Production of the new Revuelto began in mid-2023 and will be delivered in late 2023 as a 2024 model. The car will be powered by a 6.5L naturally aspirated V12 and three magnetic motors for a combined power output of 1,001 hp (1,015 PS). The Revuelto is the successor to the Aventador.[8][9]
- Huracán

The V10-powered Huracán line currently includes the all-wheel-drive LP 610-4, the low-cost rear-wheel-drive LP 580-2, and the powerful track-oriented LP 640-4 Performante, each in coupé and Spyder (convertible) versions. Since 2024 is the last year that the Huracán is being marketed, the powerful Temerario will be its successor.[10]
- Urus

Intending to double its sales volume by 2019, Lamborghini also added an SUV named Urus in its line-up which is powered by a twin-turbo V8 engine and utilizes a front engine, all-wheel drive layout.[11][12]
Marine engines
Motori Marini Lamborghini produces a large V12 marine engine block for use in World Offshore Series Class 1 powerboats. A Lamborghini branded marine engine displaces approximately 8,171 cc (8.2 L) and outputs approximately 940 hp (700 kW).[13]
Lamborghini motorcycle
In the mid-1980s, Lamborghini produced a limited-production run of a 1,000 cc (61.0 cu in) sports motorcycle. UK weekly newspaper Motor Cycle News reported in 1994—when featuring an example available through an Essex motorcycle retailer—that 24 examples were produced with a Lamborghini alloy frame having adjustable steering head angle, Kawasaki GPz1000RX engine/transmission unit, Ceriani front forks and Marvic wheels. The bodywork was plastic and fully integrated with front fairing merged into fuel tank and seat cover ending in a rear tail-fairing. The motorcycles were designed by Lamborghini stylists and produced by French business Boxer Bikes.[14]
Branded merchandise

Lamborghini licenses its brand to manufacturers that produce a variety of Lamborghini-branded consumer goods including scale models, clothing, accessories, bags, electronics[15] and laptop computers.[16]
Motorsport
 | |
| Squadra Corse | |
| Company type | Subsidiary |
| Industry |
|
| Headquarters | Sant'Agata Bolognese , Italy |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people |
|
| Owner | Automobili Lamborghini |
| Parent | Audi AG |
| Website | lamborghini |
Automobiles produced
Lamborghini Motorsport Division Squadra Corse produces GT3 cars and cars for their Super Trofeo events based on the Gallardo and Huracán. Apart from them, the Squadra Corse builds cars upon customer request.
GT3 and Super Trofeo Cars
- Gallardo LP 570-4 Super Trofeo
- Gallardo LP 560-4 Super Trofeo
- Huracán LP 620-2 Super Trofeo EVO
- Huracán LP 620-2 Super Trofeo EVO2
- Huracán Super Trofeo GT2
- Huracán GT3
- Huracán GT3 Evo
- Huracán GT3 Evo 2
Special cars
These cars were built by Squadra Corse upon customer request.
Events held
Lamborghini Super Trofeo


The Super Trofeo is a series of Motorsport events held by Squadra corse using their Super Trofeo model vehicles (currently the Huracán Super Trofeo EVO) which are racing versions of the road-approved models (Huracán and Gallardo models).
The Super Trofeo events are held in three different series, in three continents: America, Asia and Europe. Many private race team participate each of these events.
Every series consists of six rounds, each of which feature free practice sessions, qualifying and two races lasting 50 minutes each. There are four categories of drivers: Pro, Pro-Am, Am and Lamborghini Cup. The season ends in the Lamborghini Super Trofeo World Final.[17]
Lamborghini GT3

The Lamborghini GT3 is a series of Motorsport events held by The Squadra Corse using Huracán GT3 cars that comply with the FIA GT3 regulations. The racing event is open to any Huracán GT3 customer.
Lamborghini currently uses Huracán GT3 Evo cars for these events and more than 60 private race teams participate these events.[18]
Current factory drivers
Factory drivers[19]
GT3 junior drivers[20]
 Jack Bartholomew
Jack Bartholomew Glenn van Berlo
Glenn van Berlo Riccardo Cazzaniga
Riccardo Cazzaniga Pierre-Louis Chovet
Pierre-Louis Chovet Jaden Conwright
Jaden Conwright Alessio Deledda
Alessio Deledda Philippe Denes
Philippe Denes Raúl Guzmán
Raúl Guzmán Benjamin Hites
Benjamin Hites Nico Jamin
Nico Jamin Brendon Leitch
Brendon Leitch Mateo Llarena
Mateo Llarena Mattia Michelotto
Mattia Michelotto Baptiste Moulin
Baptiste Moulin Marcus Påverud
Marcus Påverud Artem Petrov
Artem Petrov Daan Pijl
Daan Pijl Mick Wishofer
Mick Wishofer
Super Trofeo junior drivers[21]
 Largim Ali
Largim Ali Filippo Berto
Filippo Berto Dougie Bolger
Dougie Bolger Amaury Bonduel
Amaury Bonduel Loris Cabirou
Loris Cabirou Hugo Condé
Hugo Condé Pedro Ebrahim
Pedro Ebrahim Marco Giltrap
Marco Giltrap Riccardo Ianniello
Riccardo Ianniello Alessandro Mainetti
Alessandro Mainetti Edgar Maloigne
