Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
| ?Hô-bé | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

| ||||||||||||||
| Hô-bé tīn, Luangwa Soaⁿ-kok (Zambia) | ||||||||||||||
| Pó-io̍k chōng-hóng | ||||||||||||||
| Seng-bu̍t-ha̍k hun-lūi | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Ha̍k-miâ | ||||||||||||||
| Hippopotamus amphibius Linnaeus, 1758 | ||||||||||||||
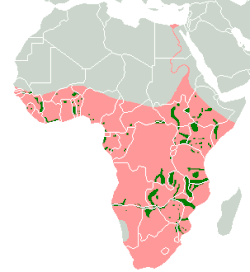 Seⁿ-thoàⁿ tē-tô͘
|
Hô-bé (Hi-lia̍p-gí: ‘ιπποπόταμος, lô-má-jī: hippopotamos, hippos sī "bé", potamos sī "hô"), ha̍k-miâ Hippopotamus amphibius, nā kap pat chéng khu-hun mā ē-tàng kiò phó͘-thong hô-bé (Eng-gí: common hippo), sī Hui-chiu ê 1 chióng chia̍h-chháu ê chhī-leng tōng-bu̍t, kho-ha̍k-kài kā i pun khì Hippopotamidae kho lāi-té. Chit ê kho bo̍k-chêng kan-taⁿ chhun 2 ê chéng, lēng-goā hit ê sī É Hô-bé.
Pún chéng ê hô-bé, ē-tàng hun 5-ê a-chéng, chóng-sī chia-ê a-chéng m̄-sī chin siū tio̍h tong-tāi gián-kiù khak-jīn--ê:[1]
Hô-bé it-poaⁿ chia̍h-chháu, chóng-sī ia̍h ū hàn--tit chhut-hiān ê chia̍h ba̍h kì-lio̍k[2].