Simultaneous quantification of 17 cannabinoids in cannabis inflorescence by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry
Contents


A border barrier, border fence or border wall is a separation barrier that runs along or near an international border. Such barriers are typically constructed for border control purposes such as curbing illegal immigration, human trafficking, and smuggling.[1][2] Some such barriers are constructed for defence or security reasons. In cases of a disputed or unclear border, erecting a barrier can serve as a de facto unilateral consolidation of a territorial claim that can supersede formal delimitation. A border barrier does not usually indicate the location of the actual border, and is usually constructed unilaterally by a country, without the agreement or cooperation of the other country.
Examples of border walls include the ancient Great Wall of China, a series of walls separating China from nomadic empires to the north. The construction of border barriers increased in the early 2000s; half of all the border barriers built since World War II, which ended in 1945, were built after 2000.[3]
List of current barriers
Note: The table can be sorted alphabetically or chronologically using the ![]() icon.
icon.
| Name | Countries affected | Built and maintained by | Date built | Length (km) | Type | Deaths during crossing attempts | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina–Paraguay | Argentina and Paraguay | Argentina | 2014 | 1.3 | Anti-illegal immigration | [4] | |
| Austrian border barrier | Austria, Italy, and Slovenia | Austria | 2015 | 3.7 | Anti-illegal immigration | [5] | |
| Belize–Guatemala | Belize and Guatemala | Belize | Proposed, agreed | N/A | Disputed territory and anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Botswana–Zimbabwe | Botswana and Zimbabwe | Botswana | 2003 | 500 | Protection of livestock against disease (Botswana), anti-immigration (purported from Zimbabwe officials) | 8 | [6] |
| Brunei–Malaysia | Brunei and the city of Limbang, Malaysia | Brunei | 2005 | 20 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Bulgaria–Turkey barrier | Bulgaria and Turkey | Bulgaria | 2014 | 30 | Anti-illegal immigration | [7] | |
| Calais border barrier | United Kingdom and France | United Kingdom and France | 2016 | 1 | Anti-illegal immigration | [8] | |
| Ceuta border fence | Spain and Morocco | Spain | 2001 | 8 | Anti-illegal immigration | 13–18 depending on estimates.[9] | |
| Costa Rica–Nicaragua | Costa Rica and Nicaragua | Costa Rica | Proposed | N/A | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Green Line (Cyprus) | Cyprus and Northern Cyprus | Cyprus and the United Nations | 1964 | 180 | Buffer Zone | ||
| Chinese–Korean border fence | China and North Korea | China | 2011 | 1,416 | Anti-illegal immigration | [10] | |
| Chile–Bolivia ditch | Chile and Bolivia | Chile | 2022 (Under construction) | N/A | Anti-illegal immigration | [11] | |
| China-Vietnam/Myanmar border wall | China, Vietnam andMyanmar | China | 2021 | 3,468 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Denmark–Germany border fence | Denmark and Germany | Denmark | 2019 | 70 | Wildlife control (official), Anti-immigration (third party claims) | [12][13][14] | |
| Dominican–Haiti border fence | Dominican Republic and Haiti | Dominican Republic | Under construction 2022 | N/A | Anti-illegal immigration and crime | [15][16] | |
| Egypt–Gaza barrier | Egypt and Gaza Strip | Egypt | 1979, subterranean barrier under construction | 3.1 | Anti-terrorism and anti-illegal immigration | [17] | |
| Estonia–Russia barrier | Estonia and Russia | Estonia | 2018 | 110 | Anti-intrusion, illegal trade and illegal immigration | [18] | |
| Finland–Russia border barrier | Finland and Russia | Finland | 2023 | 200 | Against Russian intrusion, illegal trade and illegal immigration | [19] | |
| Greece–Turkey border | Greece and Turkey | Greece | 2012, expanded 2021[20][21] | 200 | Anti-illegal immigration | [22][23][24][25] | |