Edgar Maloigne Patrick Matthiensen
Patrick Matthiensen Marzio Moretti
Marzio Moretti Lucas Petersson
Lucas Petersson Guillem Pujeu
Guillem Pujeu Wesley Slimp
Wesley Slimp Oliver Söderström
Oliver Söderström Gilles Stadsbader
Gilles Stadsbader Rodrigo Testa
Rodrigo Testa Lucas Valkre
Lucas Valkre Yuri Wagner
Yuri Wagner Jake Walker
Jake Walker Jackson Walls
Jackson Walls Ugo de Wilde
Ugo de Wilde Carter Williams
Carter Williams Xu Shenghui
Xu Shenghui
Lamborghini in Formula One
| Notable staff | Mauro Forghieri |
|---|---|
| Formula One World Championship career | |
| First entry | 1989 Brazilian Grand Prix |
| Last entry | 1993 Australian Grand Prix |
| Races entered | 80 |
| Chassis | Lola, Lotus, Lambo, Ligier, Minardi, Venturi, Larrousse |
| Constructors' Championships | 0 |
| Drivers' Championships | 0 |
| Race victories | 0 |
| Podiums | 1 |
| Points | 20 |
| Pole positions | 0 |
| Fastest laps | 0 |

In contrast to his rival Enzo Ferrari, Ferruccio Lamborghini had decided early on that there would be no factory-supported racing of Lamborghinis, viewing motorsport as too expensive and too draining on company resources.[22] This was unusual for the time, as many sports car manufacturers sought to demonstrate speed, reliability, and technical superiority through motorsport participation. Enzo Ferrari in particular was known for considering his road car business mostly a source of funding for his participation in motor racing. Ferruccio's policy led to tensions between him and his engineers, many of whom were racing enthusiasts; some had previously worked at Ferrari. When Dallara, Stanzani, and Wallace began dedicating their spare time to the development of the P400 prototype, they designed it to be a road car with racing potential, one that could win on the track and also be driven on the road by enthusiasts.[23] When Ferruccio discovered the project, he allowed them to go ahead, seeing it as a potential marketing device for the company, while insisting that it would not be raced. The P400 went on to become the Miura. The closest the company came to building a true race car under Lamborghini's supervision were a few highly modified prototypes, including those built by factory test driver Bob Wallace, such as the Miura SV-based "Jota" and the Jarama S-based "Bob Wallace Special".
In the mid-1970s, while Lamborghini was under the management of Georges-Henri Rossetti, Lamborghini entered into an agreement with BMW to develop, then manufacture 400 cars for BMW in order to meet Group 4 homologation requirements. BMW lacked experience developing a mid-engined vehicle and believed that Lamborghini's experience in that area would make Lamborghini an ideal choice of partner. Due to Lamborghini's shaky finances, Lamborghini fell behind schedule developing the car's structure and running gear. When Lamborghini failed to deliver working prototypes on time, BMW took the program in house, finishing development without Lamborghini. BMW contracted with Baur to produce the car, which BMW named the M1, delivering the first vehicle in October 1978.[24][25]
In 1985, Lamborghini's British importer developed the Countach QVX, in conjunction with Spice Engineering, for the 1986 Group C championship season. One car was built, but lack of sponsorship caused it to miss the season. The QVX competed in only one race, the non-championship 1986 Southern Suns 500 km race at Kyalami in South Africa, driven by Tiff Needell. Despite the car finishing better than it started, sponsorship could once again not be found and the programme was cancelled.[26]

Lamborghini was an engine supplier in Formula One for the 1989 through 1993 Formula One seasons. It supplied engines to Larrousse (1989–1990, 1992–1993), Lotus (1990), Ligier (1991), Minardi (1992), and to the Modena team in 1991. While the latter is commonly referred to as a factory team, the company saw itself as a supplier, not a backer. The 1992 Larrousse—Lamborghini was largely uncompetitive but noteworthy in its tendency to spew oil from its exhaust system. Cars following closely behind the Larrousse were commonly coloured yellowish-brown by the end of the race.[27] Lamborghini's best result was achieved with Larrousse at the 1990 Japanese Grand Prix, when Aguri Suzuki finished third on home soil.[28]
In late 1991, a Lamborghini Formula One motor was used in the Konrad KM-011 Group C sports car, but the car only lasted a few races before the project was cancelled. The same engine, re-badged a Chrysler, Lamborghini's then-parent company, was tested by McLaren towards the end of the 1993 season, with the intent of using it during the 1994 season. Although driver Ayrton Senna was reportedly impressed with the engine's performance, McLaren pulled out of negotiations, choosing a Peugeot engine instead, and Chrysler ended the project.

