Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
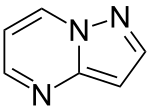
Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.227.461 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5N3 | |
| Molar mass | 119.127 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Pyrazolopyrimidines are a series of isomeric heterocyclic chemical compounds with the molecular formula C6H5N3. [1] They form the central core of a variety of more complex chemical compounds including some pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
One isomer of pyrazolopyrimidines, known as pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine, is the basis for a class of sedative and anxiolytic drugs related (in terms of their effect) to benzodiazepines.
Most of the drugs from this class marketed to date are intended to induce sleep, and are prescribed for people suffering insomnia, however some newer compounds produce anxiolytic effects with relatively little sedation, and are being developed for use as non-sedating anti-anxiety drugs.
They include:
As they are not chemically related to the benzodiazepines despite their similar effect, such drugs—as well as the imidazopyridines and cyclopyrrones—are sometimes grouped together and referred to as "nonbenzodiazepines".

A related use is in pyrazolopyrimidine organothiophosphate pesticides including chlorprazophos (insecticide) and pyrazophos (fungicide, insecticide).
