The US FDA’s proposed rule on laboratory-developed tests: Impacts on clinical laboratory testing
Contents
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
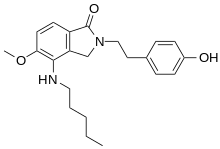
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-[2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]-5-methoxy-4-(pentylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindol-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H28N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 368.469 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
JTE 7-31 is a selective cannabinoid receptor agonist invented by Japan Tobacco.[1][2] It is a reasonably highly selective CB2 agonist, but still retains appreciable affinity at CB1, with a Ki of 0.088nM at CB2 vs 11nM at CB1.[3]
Legality
JTE 7-31 is illegal in Alabama.[4]
See also
- A-834,735
- JTE-907
- MDA-19
- N-(S)-Fenchyl-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)-7-methoxyindole-3-carboxamide
- S-444,823
- XLR-12
References
- ^ WO patent 1997/029079, Inaba T, Kaya T, Iwamura H, "Novel compounds and pharmaceutical use thereof", granted 1997-14-08
- ^ US patent 6017919, Inaba T, Kaya T, Iwamura H, "Compounds and pharmaceutical use thereof", granted 2000-01-25
- ^ Han S, Zhang FF, Qian HY, Chen LL, Pu JB, Xie X, Chen JZ (March 2015). "Design, syntheses, structure-activity relationships and docking studies of coumarin derivatives as novel selective ligands for the CB2 receptor". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 93: 16–32. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.01.054. PMID 25644673.
- ^ "Alabama Senate Bill SB 333: Controlled Substances" (PDF).
External links

