Two racing versions of the Diablo were built for the Diablo Supertrophy, a single-model racing series held annually from 1996 to 1999. In the first year, the model used in the series was the Diablo SVR, while the Diablo 6.0 GTR was used for the remaining three years.[29][30] Lamborghini developed the Murciélago R-GT as a production racing car to compete in the FIA GT Championship, the Super GT Championship and the American Le Mans Series in 2004. The car's highest placing in any race that year was the opening round of the FIA GT Championship at Valencia, where the car entered by Reiter Engineering finished third from a fifth-place start.[31][32] In 2006, during the opening round of the Super GT championship at Suzuka, a car run by the Japan Lamborghini Owners Club garnered the first victory (in class) by an R-GT. A GT3 version of the Gallardo has been developed by Reiter Engineering.[33] A Murciélago R-GT entered by All-Inkl.com racing, driven by Christophe Bouchut and Stefan Mücke, won the opening round of the FIA GT Championship held at Zhuhai International Circuit, achieving the first major international race victory for Lamborghini.[34]
Complete Formula One results
(key) (results in bold indicate pole position)
| Year | Entrant | Chassis | Engine(s) | Tyres | Drivers | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | Points | WCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | Larrousse Calmels | Lola LC88B Lola LC89 |
Lamborghini 3512 V12 | G | BRA | SMR | MON | MEX | US | CAN | FRA | GBR | GER | HUN | BEL | ITA | POR | ESP | JPN | AUS | 1 | 15th | |
| DNQ | Ret | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | ||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | Ret | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | 11 | DNPQ | DNQ | DNPQ | ||||||||||||||||
| 12 | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | DNPQ | 16 | Ret | 9 | 6 | Ret | Ret | ||||||||
| 1990 | ESPO Larrousse F1 | Lola LC89B Lola LC90 |
Lamborghini 3512 V12 | G | US | BRA | SMR | MON | CAN | MEX | FRA | GBR | GER | HUN | BEL | ITA | POR | ESP | JPN | AUS | 11 | 6th | |
| 8 | Ret | 13 | 6 | 9 | Ret | 8 | 4 | Ret | 6 | 9 | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | ||||||||
| Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | 12 | Ret | 7 | 6 | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | 14 | 6 | 3 | Ret | ||||||||
| Camel Team Lotus | Lotus 102 | Lamborghini V12 | G | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ret | Ret | 7 | Ret | 6 | 10 | 11 | Ret | 8 | 5 | 11 | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | 3 | 8th | ||||||
| DNS | Ret | 8 | Ret | Ret | 8 | 12 | Ret | Ret | 7 | 12 | Ret | Ret | DNS | ||||||||||
| Ret | Ret | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1991 | Equipe Ligier Gitanes | Ligier JS35 Ligier JS35B |
Lamborghini 3512 V12 |
G | US | BRA | SMR | MON | CAN | MEX | FRA | GBR | GER | HUN | BEL | ITA | POR | ESP | JPN | AUS | 0 | NC | |
| Ret | Ret | 7 | 7 | Ret | 8 | 12 | Ret | 9 | 17 | 11 | Ret | 16 | Ret | 9 | Ret | ||||||||
| DNQ | Ret | 10 | 10 | 8 | DNQ | 11 | DNQ | Ret | 10 | Ret | 11 | 11 | Ret | Ret | 18 | ||||||||
| Modena Team SpA | Lambo 291 | Lamborghini L3512 V12 | G | 7 | DNPQ | DNPQ | DNPQ | DNPQ | DNPQ | DNPQ | DNPQ | Ret | 16 | DNQ | 16 | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | Ret | 0 | NC | ||
| DNPQ | DNPQ | 9 | DNPQ | DNPQ | DNPQ | DNPQ | DNPQ | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | ||||||||
| 1992 | Central Park Venturi Larrousse | Venturi LC92 | Lamborghini 3512 V12 | G | RSA | MEX | BRA | ESP | SMR | MON | CAN | FRA | GBR | GER | HUN | BEL | ITA | POR | JPN | AUS | 1 | 11th | |
| Ret | 11 | Ret | Ret | Ret | 6 | DSQ | Ret | Ret | 14 | Ret | 18 | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | ||||||||
| 12 | 12 | 9 | DNQ | Ret | DNPQ | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | 17 | 9 | Ret | 11 | Ret | ||||||||
| Minardi Team | M191B M191L M192 |
Lamborghini 3512 3.5 V12 | G | Ret | Ret | Ret | 11 | Ret | 8 | 13 | DNQ | DNQ | DNQ | 12 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 12th | |||||
| DNQ | Ret | DNQ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Ret | Ret | 7 | Ret | Ret | Ret | 11 | 8 | 17 | 12 | DNQ | 16 | Ret | 14 | 14 | 10 | ||||||||
| 1993 | Larrousse F1 | Larrousse LH93 | Lamborghini 3512 V12 | G | RSA | BRA | EUR | SMR | ESP | MON | CAN | FRA | GBR | GER | HUN | BEL | ITA | POR | JPN | AUS | 3 | 10th | |
| Ret | 7 | Ret | 5 | Ret | 12 | Ret | 9 | 11 | 12 | 8 | 12 | 9 | 10 | ||||||||||
| 12 | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ret | 10 | 9 | Ret | 9 | Ret | 8 | 16 | Ret | Ret | Ret | Ret | 6 | 11 | Ret | 12 |
Marketing
Brand identity

The world of bullfighting is a key part of Lamborghini's identity.[35][36][37] In 1962, Ferruccio Lamborghini visited the Seville ranch of Don Eduardo Miura, a renowned breeder of Spanish fighting bulls. Lamborghini was so impressed by the majestic Miura animals that he decided to adopt a raging bull as the emblem for the automaker he would open shortly.[38]
Vehicle nomenclature
After producing two cars with alphanumeric designations, Lamborghini once again turned to the bull breeder for inspiration. Don Eduardo was filled with pride when he learned that Ferruccio had named a car for his family and their line of bulls; the fourth Miura to be produced was unveiled to him at his ranch in Seville.[38][39]
The automaker would continue to draw upon the bullfighting connection in future years. The Islero was named for the Miura bull that killed the famed bullfighter Manolete in 1947. Espada is the Spanish word for sword, sometimes used to refer to the bullfighter himself. The Jarama's name carried a special double meaning; though it was intended to refer only to the historic bullfighting region in Spain, Ferruccio was concerned about confusion with the also historic Jarama motor racing track.[40]

After christening the Urraco after a bull breed, in 1974, Lamborghini broke from tradition, naming the Countach (/ˈkuːntɑːʃ/ KOON-tahsh) not for a bull,[41] but for contacc (pronounced [kʊŋˈtɑtʃ]), a Piedmontese expletive.[41] Legend has it that Nuccio Bertone uttered the word in surprise when he first saw the Countach prototype, "Project 112".[42] The LM002 (LM for Lamborghini Militaire) sport utility vehicle and the Silhouette (named after the popular racing category of the time) were other exceptions to the tradition.