| North Macedonia–Greece barrier | North Macedonia and Greece | North Macedonia | 2015 | 30 | Anti-illegal immigration | [26] | |
| Malaysia–Thailand border | Thailand and Malaysia | Thailand | Proposed | 650 | Anti-terrorism | ||
| Melilla border fence | Spain and Morocco | Spain | 1998 | 11 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Hungary–Serbia barrier | Hungary and Serbia | Hungary | 2015 | 175 | Anti-illegal immigration | [27][28][29][30][31] | |
| Hungary–Croatia barrier | Hungary and Croatia | Hungary | 2015 | 41 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| India–Bangladesh barrier | India and Bangladesh | India | Under construction | 3,268 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| India–Myanmar barrier | India and Myanmar | India | Under construction | 1,624 | Anti-drug smuggling and anti-terrorism | ||
| India-Nepal barrier | India and Nepal | India | Under construction | ? | Anti-illegal immigration Anti-terrorism | ||
| India–Pakistan barrier | India and Pakistan | India | 2004 | 550 | Anti-terrorism | [32] | |
| Iran–Pakistan barrier | Iran and Pakistan | Pakistan[33] and Iran | Under construction | 959 | Anti-terrorism and Anti-drug smuggling | [34][35][36] | |
| Iran–Afghanistan barrier | Iran and Afghanistan | Iran | Under construction | 930 | Anti-illegal immigration Anti-terrorism Anti-drug smuggling | ||
| Israel-West Bank barrier | Israel and Palestine | Israel | Partially Completed | 708 | Anti-terrorism and disputed territory | [37] | |
| Israel-Egypt barrier | Israel and Egypt | Israel | 2013 | 245 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Israel-Lebanon barrier | Israel and Lebanon | Israel | 2018 | 11 | Conflict zone | ||
| Israel-Gaza barrier | Israel and Gaza Strip | Israel | 1994 | N/A | Anti-terrorism | ||
| Kazakhstan–Uzbekistan barrier | Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan | Kazakhstan | 2006 | 45 | Anti-drug smuggling | ||
| Korean Demilitarized Zone | North Korea and South Korea | North Korea and United Nations Command | 1953 | 248 | Conflict zone | ||
| Kruger National Park | South Africa and Mozambique | South Africa | 1975 | 120 | Anti-illegal immigration | 89 (Army), over 200 (Various churches) | |
| South Africa–Zimbabwe Border | South Africa and Zimbabwe | South Africa | 2000s | 225 | Anti-illegal immigration, anti-drug smuggling, anti-weapon smuggling | [38][39][40][41] | |
| Kuwait–Iraq barrier | Kuwait and Iraq | Kuwait | 1991 | 193 | Conflict zone | ||
| Latvia–Russia border fence | Latvia and Russia | Latvia | 2015 | 90 | Anti-illegal immigration | [42] | |
| Libya–Tunisia barrier | Libya and Tunisia | Tunisia | TBA | 460 | Anti-terrorism, Anti-irregular immigration and smuggling of illicit goods | ||
| Lithuania-Belarus barrier | Lithuania and Belarus | Lithuania | 2021[43] | 502 | Anti-illegal immigration | [44][45] | |
| Lithuania–Russia border fence | Lithuania and Russia | Lithuania | 2017 | 130 | Anti-smuggling, anti-illegal immigration, anti-intrusion | [46] | |
| Moroccan Western Sahara Wall | Morocco and Western Sahara | Morocco | 1980 | 2,700 | Conflict zone | [47][48] | |
| Norway–Russia border barrier | Norway and Russia | Norway | 2016 | 0,2 | Anti-illegal immigration | [49] | |
| Pakistan–Afghanistan barrier | Pakistan and Afghanistan | Pakistan | ongoing | 2,670 | Anti-terrorism, anti-illegal immigration, anti drug smuggling | [50][51] | |
| Poland–Belarus barrier | Poland and Belarus | Poland | 2022[52] | 186 | Anti-illegal immigration | 21[53] | [54][55][56][57][58] |
| Saudi–Yemen barrier | Saudi Arabia and Yemen | Saudi Arabia | 2004 | 75 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Saudi–Iraq barrier | Saudi Arabia and Iraq | Saudi Arabia | 2014 | 900 | Anti-illegal immigration and conflict zone | [59][60][61] | |
| Slovenia–Croatia barrier | Slovenia and Croatia | Slovenia | 2016 | 220 | Anti-illegal immigration | [62][63][64] | |
