Potency and safety analysis of hemp-derived delta-9 products: The hemp vs. cannabis demarcation problem
Contents
 The damaged Lorca-Sutullena railway station in Lorca | |
| UTC time | 2011-05-11 16:47:25 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 16505634 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | 11 May 2011 |
| Local time | 18:47:26 CEST (UTC+02:00) |
| Magnitude | 5.1 Mw(USGS) [1] |
| Depth | 1.0 km (0.62 mi)[2] |
| Epicenter | 37°41′56″N 1°40′19″W / 37.699°N 1.672°W |
| Areas affected | Spain |
| Max. intensity | MMI VI (Strong)[3] |
| Peak acceleration | 0.367 g[4] |
| Foreshocks | 1 (4.5 ML)[5] |
| Casualties | 9 dead 403 injured[6] |
The 2011 Lorca earthquake (Spanish: Terremoto de Lorca de 2011) was a moderate 5.1 Mw[2] earthquake that occurred 6:47 p.m. CEST (16:47 UTC) on 11 May 2011,[7] near the town of Lorca, causing significant localized damage in the Region of Murcia, Spain, and panic among locals, and displacing many from their homes. The quake was preceded by a magnitude 4.4 (Mw) foreshock at 17:05 (15:05 UTC), that inflicted substantial damage to many older structures in the area, including the historical Espolón Tower of Lorca Castle, the Hermitage of San Clemente and the Convent of Virgen de Las Huertas.[8][9] Three people were killed by a falling cornice.[10] A total of nine deaths have been confirmed, while dozens are reported injured.[11] The earthquake was the worst to hit the region since a 5.0 Mw tremor struck west of Albolote, Granada in 1956.[12]
Geology
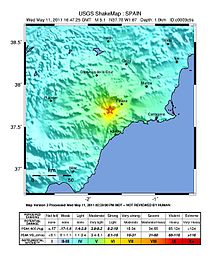
The magnitude 5.1 Mw[2] main shock occurred inland on 11 May 2011 at 18:47 local time (16:47 UTC) in the locality of Lorca, Spain,[12] at a depth of 6.7 km (4.2 mi).[2] Much of the southern Iberian Peninsula – in particular the Murcia Region – is located on a tectonic zone of common seismic activity, where a plate boundary separating the Eurasia and African plates is formed.[13] However, most tremors in the region do not exceed perceptible magnitudes.[14] The earthquake was estimated to be a direct result of strike-slip faulting near the major Alhama de Murcia fault,[13][15] along an unusually shallow fault of between 40 and 50 km (25 to 31 mi) long. Local specialists also reported the presence of surface rupturing in the vicinity of the fault.[16] Due to the shallow depth, the earthquake resulted in significant shaking throughout much of Murcia. In Lorca, near the epicentre of the quake, strong ground motions registered a maximum intensity of VI on the Mercalli scale, while many adjacent areas reported moderate shaking (MM V). Widespread light tremors were observed in locations up to several hundred kilometers from the epicentre, including Alicante (MM III) and Madrid.[17]

Foreshock
The earthquake was preceded by a magnitude 4.5 (ML) foreshock that struck very close to its epicentre at 17:05 local time (15:05 UTC).[5] It was reported to be centred along the same fault zone, with a similar focal mechanism as the main shock.[16] Though the tremor was relatively mild, some cracks and crumbled walls were reported, while downed power lines sparked a small fire in Lorca.[18]
Aftershock
As of 11 May, at least eight light aftershocks were reported near the initial quake epicentres;[19] the strongest registered a magnitude of 4.1 (ML) and occurred at 22:37 local time (20:37 UTC).[20]
Emergency management
Shortly after the second earthquake struck, the Spanish government, at the request of regional government of Murcia, activated the Military Emergencies Unit, a branch of the Spanish Armed Forces responsible for providing disaster relief. 340 members from three battalions (based at Bétera, Torrejón de Ardoz and Morón de la Frontera) were dispatched to Lorca under the management of the Lieutenant Colonel of the Bétera battalion; these were later joined by army units.[21] A field hospital was set up by the Military Emergencies Unit in the Plaza del Ayuntamiento where those injured were attended to by members of Protección Civil and the Red Cross.

 earthquake epicentre
earthquake epicentre  zones with damaged buildings
zones with damaged buildings  deaths
deathsPossible causes
Several research groups investigated the cause of this earthquake. The Active Tectonics Group of the Complutense University of Madrid in collaboration with the Instituto Andaluz de Geofísica using tectonic evidences, InSAR analysis and seismological analysis of the rupture concluded that this earthquake was produced by the reactivation of a small section (3 km x 4 km) of the Alhama de Murcia Fault (AMF)[23] located 3 km northeast of Lorca, Spain. These conclusions were published in the journal Tectonophysics (journal) in April 2012. The great damage produced by this moderate magnitude earthquake may be explained by the southwestward directivity of a shallow rupture that induced high acceleration values in Lorca village.[24] From the tectonic point of view this earthquake can be considered as an ordinary event coherent with the tectonic evolution and mechanical characteristics of the Alhama de Murcia Fault. In fact, similar earthquakes occurred in Lorca in the 16th and 17th centuries. Several research projects conducted during the last 25 years on this fault recognized the occurrence of much larger earthquakes (Mw > 6.0) during the last 10,000 years.[25]
Other scientific research has suggested that the earthquake was caused by human activity. A team led by Pablo Gonzalez of the University of Western Ontario in Canada reported in the journal Nature Geoscience in October 2012 that the pattern of earth movement was consistent with changes in stresses caused by the removal of water from underground reservoirs.[26][27]
See also
References
- ^ International Seismological Centre. ISC-EHB Bulletin. Thatcham, United Kingdom. [Event 16505634].