The Jalpa of 1982 was named for a bull breed; Diablo, for the Duke of Veragua's ferocious bull famous for fighting an epic battle against El Chicorro in Madrid in 1869;[43][44][45] Murciélago, the legendary bull whose life was spared by El Lagartijo for his performance in 1879; Gallardo, named for one of the five ancestral castes of the Spanish fighting bull breed;[46] and Reventón, the bull that defeated young Mexican torero Félix Guzmán in 1943. The Estoque concept of 2008 was named for the estoc, the sword traditionally used by matadors during bullfights.[47]
Concept vehicles
Throughout its history, Lamborghini has envisioned and presented a variety of concept cars, beginning in 1963 with the first Lamborghini prototype, the 350GTV. Other famous models include Bertone's 1967 Marzal, 1974 Bravo, and 1980 Athon, Chrysler's 1987 Portofino, the Italdesign-styled Cala from 1995, the Zagato-built Raptor from 1996.
A retro-styled Lamborghini Miura concept car, the first creation of chief designer Walter de'Silva, was presented in 2006. President and CEO Stephan Winkelmann denied that the concept would be put into production, saying that the Miura concept was "a celebration of our history, but Lamborghini is about the future. Retro design is not what we are here for. So we won't do the [new] Miura."[48]

At the 2008 Paris Motor Show, Lamborghini revealed the Estoque, a four-door sedan concept. Although there had been much speculation regarding the Estoque's eventual production,[49][50] Lamborghini management has not made a decision regarding production of what might be the first four-door car to roll out of the Sant'Agata factory.[51]

At the 2010 Paris Motor Show, Lamborghini unveiled the Sesto Elemento. The concept car is made almost entirely of carbon fibre making it extremely light, with a weight of 999 kg (2,202 lb). The Sesto Elemento shares the same V10 engine found in the Lamborghini Gallardo. Lamborghini hopes to signal a shift in the company's direction from making super cars focused on top speed to producing more agile, track focused cars with the Sesto Elemento. The concept car can reach 0–62 mph (0–100 km/h) in 2.5 seconds and can reach a top speed of over 180 mph (290 km/h).[52]
At the 2012 Geneva Motor Show, Lamborghini unveiled the Aventador J—a roofless, windowless version of the Lamborghini Aventador. The Aventador J uses the same 700 hp engine and seven-speed transmission as the standard Aventador.[53]
At the 2012 Beijing Motor Show, Lamborghini unveiled the Urus SUV. This is the first SUV built by Lamborghini since the LM002.
As part of the celebration of 50 years of Lamborghini, the company created the Egoista. Egoista is for one person's driving and only one Egoista is to be made.[54]
At the 2014 Paris Motor Show, Lamborghini unveiled the Asterion LPI910-4 hybrid concept car. Named after the half-man, half-bull hybrid (Minotaur) of Greek legend, it is the first hybrid Lamborghini in the history of the company. Utilizing the Huracán's 5.2 litre V10 producing 607 hp (453 kW; 615 PS), along with one electric motor mounted on the transaxle and an additional two on the front axle, developing an additional 300 hp (224 kW; 304 PS). This puts the power at a combined figure of 907 hp (676 kW; 920 PS). The 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph) time is claimed to be just above 3 seconds, with a claimed top speed of 185 mph (298 km/h).[55]
Corporate affairs
Structure
As of 2011, Lamborghini is structured as a wholly-owned subsidiary of Audi AG named Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A.[Notes 1][56]
Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. controls five principal subsidiaries: Ducati Motor Holding S.p.A., a manufacturer of motorcycles; Italdesign Giugiaro S.p.A., a design and prototyping firm that provides services to the entire Volkswagen Group; MML S.p.A. (Motori Marini Lamborghini), a manufacturer of marine engine blocks; and Volkswagen Group Italia S.p.A. (formerly Autogerma S.p.A.), which sells Audi and other Volkswagen Group vehicles in Italy.[56][57]
