The US FDA’s proposed rule on laboratory-developed tests: Impacts on clinical laboratory testing
Contents
Mangas Coloradas | |
|---|---|
| Mimbreño Apache leader | |
| Succeeded by | Delgadito (killed 1864) |
| Personal details | |
| Born | A Bedonkohe c. 1793 |
| Died | January 18, 1863 (aged 69–70) |
| Military service | |
| Battles/wars | Apache Wars |
Mangas Coloradas or Mangus-Colorado (La-choy Ko-kun-noste, alias "Red Sleeves"), or Dasoda-hae (c. 1793 – January 18, 1863) was an Apache tribal chief and a member of the Mimbreño (Tchihende) division of the Central Apaches, whose homeland stretched west from the Rio Grande to include most of what is present-day southwestern New Mexico. He was the father-in-law of Chiricahua (Tsokanende) chief Cochise, Mimbreño chief Victorio, and Mescalero (Sehende) chief Kutu-hala or Kutbhalla (probably to be identified with Caballero). He is regarded as one of the most important Native American leaders of the 19th century because of his fighting achievements against the Mexicans and Americans.
The name Mangas Coloradas (red sleeves) was given to him by Mexicans. Named A Bedonkohe (Bi-dan-ku – 'In Front of the End People', Bi-da-a-naka-enda – 'Standing in front of the enemy') by birth, he married into the Copper Mines local group of the Tchihende and became the principal chief of the whole Tchihende Apache division. His influence also included the neighboring Mimbreño local group of the Warm Springs Tchihende, directly led by chief Cuchillo Negro (in Apache language, Baishan), second chief of the Tchihende Apache division and his long-time companion.

Apache war chief
During the 1820s and 1830s, the Apaches' main enemy were the Mexicans, who had won their independence from Spain in 1821. By 1835, Mexico had placed a bounty on Apache scalps. After Juan José Compa, the leader of the Coppermine Mimbreño Apaches, was killed for bounty money in 1837 in the massacre at Santa Rita del Cobre, Mangas became a war leader and a chief, joining forces with his friend and long-time companion (and possibly brother-in-law) Cuchillo Negro (Spanish: Black Knife).[A] They began a series of retaliatory raids against the Mexicans, around the mining town and sieged Santa Rita, attacking the column of fleeing Mexicans and slaughtering a large number.[quantify] Mangas Coloradas became the principal leader of the Coppermine Mimbreños and led them for about 25 years while Cuchillo Negro led the Warm Springs Mimbreños.
In 1846, when the United States went to war with Mexico, the Apache Nation promised U.S. soldiers safe passage through Apache lands. Once the U.S. occupied New Mexico in 1846, Mangas Coloradas signed a peace treaty, respecting them as conquerors of the hated Mexican enemy. An uneasy peace between the Apache and the United States lasted until an influx of gold miners into New Mexico's Pinos Altos Mountains led to open conflict.
In 1851 the settlement at Santa Rita del Cobre of the U.S. delegation (with John Russell Bartlett) in the Mexican-American Border Commission[2] and the reopening of the Santa Rita del Cobre copper mines increased tensions as well. Mangas Coloradas, like Cuchillo Negro, Delgadito, Ponce, Coleto Amarillo, and the most important Tchihende and Ndendahe chiefs, had to face new problems. In June 1851 Mangas Coloradas, Delgadito, Ponce, and Coleto Amarillo met Bartlett in Santa Rita del Cobre; the discussions continued until the Apaches no longer felt disappointed and betrayed by the newcomers.
According to John C. Cremony's book, Life Among the Apaches, in 1861, near the Pinos Altos mining camp, Mangas Coloradas was attacked by a group of white miners who tied him to a tree and severely flogged him.[3] Yet historian Edwin R. Sweeney finds issue with this claim in his biography of the chief: if it was true, Geronimo, who spent a great deal of time with Mangas Coloradas during the 1850s and 1860s, would have likely mentioned it to his biographer.[4]
In December 1860, 30 miners launched a surprise attack on an encampment of Bedonkohes on the west bank of the Mimbres River. Historian Edwin R. Sweeney reported, the miners "... killed four Indians, wounded others, and captured thirteen women and children." Shortly after that, Mangas began raids against U.S. citizens and their property.
Mangas Coloradas' daughter Dos-Teh-Seh married Cochise, principal chief of the Tsokanende or Chiricahua Apache.
