The US FDA’s proposed rule on laboratory-developed tests: Impacts on clinical laboratory testing
Contents
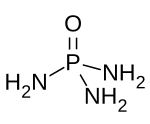
Phosphoramides are a class of phosphorus compounds with the formula O=P(NR2)3-n(OH)n. They can be considered derivatives of phosphoric acid where OH groups have been replaced with an amino or R-substituted amino group. In practise the term is commonly confined to the phosphoric triamides (P(=O)(NR2)3), essentially phosphoramide and derivatives thereof.[1] Derivatives with the general structures P(=O)(OH)(NR2)2 or P(=O)(OH)2(NR2) are usually referred to as phosphoramidic acids.
Examples
- Na[PO2(OH)(NH2)], the lightly studied parent monoamide of phosphoric acid.[2]
- Phenyl phosphorodiamidate, a phosphoramide but also a phosphate ester, is used in agriculture to enhance the effectiveness of urea-based fertilizers.
- Hexamethylphosphoramide (HMPA) is a polar solvent.
References
- ^ "Phosphoramide". IUPAC GoldBook.
- ^ Steger, E.; Versuchen, Nach; Stopperka, K. (1963). "Infrarotspektroskopische Untersuchungen zur Frage der Wasserstoffbrücken‐Absorptionen bei Natriumhydrogenamidophosphat und Amidosulfonsäure" [Phosphoramidic acid and its salts and their infrared spectra]. Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 325 (1–2): 89–97. doi:10.1002/zaac.19633250113.

