The Lamborghini headquarters and main production site is located in Sant'Agata Bolognese, Italy. With the launch of its Urus SUV, the production site expanded from 80,000 m2 (8.0 ha) to 160,000 m2 (16 ha).[58]
On 13 November 2020, Stephan Winkelmann, current President of Bugatti, was appointed to be the new CEO of Lamborghini. He took his new position on 1 December 2020.[1]
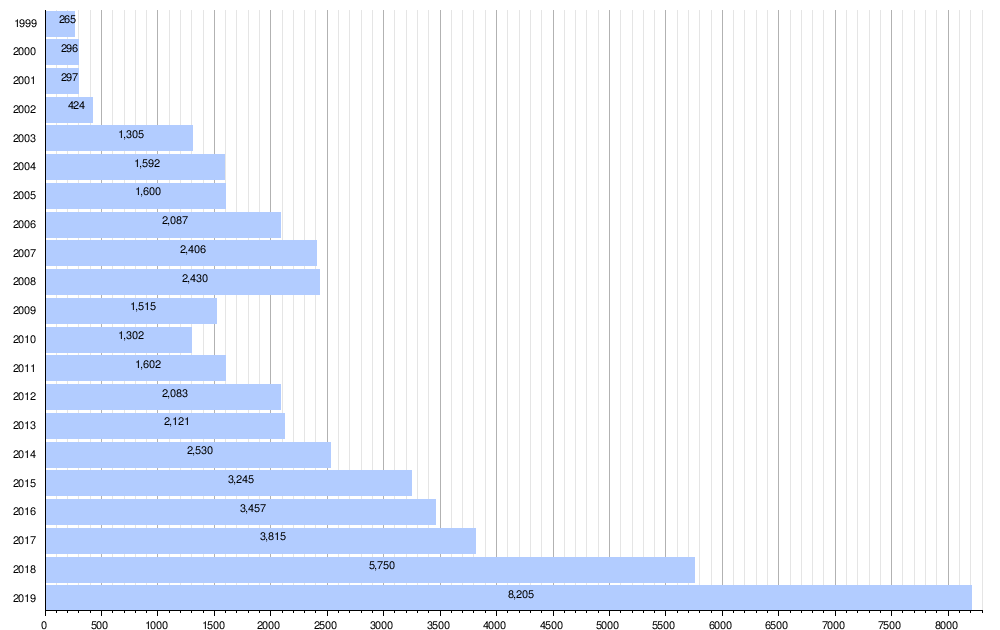
Sales results

By sales, the most important markets in 2004 for Lamborghini's sports cars were the U.S. (41%), Germany (13%), Great Britain (9%) and Japan (8%). Prior to the launch of the Gallardo in 2003, Lamborghini produced approximately 400 vehicles per year; in 2011 Lamborghini produced 1,711 vehicles.[59]
- Annual Lamborghini new car sales
| Year | Sales |
|---|---|
| 1968[60] | 353 |
| Data missing | |
| 1991[61] | 673 |
| 1992[61] | 166 |
| 1993[61] | 215 |
| Data missing | |
| 1996[62] | 211 |
| 1997[61] | 209 |
| Data missing | |
| 1999[63] | 265 |
| Year | Sales |
|---|---|
| 2000[64] | 296 |
| 2001[65] | 297 |
| 2002[66] | 424 |
| 2003[67] | 1,305 |
| 2004[67] | 1,592 |
| 2005[68] | 1,600 |
| 2006[69] | 2,087 |
| 2007[70] | 2,406 |
| 2008[71] | 2,430 |
| 2009[72] | 1,515 |
| Year | Sales |
|---|---|
| 2010[73] | 1,302 |
| 2011[74] | 1,602 |
| 2012[75] | 2,083 |
| 2013[76] | 2,121 |
| 2014[77] | 2,530 |
| 2015[78] | 3,245 |
| 2016[79] | 3,457 |
| 2017[80] | 3,815 |
| 2018[81] | 5,750 |
| 2019[82] | 8,205 |
 |
Licensing
Automóviles Lamborghini Latinoamérica
Automóviles Lamborghini Latinoamérica S.A. de C.V. (Lamborghini Automobiles of Latin America Public Limited Company) is an authorized distributor and manufacturer of Lamborghini-branded vehicles and merchandise in Latin America and South America.[83]
In 1995, Indonesian corporation MegaTech, Lamborghini's owner at the time, entered into distribution and license agreements with Mexican businessman Jorge Antonio Fernández García. The agreements give Automóviles Lamborghini Latinoamérica S.A. de C.V. the exclusive distributorship of Lamborghini vehicles and branded merchandise in Latin America and South America. Under the agreements, Automóviles Lamborghini is also allowed to manufacture Lamborghini vehicles and market them worldwide under the Lamborghini brand.[83]
Automóviles Lamborghini has produced two rebodied versions of the Diablo called the Eros and the Coatl. In 2015, Automóviles Lamborghini transferred the IP-rights to the Coatl foundation (chamber of commerce no. 63393700) in The Netherlands in order to secure these rights and to make them more marketable.[84] The company has announced the production of a speedboat called the Lamborghini Glamour.[85]
Museums
There are two museums in Bologna, Emilia-Romagna, centered around the brand.
Museo Lamborghini

This two-storey museum is attached to the headquarters, and covers the history of Lamborghini cars and sport utility vehicles, showcasing a variety of modern and vintage models. The museum uses displays of cars, engines and photos to provide a history and review important milestones of Lamborghini.
Museo Ferruccio Lamborghini
A 9,000 square-foot museum about Ferruccio Lamborghini houses several cars, industrial prototypes, sketches, personal objects and family photos from Ferruccio's early life.[86]
See also
Notes
- ^ According to Audi AG's 2011 Annual Financial Report, on 1 July 2011, Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A., Lamborghini AntiMarca S.p.A. and STAR Design S.R.L. were merged into Automobili Lamborghini Holding S.p.A., which was renamed Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. (S.p.A. stands for Società per Azioni, the Italian designation for a joint stock company. S.R.L. stands for Società a Responsabilità Limitata, the Italian designation for a private limited company).
Citations
- ^ a b "Stephan Winkelmann appointed as CEO of Lamborghini". Luxus Plus. 20 November 2020. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- ^ "A record-breaking 2021 for Automobili Lamborghini – The company recorded its best year ever, with 8,405 cars delivered". Lamborghini Media Center. 12 January 2022. Archived from the original on 24 January 2022. Retrieved 23 February 2022.