| Serbia–North Macedonia barrier | Serbia and North Macedonia | Serbia | 2020 | 240 | Anti-illegal immigration | [65] | |
| Turkey–Syria border barrier | Turkey and Syria | Turkey | 2018 | 828 | Anti-terrorism, anti-illegal immigration and smuggling | [66] | |
| Turkey–Iran border barrier | Turkey and Iran | Turkey | 2019 | 144 | Anti-terrorism, anti-illegal immigration and smuggling | ||
| Turkmen–Uzbekistan barrier | Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan | Turkmenistan | 2001 | 1,700 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Ukraine–Russia barrier | Ukraine, Russia and Belarus | Ukraine | Under construction | 2,000 | Anti Weapon Smuggling and Conflict zone | ||
| United Arab Emirates–Oman barrier | United Arab Emirates and Oman | United Arab Emirates | 2018 | 410 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Mexico–United States barrier | United States and Mexico | United States | Partially Constructed | 1,000 | Anti-illegal immigration and smuggling | [67][68][69][70][71][72][73][74][75][76] | |
| Uzbek–Afghanistan barrier | Uzbekistan and Afghanistan | Uzbekistan | 2001 | 209 | Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Uzbek–Kyrgyzstan barrier | Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan | Uzbekistan | 1999 | 870 | Conflict zone | ||
| Hong Kong-China barrier and Forts | Hong Kong and mainland China | United Kingdom and Hong Kong | 1950s | ? | Anti-terrorism Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| (Gibraltar) United Kingdom-Spain barrier | (Gibraltar) United Kingdom and Spain | United Kingdom and Gibraltar | 1909 | 1.24 | Anti-terrorism Anti-illegal immigration | ||
| Ethiopia–Eritrea barrier | Ethiopia and Eritrea | Ethiopia and Eritrea | 1990s–2000s | ? | Anti-terrorism |
Border barriers in history
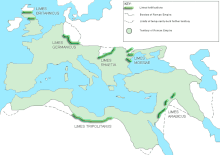
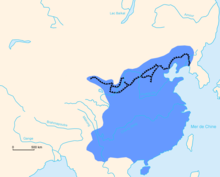
Antiquity
- Antonine Wall (began in AD 142 by the Roman province in Britain)
- Anastasian Wall (built from AD 469, west of Istanbul, Turkey)
- Great Wall of China (parts were built as early as the 7th century BC by the Qi dynasty in China)
- Great Wall of Gorgan (built in 5th or 6th century AD)
- Hadrian's Wall (begun in AD 122)
- Madukkarai Wall (may have been built as early as the 1st century AD in India)
- Southern Great Wall, southern counterpart wall to the Great Wall, erected to protect and divide the Chinese from the "southern barbarians" called Miao (meaning barbaric and nomadic)[77]
Middle Ages
- Cheolli Jangseong
- The fortifications, castles and border walls between the Emirate of Granada and the Crown of Castile, later Spain between 1238 and 2 January 1492 although it continued as the internal border of the Crown of Castile, then Spain as Kingdom of Granada from 2 January 1492 to 29 September 1833. A large part of the fortifications, castles and walls is currently in good condition.
- Asilah: The King Alfonso V of Portugal built walls on the outskirts of the city of Asilah, serving as a border between the Kingdom of Portugal and the Marinid dynasty (1471–1472), the Saadi Sultanate (1472–1550), the Wattasid dynasty (1577–1589), in the area of the sea there are still cannons next to a Portuguese square tower. Currently the Wall is in good condition.
- Macau: Ming dynasty (currently China) built a wall around Macau in 1570.
Early modern period
- Great Hedge of India, built by the British in 1803
- The border forts between the Captaincy General of Chile later Chile and the Mapuche territory that served as the border between the two from 1598 to 1883, which was delimited mainly by the Biobío river, the route passed through the Province of Biobío, Region of Biobío and the Region of Araucanía.
- Zanja de Alsina, built in the 1870s along the southern frontier of Argentina
- The points, forts and border barriers that functioned between the French Conchinchina and the Nguyễn dynasty that functioned between 1862 and 1887.