In early February 1861, U.S. Army Lieutenant George Nicholas Bascom, investigating the "Indian" kidnapping of a rancher's son, apparently without orders, lured an innocent Cochise, his family and several warriors into a trap at Apache Pass, southeastern Arizona. Cochise managed to escape, but his family and warriors remained in custody. Negotiations were unsuccessful and fighting erupted. This incident, known as the "Bascom affair", ended with Cochise's brother and five other warriors being hanged by Bascom. Later that year, Mangas Coloradas and Cochise struck an alliance, agreeing to drive all Americans out of Apache territory. They were joined in their effort by middle-aged Delgadito and Nana, Victorio, Juh and Geronimo. Although the goal was never achieved, the White population in Apache territory was greatly reduced for a few years during the Civil War, after federal troops had been withdrawn to the east.
Death
In the summer of 1862, after recovering from a bullet wound in the chest, Mangas Coloradas met with an intermediary to call for peace. In January 1863, he decided to meet with U.S. military leaders at Fort McLane (Apache Tejo) in southwestern New Mexico. He was promised provisions in return for peace, but the American government did not want to have peace with them.[5] Mangas arrived under a flag of truce to meet with Brigadier General Joseph R. West, an officer of the California militia and a future Reconstruction senator from Louisiana. Armed soldiers took Mangas into custody. West gave an execution order to the sentries.

Men, that old murderer has got away from every soldier command and has left a trail of blood for 500 miles on the old stage line. I want him dead tomorrow morning. Do you understand? I want him dead.
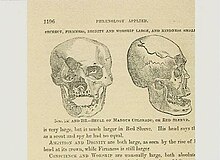
That night, Mangas was tortured, shot, and killed under the pretext of a supposed escape attempt. While tied on the ground, Mangas was provoked with red hot bayonets until he moved to simulate his attempt to "escape."[6] The following day, some soldiers who were fascinated by the size of the Apache (Mangas was 6 feet, 6 inches tall), cut off his head, boiled it, and sent the skull to Orson Squire Fowler, a phrenologist in New York City. Analysis of the skull and two sketches of it appear in Fowler's book.[7]
Daklugie, one of informants in Eve Ball's book,[8] said the skull went to the Smithsonian Institution. However, the Smithsonian reported that it never received the skull. Mangas's descendants and sources based on their testimony may have confused the Smithsonian with Fowler's Phrenological Cabinet in New York, where the skull was on display, leading to the misattribution. Another possible fate of the skull was that it was returned to the Apaches by the Smithsonian in a 1990 transfer but was not individually labeled.[9]
The mutilation of Mangas's body especially enraged the Apaches since they believed he would not enter the afterlife without his head.[10] This further envenomed the conflict between the Apaches and the United States, leading Cochise to engage in nine-year campaign of reprisals in Arizona and Sonora.[11]
Notes and references
- ^ His father Fuerte, also known as Soldado Fiero (Spanish: Proud Soldier), had been killed near Santa Rita del Cobre by troops from the Janos garrison in 1835 or 1837
- ^ Legends of America: Mangas Coloradas Archived 2012-04-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "TSHA | Mexican-United States Boundary Commission".
- ^ Cremony, John (2010). Life among the Apaches. Carlisle, MA: Applewood Books. p. 173. ISBN 9781429022453.
- ^ Sweeney, Edwin R. (1998). Mangas Coloradas, chief of the Chiricahua Apaches. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. p. 404. ISBN 978-0806130637.
- ^ Geronimo, S.M. Barrett Geronimo: The True Story of America's Most Ferocious Warrior, 1906, republished 2011 ISBN 1616087536, p. 73-74
- ^ Waters, Frank. Brave Are My People. Santa Fe, NM: Clear Light Publishers, 1993.
- ^ Fowler, O.S. 1873. Human Science or Phrenology. p. 1196. (Available at [1])
- ^ Ball, Eve; Henn, Nora; Sanchez, Lynda A. (1988). Indeh: An Apache Odyssey (reprint). University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 0-8061-2165-3.
- ^ The Apaches: Destined for Change
- ^ Reed, Ollie Jr. (1 September 2019). "UNM professor to give talk on Mangas Coloradas in Santa Fe". Albuquerque Journal. Retrieved 5 October 2020.
- ^ Vandervort, Bruce (2006). Indian wars of Mexico, Canada and the United States, 1812-1900. New York: Routledge. p. 201. ISBN 978-0415224727.
Further reading
- Etulain, Richard W. New Mexican Lives: A Biographical History. University of New Mexico Center for the American West, University of New Mexico Press, 2002. ISBN 0-8263-2433-9
- Haley, James L. Apaches: A History and Culture Portrait. University of Oklahoma Press, 1997. ISBN 0-8061-2978-6
- Sweeney, Edwin R. Mangas Coloradas: Chief of the Chiricahua Apaches. University of Oklahoma Press, 1998. ISBN 0-8061-3063-6
- Yarbrough, Leroy. 1968. The Apache and the Sioux. REAL WEST magazine

