- ^ a b c "2015 Annual Financial Report". Audi. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ^ "Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. (Italy)". Audi Media Center. 31 December 2020. Archived from the original on 22 February 2022. Retrieved 22 February 2022.
- ^ "Lamborghini's Innovators from the Past". Lamborghini. Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
- ^ Valdes-Dapena, Peter (18 May 2021). "Every Lamborghini will have an electric motor by 2024". CNN Business. Archived from the original on 3 July 2021. Retrieved 18 May 2021.
- ^ "New Lamborghini Cars". Lamborghini. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ^ "Lamborghini Revuelto – launch success covers orders spanning two years". Lamborghini. 26 July 2023. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Lamborghini Revuelto (2023): Alle Infos – vom Preis bis zum Motor". Auto Bild (in German). 29 March 2023. Archived from the original on 4 June 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ "Huracán Line up". Lamborghini. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- ^ "Lamborghini sees worldwide sales doubling by 2019 after SUV launch". Yahoo! Finance. 24 August 2016. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 25 August 2016.
- ^ "Lamborghini Urus". Lamborghini. Archived from the original on 15 December 2020. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ^ "Introducing the Class 1 Championship – The Engines". Class 1 UK. Archived from the original on 24 November 2009. Retrieved 9 April 2008.
- ^ "Car-vaceous Lamborghini up for sale". Motor Cycle News. 23 March 1994. p. 5.
- ^ "Terms and Conditions". Lamborghini Store. EPI srl. Archived from the original on 29 August 2012. Retrieved 4 August 2012.
EPI srl is an official licensee of Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A.
- ^ "ASUS-Automobili Lamborghini VX7SX - Laptops". ASUS Global. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 24 July 2020.
- ^ "Squadra Corse – Super Trofeo". Lamborghini. Archived from the original on 22 August 2021. Retrieved 22 August 2021.
- ^ "Customer Racing – GT3". Lamborghini. Archived from the original on 22 August 2021. Retrieved 22 August 2021.
- ^ "Factory Drivers". Lamborghini. Archived from the original on 2 December 2023. Retrieved 30 October 2023.
- ^ "GT3 Junior Drivers". Lamborghini. Archived from the original on 30 November 2023. Retrieved 30 October 2023.
- ^ "Super Trofeo Junior Drivers". Lamborghini. Archived from the original on 2 October 2023. Retrieved 30 October 2023.
- ^ "Lamborghini Miura P400 Conversion to Miura SV". Lamborghini Miuras. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- ^ Jolliffe & Willard 2004, p. 29.
- ^ Lewin 2004, pp. 119–120.
- ^ Mitchel 2005, p. 219.
- ^ "Lamborghini QVX Car Guide". Qv500.com. Archived from the original on 24 June 2009. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ "Lamborghini". NCE. 29 May 2012. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- ^ Henry, Alan (12 June 2004). "Sato shapes as the rising son". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ^ "Lamborghini Diablo SVR". Qv500.com. Archived from the original on 2 March 2010. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ "Lamborghini Diablo 6.0 GTR Car Guide". Qv500.com. Archived from the original on 2 March 2010. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ "Lamborghini Murciélago R-GT Car Guide". Qv500.com. Archived from the original on 2 March 2010. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ "Lamborghini Murciélago R-GT 2004 Season". Qv500.com. Archived from the original on 23 April 2009. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ "Lamborghini Gallardo GT3 Car Guide". Qv500.com. Archived from the original on 10 June 2010. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ "FIA GT Championship Results: 2007 Round 1 – Zhuhai". FIA GT. Archived from the original on 3 January 2010. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ Cockerham, Paul W. (1997). Lamborghini: the spirit of the bull. Tiger Books.
- ^ Schleifer, Jay (1993). Lamborghini: Italy's raging bull. Crestwood House.
- ^ Lieberman, Jonny (12 September 2007). "The Baddest Bull: Lamborghini Miura Vs Countach Vs Murcielago LP640". Jalopnik. Gawker Media. Archived from the original on 27 September 2012. Retrieved 4 August 2012.
- ^ a b Sackey 2008, p. 15.
- ^ Jolliffe & Willard 2004, p. 31.
- ^ Jolliffe & Willard 2004, p. 43.
- ^ a b "Countach LP500". Lamborghini Registry. Archived from the original on 12 November 2004. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ Lawrence 1996, p. 183.
- ^ Jolliffe & Willard 2004, p. 90.
- ^ Smeyers, Mark (2006). "Diablo" (PDF). Lambocars.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 May 2011. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ "Lamborghini Diablo 6.0VT". Classic and Performance Car. 30 March 2009. Archived from the original on 27 January 2011. Retrieved 16 August 2009.
- ^ "Gallardo – The Name". Lamborghini Registry. 22 November 2003. Archived from the original on 14 March 2008. Retrieved 21 January 2010.
- ^ Stahl, Andreas (1 October 2008). "Edmunds Inside Line – Lamborghini Estoque Concept First Look". Edmunds. Archived from the original on 21 March 2009.
- ^ Kable, Greg (22 October 2006). "Lambo plans: Espada, Miura out, SUV in". AutoWeek. Archived from the original on 17 January 2024. Retrieved 17 January 2024.