Defunct barriers in modern times
- The posts and barriers between Kiautschou Bay Leased Territory and Qing dynasty later China between 1898 and 1914 and later served as the border between the Empire of Japan and the China, that worked between November 7, 1914, and December 10, 1922, and reoccupied in the Second Sino-Japanese War from 1937 and 1945.
- The posts and border barriers between Leased Territory of Guangzhouwan and Qing dynasty later China that worked between 1898 and 1945.
- The Czechoslovak border fortifications and fortified defensive lines built between 1935 and 1938 as a defensive countermeasure against the rising threat of Nazi Germany.
- The Maginot Line, built between 1929 and 1938 by France on the French–German border as a defensive structure.
- The border posts and barriers between the (Empire of Japan) through the (Karafuto Prefecture) and the (Russian Empire after Russian SSR after USSR) through the Sakhalin Oblast that operated between 5 September 1907 and 25 August 1945.
- The border posts, forts and walls between the Russian Dalian (Russian Empire) and the Qing dynasty between 27 March 1898 – 5 September 1905 and between the Kwantung Leased Territory (Empire of Japan) and the (Qing dynasty 5 September 1905 – 10 October 1911 and the Republic of China 10 October 1911 – 1932), later Manchukuo (1932 – 14 August 1945) later by the USSR as the Soviet occupation of Manchuria between August 14, 1945, and May 3, 1946, when it was returned to the Republic of China.
- The posts, forts and border barriers that operated between the British Burma (1824–1858, 1947–1948) later British Raj through the province of British Burma and French Indochina, Kingdom of Siam and Qing dynasty later China).
- The frontier posts, forts and barriers that operated between the colony and overseas territory of the French India and (Mughal Empire after Maratha Empire after Company Rule in India after British Raj after India) which operated between 1664 and 1 November 1954.
- The posts, forts and border barriers between Finland and the former Soviet Union, in the Hanko peninsula (1940–1941) and in the Porkkala peninsula (1945–1956).
- The frontier posts, forts and barriers that operated between the colony and overseas province of the Portuguese India and (Mughal Empire after Bijapur Sultanate after Maratha Empire after Company Rule in India after British Raj after India) which functioned between 15 August 1505 and 19 December 1961.
- The coastal posts, forts and walls that were in Dutch New Guinea (27 December 1949 – 1 October 1962) after United Nations Provisional Executive Authority (1 October 1962 – 1 May 1963) and served to ward off the United States of Indonesia (27 December 1949 – 17 August 1950) and after Indonesia (17 August 1950 – 1 May 1963).
- The frontier posts, forts and barriers that operated between the colony and overseas province of the Portuguese Timor, (Independent East Timor between November 1975 to December 7, 1975) and (Dutch East Indies (15 August 1702 – 27 December 1949) later United States of Indonesia (27 December 1949 – 17 August 1950) later Indonesia (17 August 1950 – 7 December 1975) which functioned between 15 August 1702 and 7 December 1975, the border continues to function but is currently free passage.
- The border posts, forts and barriers between the (Panama Canal Zone) United States and Panama in operation between November 18, 1903, until October 1, 1979, partially and totally the July 1, 1999.
- The former Soviet Union had a security barrier (see С-175 "curtain") along its entire border from Norway and Finland to North Korea and China. The barrier also existed along to direct border to Soviet allies, e.g. Poland. In Europe, the more than 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) long direct border between the Soviet Union and Finland/Norway was of particular importance during the Cold War. Along the Finnish border, the barrier was not so well guarded however since Finland agreed to send back all Soviet citizens who escaped.[citation needed] The fence was located a few kilometers (miles) from the border, and still partly remains. Russian law still forbids crossing the border outside of a border station.

- Iron Curtain in Europe and Asia: apart from the direct border between the former Soviet Union and Norway/Finland, this former barrier includes:
Other
- Danevirke
- Gates of Alexander
- Götavirke
- Limes Germanicus
- Limes Saxoniae
- Offa's Dyke
- Willow Palisade
- Zasechnaya cherta
See also
- Buffer zone
- Canada–United States border
- Canal
- Citadel
- Defense line
- Peace lines
- Demilitarised zone
- Defensive walls
- List of cities with defensive walls
- List of fortifications
- List of walls
- Second Amendment sanctuary
- Trump wall
- Fences in Rio de Janeiro
References
- ^ "Return of the Fence: Immigration crisis spurs renewed calls for border barrier". Fox News. 2014-07-09. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- ^ "Border Barrier". Frontline. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- ^ Friedman, Uri (19 May 2016). "A World of Walls". The Atlantic. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
- ^ "A Wall Divides Latin America — but Not the One You're Thinking of". BuzzFeed News. 5 March 2017.
