The US FDA’s proposed rule on laboratory-developed tests: Impacts on clinical laboratory testing
Contents
A reductone is a special class of organic compounds. They are enediols with a carbonyl group adjacent to the enediol group, i.e. RC(OH)=C(OH)-C(O)R. The enediol structure is stabilized by the resonance resulting from the tautomerism with the adjacent carbonyl. Therefore, the chemical equilibrium produces mainly the enediol form rather than the keto form.[1]
Reductones are reducing agents, thus efficacious antioxidants. Some are fairly strong acids.[2] Examples of reductones are tartronaldehyde, reductic acid and ascorbic acid.
| Examples of reductones | ||
|---|---|---|
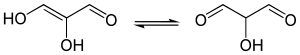 |
 |

|
| Tartronaldehyde | Reductic acid | Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) |
References
- ^ Schank, Kurt (1972). "Reductones". Synthesis. 1972 (4): 176–90. doi:10.1055/s-1972-21845.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "reductones". doi:10.1351/goldbook.R05224

