- ^ "Secret new Lambo revealed". Top Gear. Archived from the original on 10 January 2010. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ "Edmunds Inside Line – The Radical Lamborghini Sedan From the Paris Auto Show". Edmunds.com. 30 September 2008. Archived from the original on 21 March 2009. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ "Edmunds Inside Line – IL Exclusive: No Green Light – Yet – for Lamborghini Estoque". Edmunds.com. 23 March 2009. Archived from the original on 27 March 2009. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ "Paris 2010: Lamborghini Sesto Elemento". Top Gear. 30 September 2010. Archived from the original on 21 October 2014. Retrieved 30 September 2010.
- ^ "Lamborghini Aventador J Blends Exotic, Superbike". Automoblog.net. 6 March 2012. Archived from the original on 1 March 2021. Retrieved 8 March 2012.
- ^ "Lamborghini Egoista Concept". thecarwallpapers.com. 16 May 2013. Archived from the original on 6 February 2020. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
- ^ Barlow, Jason (1 October 2014). "It's the 907bhp Lambo Asterion Hybrid". Top Gear. Archived from the original on 9 April 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2014.
- ^ a b Audi AG 2011a, p. 62.
- ^ Audi AG 2012b, p. 24.
- ^ "The new Lamborghini factory in Sant'Agata Bolognese". Volkswagen AG. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ^ Audi AG 2012a, p. 152.
- ^ Jolliffe & Willard 2004, p. 40.
- ^ a b c d "Automobili Lamborghini Holding S.p.A. Company History". Funding Universe. Archived from the original on 17 October 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2009.
- ^ "Lamborghini Reports Record Figures". carpages.co.uk. 21 February 2004. Archived from the original on 2 March 2012. Retrieved 3 August 2012.
In 1996, Automobili Lamborghini sold a total of 211 cars worldwide.
- ^ Volkswagen AG 2000, p. 50.
- ^ Volkswagen AG 2001, p. 23.
- ^ Volkswagen AG 2002, p. 24.
- ^ Audi AG 2003, p. 3.
- ^ a b Audi AG 2004, p. 5.
- ^ Audi AG 2006, p. 3.
- ^ Audi AG 2007, p. 4.
- ^ Audi AG 2008, p. 4.
- ^ Audi AG 2009, p. 4.
- ^ Audi AG 2010, p. 4.
- ^ Audi AG 2011, p. 151.
- ^ Audi AG 2012, p. 154.
- ^ "fy2012". Volkswagen AG. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013.
- ^ "Lamborghini increases worldwide sales for the third year in a row to 2,121 cars delivered to customers". Volkswagen AG. 13 January 2014. Archived from the original on 31 October 2014. Retrieved 12 June 2014.
- ^ "Record Year for Automobili Lamborghini: Deliveries increased to 2,530 units in 2014". Lamborghini. 12 January 2015. Archived from the original on 15 January 2015. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ^ "Automobili Lamborghini makes 2015 the best year in company history". Lamborghini. 3 March 2016. Archived from the original on 24 July 2016. Retrieved 11 July 2016.
- ^ "Volkswagen Group deliveries". Volkswagen AG. 24 February 2017. Archived from the original on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 8 November 2017.
- ^ "Volkswagen Group deliveries". Volkswagen AG. 10 October 2018. Archived from the original on 20 October 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- ^ "Lamborghini delivers record-high 5,750 cars in 2018, up 51%". AutoCarPro. 8 February 2019. Archived from the original on 24 October 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2019.
- ^ "Automobili Lamborghini continues its global growth and marks new historic highs: 8,205 cars delivered in 2019". Audi Media Center. 14 January 2020. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- ^ a b Automóviles Lamborghini Latinoamérica S.A. de C.V 1995.
- ^ "Sitio Oficial". Lamborghini Latinoamerica. Archived from the original on 9 March 2017. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Sitio Oficial". Lamborghini Latinoamerica. Archived from the original on 2 January 2014. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ "Museo Ferruccio Lamborghini". Lambocars.com. Archived from the original on 3 September 2019. Retrieved 3 September 2019.
References
- DeMatio, Joe (May 2003). "Lamborghini's Big Four-O". Automobile. Ann Arbor, Michigan: Source Interlink Media. ISSN 0894-3583. Archived from the original on 31 July 2012. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- Henshaw, Peter (2002). Illustrated Directory of Tractors (Paperback ed.). London: Salamander Books. ISBN 978-0-7603-1342-8. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- Holusha, John (24 April 1987). "Lamborghini Goes to Chrylser". The New York Times. New York. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 7 June 2022. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- Ireson, Nelson (12 February 2010). "Lamborghini Builds 4,000th Murcielago". MotorAuthority. High Gear Media. Archived from the original on 3 July 2014. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- Jolliffe, David; Willard, Tony (2004). Lamborghini: Forty Years (Hardcover ed.). St. Paul, Minnesota: Motorbooks International. doi:10.1007/b62130. ISBN 978-0-7603-1945-1. ISSN 0075-8434. Archived from the original on 20 July 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2012.
- Lawrence, Mike (1996) [1991]. A to Z of Sports Cars, 1945–1990: The Encyclopaedic Guide to More Than 850 Marques and Thousands of Models (Paperback ed.). St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing Company. ISBN 978-1-870979-81-8. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
- Lewin, Tony (2004). The Complete Book of BMW: Every Model Since 1950 (Hardcover ed.). St. Paul, Minnesota: Motorbooks International. ISBN 978-0-7603-1951-2. Archived from the original on 26 September 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- Lyons, Pete (1988). The Complete Book of Lamborghini. The Auto Editors of Consumer Guide (Hardcover ed.). Woodstock, New York: Beekman House. ISBN 9780517667156. Archived from the original on 13 February 2023. Retrieved 26 July 2022 – via Barbarossa books.