- ^ "Mikl-Leitner baut "Grenz-Zaun"". Oe24.at. 2015-01-12. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- ^ Phillips, Barnaby (2004-03-30). "Zimbabwe crisis spills over border". BBC News. Retrieved January 4, 2010.
- ^ Caroline Mortimer. Bulgaria builds final part of razor wire fence to keep out refugees. The Independent. 4 August 2015.
- ^ McAuley, James (29 September 2016). "France and Britain just beat Donald Trump to building a border wall". Washington Post. Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ "Op-Ed - Ceuta, the Border-fence of Europe - Worldpress.org". www.worldpress.org. Retrieved 2021-12-25.
- ^ "JURIST – Paper Chase: China building border fence facing North Korea". Archived from the original on August 20, 2012. Retrieved October 23, 2012.
- ^ "Chile construirá nueva zanja en la frontera con Bolivia para frenar migración". SWI swissinfo.ch (in Spanish). 2022-03-05. Retrieved 2023-06-11.
- ^ "Denmark builds a border fence but it has nothing to do with migrants". NBC News. 29 January 2019. Retrieved 2021-12-25.
- ^ Bolongari, Kait (28 January 2019). "Denmark building wild boar fence along border with Germany". Politico.
- ^ Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche. "Denmark to build controversial German border fence | DW | 14.08.2018". DW.COM. Retrieved 2021-12-25.
- ^ "Dominican Republic to construct fence along border with Haiti". news.yahoo.com. Reuters. February 27, 2021. Retrieved February 28, 2021.
- ^ "Archive.ph". Bloomberg News. Archived from the original on 2022-09-29. Retrieved 2022-10-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Fraser, Christian (9 December 2009). "Egypt starts building steel wall on Gaza Strip border". BBC. Retrieved 17 February 2017.
- ^ Estonia 'plans Russia border fence' amid Ukraine tensions. BBC News. 28 August 2015
- ^ "Finland starts construction of Russia border fence". 1 March 2023 – via www.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ "Greece finishes fence at Turkey border amid warnings of Afghan migrant surge". BBC News. August 21, 2021. Retrieved October 24, 2021.
- ^ Picheta, Rob; Liakos, Chris (August 21, 2021). "Greece finishes wall on border with Turkey, amid fears of Afghan migrant crisis". CNN. Retrieved October 24, 2021.
- ^ Danae Leivada. Why Greece Shut The Shortest, Safest Route For Migrants And Refugees. The Huffington Post. Published on 09/24/2015.
- ^ "Turkey – Greece to put up anti-migrant wall on Turkish border". Hurriyetdailynews.com. 2011-01-02. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- ^ Συντάχθηκε απο τον/την theInsider (2010-03-14). "Τείχος κατά μεταναστών στον Έβρο!". Theinsider.gr. Archived from the original on 2013-09-27. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- ^ "Frontex signs seat agreement with Greece". Archived from the original on March 16, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2013.
- ^ Yannis Behrakis. Police, migrants clash on Macedonia border; soldiers build fence Archived 2015-12-02 at the Wayback Machine. Reuters. November 28, 2015.
- ^ "Hungary to fence off border with Serbia to stop migrants". Reuters. 2015-06-17. Archived from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved June 18, 2015.
- ^ "Reinforcement of temporary border barrier starts on the Hungarian–Serbian border". Archived from the original on 29 July 2020. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ^ Hungary's PM plans 'more massive' fence to keep out migrants. theguardian.com. 26 August 2016.
- ^ "Hungary Completes 2nd Border Fence Meant to Stop Migrants". Fox News (from the Associated Press). April 28, 2017. Retrieved September 13, 2017.
- ^ "Hungary Completes Second Fence to Keep Out Migrants". Deutsche Welle. April 28, 2017. Retrieved September 13, 2017.
- ^ "BSF activates 'laser walls' along India-Pakistan border".
