Potency and safety analysis of hemp-derived delta-9 products: The hemp vs. cannabis demarcation problem
Contents
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
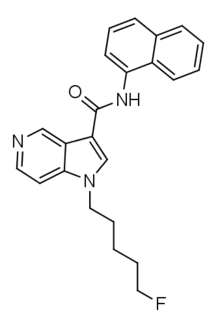
| Formula | C23H22FN3O |
| Molar mass | 375.447 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
5F-PCN (also known as 5F-MN-21) is an azaindole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is presumed to be a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug.[1][2] It is closely related to NNE1. Given the known metabolic liberation (and presence as an impurity) of amantadine in the related compound APINACA, it is suspected that metabolic hydrolysis of the amide group of 5F-PCN may release 1-naphthylamine, a known carcinogen.
Legal status
Sweden's public health agency suggested to classify 5F-PCN as hazardous substance on November 10, 2014.[3]
See also
References
- ^ "5F-PCN". Cayman Chemical. Retrieved 22 July 2015.
- ^ Blaazer AR, Lange JH, van der Neut MA, Mulder A, den Boon FS, Werkman TR, et al. (October 2011). "Novel indole and azaindole (pyrrolopyridine) cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonists: design, synthesis, structure-activity relationships, physicochemical properties and biological activity". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 46 (10): 5086–98. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.08.021. PMID 21885167.
- ^ "Cannabinoider föreslås bli klassade som hälsofarlig vara". Folkhälsomyndigheten. Retrieved 22 July 2015.