- Mitchel, Doug (2006) [2005-10-20]. Collins, Tom (ed.). Supercars Field Guide (Paperback ed.). Iola, Wisconsin: KP Books. ISBN 978-0-89689-227-9. Archived from the original on 11 October 2013. Retrieved 3 August 2012.
- Neher, Jacques (9 February 1994). "Toy or Supercar for Asia?". The New York Times. New York. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 12 May 2013. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- Sackey, Joe (2008). The Lamborghini Miura Bible (Hardcover ed.). Dorchester, England: Veloce Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84584-196-6. Retrieved 5 August 2012.[permanent dead link]
- Welsh, Jonathan (5 November 2010). "Lamborghini Marks The End Of Its Murcielago Supercar". The Wall Street Journal. New York: Dow Jones & Company, Inc. ISSN 0099-9660. Archived from the original on 26 October 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- Winterbottom, Jo (10 June 2009). "Lamborghini sees no recovery until 2011". Reuters. New York: Thomson Reuters Corporation. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- Wood, Jonathan (23 February 1993). "Obituary: Ferruccio Lamborghini". The Independent. London: independent.co.uk. ISSN 0951-9467. Archived from the original on 7 November 2012. Retrieved 4 August 2012.
- Woodyard, Chris (17 December 2010). "Lamborghini launches its 4,000 series Murcielago". USA Today. New York: Gannett Co. Inc. ISSN 0734-7456. Archived from the original on 6 July 2014. Retrieved 12 August 2012.
- Filippo Perini ci racconta il design della Lamborghini Aventador [Filippo Perini discusses the design of the Lamborghini Aventador] (Streaming video) (YouTube) (in Italian). Rome: Edimotive S.r.l. 28 April 2011. Archived from the original on 2 May 2020. Retrieved 14 August 2012.
- "Lamborghini". Museo Storico Gruppo SAME Deutz-Fahr. Gruppo SAME Deutz-Fahr. 2012. Archived from the original on 29 July 2012. Retrieved 4 August 2012.
- "Lamborghini Latinoamérica quiere radicarse en Santiago del Estero" [Lamborghini Latin America wants to settle in Santiago del Estero]. La Gaceta (in Spanish). San Miguel de Tucumán, Argentina. 11 December 2010. Archived from the original on 12 May 2013. Retrieved 18 December 2010.
- "Principales cláusulas de los contratos con USA e Italia" [Main Contract Terms between USA and Italy]. lamborghini-latinoamerica.com (in Spanish). Automóviles Lamborghini Latinoamérica S.A. de C.V. 5 August 1995. Archived from the original (JPG) on 2 October 2013. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
Corporate documents
- "Audi 2010 Annual Report" (PDF). Audi AG. 9 March 2011b. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 September 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- "Audi 2011 Annual Financial Report" (PDF). Audi AG. 17 February 2012a. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- "Audi 2011 Annual Report" (PDF). Audi AG. 1 March 2012b. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 October 2014. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- "Audi Facts and Figures 2002" (PDF). Audi AG. 2003. Retrieved 2 August 2012.[dead link] Alt URL Archived 26 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- "Audi Facts and Figures 2004" (PDF). Audi AG. 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 September 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- "Audi Facts and Figures 2005" (PDF). Audi AG. 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- "Audi Facts and Figures 2006" (PDF). Audi AG. 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- "Audi Facts and Figures 2007" (PDF). Audi AG. 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 September 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- "Audi Facts and Figures 2008" (PDF). Audi AG. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 September 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- "Audi in Fakten und Zahlen 2009" [Audi Facts and Figures 2009] (PDF) (in German). Audi AG. 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 April 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- "Audi in Fakten und Zahlen 2010" [Audi Facts and Figures 2010] (PDF) (in German). Audi AG. 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 September 2012. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- "Audi in Fakten und Zahlen 2011" [Audi Facts and Figures 2011] (PDF) (in German). Audi AG. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 October 2014. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- "Interim Financial Report 2012" (PDF). Audi AG. 23 July 2012c. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 August 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- "Shareholdings in accordance with sections 285 and 313 of the Handelsgesetzbuch (HGB – German Commercial Code) for Volkswagen AG and Volkswagen Group as of December 31, 2010" (PDF). Volkswagen AG. 10 March 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 May 2012. Retrieved 15 August 2012.
- "Statement of Interests Pursuant to Sections 285 and 313 of the German Commercial Code" (PDF). Audi AG. 17 February 2011a. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 September 2019. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- "Volkswagen AG Annual Report 1999" (PDF). Annual Report. Volkswagen AG. 17 March 2000. ISSN 0933-7504. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 October 2013. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- "Volkswagen AG Annual Report 2000" (PDF). Annual Report. Volkswagen AG. 16 March 2001. ISSN 0933-7504. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 October 2013. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- "Volkswagen AG Annual Report 2001" (PDF). Annual Report. Volkswagen AG. 1 March 2002. ISSN 0933-7504. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 October 2013. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- "Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft Facts and Figures 2012" (PDF). volkswagenag.com. Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft. 11 June 2012. 1058.809.453.20. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 October 2013. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. (867 employees, founded in 1963, wholly owned by Audi AG since 1998)
External links
- Official website Archived 27 February 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- Lamborghini of Latinoamerica Official page
- Lamborghini Car Register Archived 17 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine

