- ^ "Pakistan army says border fencing with Iran to be completed by end of 2021". IRNA. Retrieved 2020-08-14.
- ^ "Debate on Iran border wall disallowed". dawn.com. May 27, 2007. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- ^ "BAE Systems to deliver 145 M777 Ultra Light Howitzers to the Indian Army". Archived from the original on November 18, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2013.
- ^ "South Asia | World's barriers: Pakistan–Iran". BBC News. 2009-11-05. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- ^ "Behind the Wall – Shuafat Refugee Camp". Ir Amim. Archived from the original on May 23, 2012.
- ^ "RSA – Mozambique Border Fence". Home.telkomsa.net. Archived from the original on 2013-09-27. Retrieved 2013-09-22.
- ^ Monteiro, Tania (1990-01-27). "'Hundreds killed' by South Africa's border fence". New Scientist. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- ^ "Cross-Border Park is Africa's Largest Wildlife Refuge". Archived from the original on May 23, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2013.
- ^ "IOL: News for South Africa and the World". Archived from the original on January 24, 2009. Retrieved September 22, 2013.
- ^ Jeremy Bender. A nation bordering Russia is building a fence along a third of its border. Business Insider. Published on December 16, 2015.
- ^ "Lithuania completes building fence along border with Belarus". BNS, lrt.lt. 2022-08-29. Retrieved 2023-03-08.
- ^ "Lithuania on Monday said it had finished building a fence along its border with Belarus to fight illegal immigration which the West accuses Minsk of orchestrating". www.france24.com. Vilnius: France 24. AFP. 2022-08-29. Retrieved 2023-03-08.
- ^ RFE/RL (2022-08-29). "Lithuania Finishes Building Wall On Belarusian Border To Stem Flow Of Illegal Migrants". www.rferl.org. RFE/RL. Retrieved 2023-03-08.
- ^ Lithuania builds Russian border fence as Nato boosts Baltic defences. The Irish Times. January 18, 2017.
- ^ Deployment of Minurso (PDF) (Map). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 27, 2007. Retrieved October 27, 2007 – via minurso.unlb.org.
- ^ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "UNHCR – Western Sahara Atlas Map – June 2006". Unhcr.org. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- ^ Osborne, Samuel (25 August 2016). "Norway to build border fence with Russia to keep out refugees". The Independent.
- ^ "Pakistan doing all it can in terror war – Musharraf". Turkish weekly. February 28, 2006. Archived from the original on October 9, 2006. Retrieved 2006-12-03.
Washington (Reuters) – Pakistani President Pervez Musharraf said on Monday his country was doing all it could in the U.S.-led war against terrorism and offered to fence and mine its border with Afghanistan to stem Taliban infiltration. "I have been telling Karzai and the United States, 'Let us fence the border and let us mine it.' Today I say it again. Let us mine their entire border. Let us fence it. It's not difficult", Musharraf said, referring to Afghan President Hamid Karzai.
- ^ Plett, Barbara (March 1, 2006). "Musharraf interview: Full transcript". BBC News. Retrieved 2006-12-03.
Now the other thing that I've said: if he thinks everyone is crossing from here, I've been saying let us fence the border and let us also mine the border. We are experts at mining, they should mine the border on their side. We will fence it on our side. If that is all right I am for it, so that they are not allowed to go across at all. And then let us see what is happening in Afghanistan. Why don't they agree to this, I've said this openly many times before, they don't do it, for whatever are their reasons. I know how effective the fence, the Indian fence which is about 1,800 kilometres, and they are fencing the Kashmir mountains also, it is so difficult. Why are they doing that, are they mad, they are spending billions of rupees. Because it is effective. Let's fence this border so that this blame game is killed once for ever.
- ^ "Poland completes 186-kilometre border wall with Belarus". euronews. 2022-06-30. Retrieved 2022-09-11.
- ^ "Europe | Missing Migrants Project". missingmigrants.iom.int. Retrieved 2021-12-25.
- ^ Kucharczyk, Maciek (2021-10-16). "Patrząc na inne płoty fortecy Europa, ten polski będzie z rozmachem. Tak wyglądają pozostałe [ZDJĘCIA]". Gazeta.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 2021-10-16.
