The US FDA’s proposed rule on laboratory-developed tests: Impacts on clinical laboratory testing
Contents
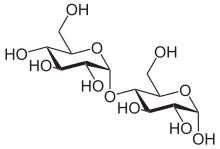 α-Maltose
| |
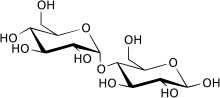 β-Maltose
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-O-α-D-Glucopyranosyl-D-glucose
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3R,4R,5S,6R)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-5-{[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}oxane-2,3,4-triol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.651 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.297 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder or crystals |
| Density | 1.54 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 160 to 165 °C (320 to 329 °F; 433 to 438 K) (anhydrous) 102–103 °C (monohydrate) |
| 1.080 g/mL (20 °C) | |
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
+140.7° (H2O, c = 10) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related
|
Sucrose Lactose Trehalose Cellobiose |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Maltose (/ˈmɔːltoʊs/[2] or /ˈmɔːltoʊz/[3]), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the two-unit member of the amylose homologous series, the key structural motif of starch. When beta-amylase breaks down starch, it removes two glucose units at a time, producing maltose. An example of this reaction is found in germinating seeds, which is why it was named after malt.[4] Unlike sucrose, it is a reducing sugar.[5]
History
Maltose was discovered by Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut, although this discovery was not widely accepted until it was confirmed in 1872 by Irish chemist and brewer Cornelius O'Sullivan.[5][6] Its name comes from malt, combined with the suffix '-ose' which is used in names of sugars.[4]
Structure and nomenclature
Carbohydrates are generally divided into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides depending on the number of sugar subunits. Maltose, with two sugar units, is a disaccharide, which falls under oligosaccharides. Glucose is a hexose: a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms. The two glucose units are in the pyranose form and are joined by an O-glycosidic bond, with the first carbon (C1) of the first glucose linked to the fourth carbon (C4) of the second glucose, indicated as (1→4). The link is characterized as α because the glycosidic bond to the anomeric carbon (C1) is in the opposite plane from the CH
2OH substituent in the same ring (C6 of the first glucose). If the glycosidic bond to the anomeric carbon (C1) were in the same plane as the CH
2OH substituent, it would be classified as a β(1→4) bond, and the resulting molecule would be cellobiose. The anomeric carbon (C1) of the second glucose molecule, which is not involved in a glycosidic bond, could be either an α- or β-anomer depending on the bond direction of the attached hydroxyl group relative to the CH
2OH substituent of the same ring, resulting in either α-maltose or β-maltose.[citation needed]
An isomer of maltose is isomaltose. This is similar to maltose but instead of a bond in the α(1→4) position, it is in the α(1→6) position, the same bond that is found at the branch points of glycogen and amylopectin.[citation needed]
Properties
Like glucose, maltose is a reducing sugar, because the ring of one of the two glucose units can open to present a free aldehyde group; the other one cannot because of the nature of the glycosidic bond. Maltose can be broken down to glucose by the maltase enzyme, which catalyses the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond.[citation needed]
Maltose in aqueous solution exhibits mutarotation, because the α and β isomers that are formed by the different conformations of the anomeric carbon have different specific rotations, and in aqueous solutions, these two forms are in equilibrium. Maltose can easily be detected by the Woehlk test or Fearon's test on methylamine.[7]
It has a sweet taste, but is only about 30–60% as sweet as sugar, depending on the concentration.[8] A 10% solution of maltose is 35% as sweet as sucrose.[9]
Sources and absorption

Maltose is a malt component, a substance obtained when the grain is softened in water and germinates. It is also present in highly variable quantities in partially hydrolyzed starch products like maltodextrin, corn syrup and acid-thinned starch.[10]
Outside of plants, maltose is also (likely) found in sugarbag.[11]
In humans, maltose is broken down by various maltase enzymes, providing two glucose molecules that can be further processed: either broken down to provide energy, or stored as glycogen. The lack of the sucrase-isomaltase enzyme in humans causes sucrose intolerance, but complete maltose intolerance is extremely rare because there are four different maltase enzymes.[12]
References
- ^ Weast, Robert C., ed. (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. C-367. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8..
- ^ Dictionary Reference: maltose
- ^ Cambridge dictionary: maltose
- ^ a b Stoker, H. Stephen (2 January 2015). Organic and Biological Chemistry. Cengage Learning. ISBN 9781305686458.
- ^ a b Fruton, Joseph S (1999). Proteins, Enzymes, Genes: The Interplay of Chemistry and Biology. Chelsea, Michigan: Yale University Press. p. 144. ISBN 0300153597. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- ^ O'Sullivan, Cornelius (1872). "XXI.?On the transformation-products of starch". Journal of the Chemical Society. 25: 579–588. doi:10.1039/JS8722500579. Retrieved 11 December 2014.
- ^ Ruppersberg, Klaus; Blankenburg, Janet (6 March 2018). "150 Years Alfred Wöhlk :: Education". ChemistryViews. doi:10.1002/chemv.201800002.
- ^ Belitz, H.-D.; Grosch, Werner; Schieberle, Peter (15 January 2009). Food Chemistry. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 863. ISBN 9783540699330.
- ^ Spillane, W. J. (17 July 2006). Optimising Sweet Taste in Foods. Woodhead Publishing. p. 271. ISBN 9781845691646.
- ^ Furia, Thomas E. (2 January 1973). CRC Handbook of Food Additives, Second Edition. CRC Press. ISBN 9780849305429.
- ^ Heard, Tim (30 October 2015). The Australian Native Bee Book. Sugarbag Bees. ISBN 9780646939971.
- ^ Whelan, W. J.; Cameron, Margaret P. (16 September 2009). Control of Glycogen Metabolism. John Wiley & Sons. p. 60. ISBN 9780470716885.

















