Potency and safety analysis of hemp-derived delta-9 products: The hemp vs. cannabis demarcation problem
Contents
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
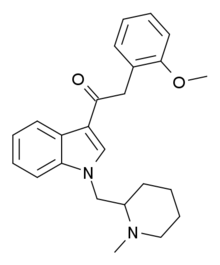
| Formula | C24H28N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 376.500 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cannabipiperidiethanone (CPE or 1-(N-methylpiperidin-2-ylmethyl)-3-(2-methoxyphenylacetyl)indole) is a synthetic cannabinoid that has been found as an ingredient of "herbal" synthetic cannabis blends sold in Japan, alongside JWH-122 and JWH-081.
Its binding affinity was measured at the CB1 and CB2 receptors and it was found to have an IC50 of 591 nM at CB1 and 968 nM at CB2, making it 2.3 times and 9.4 times weaker than JWH-250 at these two targets respectively.[1]
In the United States, CB1 receptor agonists of the 3-phenylacetylindole class such as cannabipiperidiethanone are Schedule I Controlled Substances.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Uchiyama N, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2011). "Identification of a novel cannabimimetic phenylacetylindole, cannabipiperidiethanone, as a designer drug in a herbal product and its affinity for cannabinoid CB₁ and CB₂ receptors". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 59 (9): 1203–5. doi:10.1248/cpb.59.1203. PMID 21881274.
- ^ : Schedules of controlled substances

