- ^ WZI (2021-10-12). "Mur na granicy z Białorusią powstanie. Rząd przyjął projekt ustawy". Money.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 2021-10-16.
- ^ Huemer, Sarah (October 14, 2021). "Polish MPs approve €350M wall on Belarusian border as migrant death toll rises". Politico. Retrieved 24 October 2021.
- ^ Porter, Fred (October 16, 2021). "oland parliament authorizes border wall with Belarus". Jurist. Retrieved 24 October 2021.
- ^ Plucinska, Joanna; Pempel, Kacper (August 26, 2021). "On the EU's eastern border, Poland builds a fence to stop migrants". Reuters. Retrieved 24 October 2021.
- ^ Theodoulou, Michael (6 April 2006). "Saudis plan to fence off border with chaos". Timesonline.co.uk. Archived from the original on 29 September 2006.
- ^ Spencer, Richard (2015-01-14). "Revealed: Saudi Arabia's 'Great Wall' to keep out Isil". Telegraph. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ Surk, Barbara (11 November 2015). "Slovenia Starts Building Border Fence to Stem Flow of Migrants". New York Times. Retrieved 11 November 2015.
- ^ "40 kilometres of new fences will be built in Slovenia in 2019" (in Slovenian). 24ur.com. Retrieved 28 July 2019.
- ^ "One third of south border in fences" (in Slovenian). 24ur. Retrieved 3 March 2020.
- ^ "RFE: Serbia builds wire fence on border with North Macedonia". rs.n1info.com/. N1. Archived from the original on 18 September 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ "Turkey-Syria border wall to be completed by spring – Turkey News". 19 December 2017.
- ^ "Trump-O-Meter: | PolitiFact". politifact.com. Retrieved 2020-02-24.
- ^ Davis, Julie Hirschfeld (2017-01-25). "Trump Orders Mexican Border Wall to Be Built and Plans to Block Syrian Refugees". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2020-02-24.
- ^ Kerns, Jen (2018-02-03). "New polling proves President Trump is right – 'Americans are #Dreamers, too'". The Hill. News Communication.
61 percent think that current border security is inadequate, and ... 54 percent support a physical barrier
- ^ De Pinto, Jennifer; Backus, Fred; Khanna, Kabir; Salvanto, Anthony (20 January 2018). "Most Americans support DACA, but oppose border wall – CBS News poll". CBS.
Most Americans ... oppose building a border wall, but seven in 10 Republicans support it.
- ^ Salvanto, Anthony; De Pinto, Jennifer (21 December 2018). "Most Americans don't support building the wall". CBS.
59 percent of Americans oppose building a wall... A large majority of Republicans support the wall – 79 percent. A majority of independents – 66 percent – oppose the wall, and 84 percent of Democrats are also against it.
- ^ Kurtzleben, Danielle (23 January 2018). "What The Latest Immigration Polls Do (And Don't) Say". NPR.
Given the choice between "open borders" ... and a "secure border," 79 percent of Americans agreed that the U.S. needs "secure borders." ... In a different poll, 58 percent of Americans support "building a combination of physical and electronic barriers across the U.S.-Mexico border."
- ^ "Government Shutdown 2019". Politico. Retrieved 2020-02-24.
- ^ Baker, Peter (2019-02-15). "Trump Declares a National Emergency, and Provokes a Constitutional Clash". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2020-02-24.
- ^ Gramlich, John. "How Americans see illegal immigration, the border wall and political compromise". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- ^ Norman, Jim (4 February 2019). "Solid Majority Still Opposes New Construction on Border Wall". Gallup News. Gallup. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- ^ Learned, J.G. "The Hmong: Part 1 Legend and History". North-by-North-East.com. Archived from the original on December 8, 2010. Retrieved September 22, 2013.
External links
- "Around Globe, Walls Spring Up to Divide Neighbors". Reuters. April 30, 2007.
- "Border to Border, Wall to Wall, Fence to Fence". Subtopia.
- "CityWalls". Erasmuspc. Archived from the original on 2012-02-06.
- "Obama's Border Fence". NOW. PBS. July 3, 2009.
- "Security Fences". The Atlantic Monthly.


