- ^ a b c d ISC-EHB Event 16505634 [IRIS].
- ^ ANSS. "Spain 2011: M 5.1 - Spain". Comprehensive Catalog. U.S. Geological Survey.
- ^ Méndez, Rafael (13 May 2011). "Los terremotos paradójicos". El País.
- ^ a b "Magnitude 4.5 – SPAIN – 2011-05-11 15:05 UTC". EMSC. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- ^ "CATDAT Damaging Earthquakes Database 2011 – Annual Review". Earthquake Report. 9 January 2012. Archived from the original on 18 November 2020. Retrieved 14 January 2012.
- ^ "Magnitude 5.1 – Spain". United States Geological Survey. 11 May 2011. Archived from the original on 3 June 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- ^ M. Carmen Cruz. "Minuto a minuto: El funeral por las víctimas será esta tarde en el recinto de Santa Quiteria". RTVE.es. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ^ El terremoto de Lorca causa la "mayor catástrofe" patrimonial en Europa en los últimos años (in Spanish)
- ^ "Dos terremotos sacuden Lorca y causan ocho muertos · ELPAÍS.com". El País. Elpais.com. 11 May 2011. Archived from the original on 20 May 2011. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ^ Tremlett, Giles (12 May 2011). "Spain Shocked by Deadly Earthquake". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ^ a b EFE (11 May 2011). "El seísmo de Lorca, el que ha causado más víctimas desde 1956". ABC. Archived from the original on 18 May 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- ^ a b "Magnitude 5.1 – Spain: Tectonic Summary". United States Geological Survey. 11 May 2011. Archived from the original on 8 June 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- ^ "Murcia es una zone habitual de movimientos sísmicos pero no de los dos terremotos registrados este miércoles". Europa Press. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- ^ Martínez-Díaz, J. J.; Masana, E.; Hernández-Enrile, J. L.; Santanach, P. (2003). "Effects of repeated paleoearthquakes on the Alhama de Murcia Fault (Betic Cordillera, Spain) on the Quaternary evolution of an alluvial fan system". Annals of Geophysics. 46 (5): 775–791. doi:10.4401/ag-3455. ISSN 1593-5213. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ^ a b EFE (11 May 2011). "Los dos seísmos se deben a un deslizamiento horizontal de falla de Lorca". ABC. Archived from the original on 11 September 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- ^ ANSS: Spain 2011, Did You Feel It? .
- ^ "Un terremoto de 4,5 grados con epicentro en Lorca sacude la Región". Teleprensa. 11 May 2011. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- ^ EFE (11 May 2011). "Los sismógrafos detectan varias réplicas tras el segundo terremoto de Lorca". ABC. Archived from the original on 17 October 2012. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- ^ "Magnitude 4.1 – SPAIN – 2011-05-11 20:37 UTC". EMSC. 11 May 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- ^ "El Ejército instala un hospital de campaña para los damnificados por el terremoto" [The army sets up a field hospital for those affected by the earthquake]. El País. 12 May 2011.
- ^ Mariano Zafra (13 May 2011). "Consecuencias de los seísmos en Lorca". El País (in Spanish). Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ Bousquet, J.C. (1979). "Quaternary strike-slip faults in southeastern Spain". Tectonophysics. 52 (1–4): 277–286. Bibcode:1979Tectp..52..277B. doi:10.1016/0040-1951(79)90232-4.
- ^ Martínez-Díaz, José J.; Bejar-Pizarro, Marta; Álvarez-Gómez, José A.; de Lis Mancilla, Flor; Stich, Daniel; Herrera, Gerardo; Morales, Jose (2012). "Tectonic and seismic implications of an intersegment rupture. The damaging May 11th 2011 Mw 5.2 Lorca, Spain, earthquake" (PDF). Tectonophysics. 546–547: 28–37. Bibcode:2012Tectp.546...28M. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2012.04.010. hdl:10261/276856.
- ^ Ortuño, C.Canora; Masana, M. E.; García-Meléndez, E.; Martínez-Díaz, J. J.; Štěpančíková, P.; Cunha, P.; Sohbati, R.; Buylaert, J.P.; Murray, A.S. (2012). "An exceptionally long paleoseismic record of a slow-moving fault: The Alhama de Murcia fault (Eastern Betic shear zone, Spain)". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 124 (9–10): 1474–1494. Bibcode:2012GSAB..124.1474O. doi:10.1130/B30558.1. hdl:10316/79929.
- ^ "Spanish quake was man-made – study". Irish Independent. 21 October 2012.
- ^ Pablo J. González; Kristy F. Tiampo; Mimmo Palano; Flavio Cannavó; José Fernández (21 October 2012). "The 2011 Lorca earthquake slip distribution controlled by groundwater crustal unloading". Nature Geoscience. 5 (11): 821–825. Bibcode:2012NatGe...5..821G. doi:10.1038/ngeo1610. hdl:10261/73773.
External links
- The International Seismological Centre has a bibliography and/or authoritative data for this event.



















