Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Hercules |
| Right ascension | 17h 39m 27.8864s[1] |
| Declination | +46° 00′ 22.795″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.80[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B3IV[1] |
| U−B color index | –0.71 |
| B−V color index | –0.18[3] |
| Variable type | Beta Cephei[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | –20.0[1] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 7.48[5] mas/yr Dec.: 4.53[5] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 7.17 ± 0.13 mas[5] |
| Distance | 455 ± 8 ly (139 ± 3 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | –1.97[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 6.7 ± 0.1[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 5.29 ± 0.45[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2,489[2] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.82 ± 0.06[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 18,070 ± 294[8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.40[9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 6±1[2] km/s |
| Age | 37.8 ± 8.6[7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Iota Herculis (ι Herculis, ι Her) is a fourth-magnitude variable star system in the constellation Hercules, consisting of at least four stars all about 139 parsecs (450 light-years) away. The brightest is a β Cephei variable, a pulsating star.
Iota Herculis is dim enough that in cities with a lot of light pollution it is unlikely to be visible with the naked eye. In rural areas it will usually be visible, and for much of the Northern Hemisphere the star is circumpolar and visible year around.
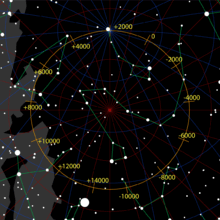
As a visible star, the proximity of Iota Herculis to the precessional path the Earth's North Pole traces across the celestial sphere makes it a pole star, a title currently held by Polaris. In 10,000 BCE it was the pole star, and in the future it will be again. While Polaris is only 0.5° off the precessional path Iota Herculis is 4° off.
| Preceded by | Pole star | Succeeded by |
|---|---|---|
| Vega | ~16,000 CE | Tau Herculis |
Iota Herculis is a B-type subgiant star that is at the end of its hydrogen fusion stage.[10] With a stellar classification B3IV, it is considerably larger than the Sun, having a mass that is 6.5 times solar and a radius 5.3 times. Though its apparent magnitude is only 3.80, it is 2,500 times more luminous than the Sun, yielding an absolute magnitude of −2.11, brighter in fact than most of the hot B stars in the Pleiades open star cluster. The Hipparcos satellite mission estimated its distance at roughly 152 parsecs (pc) from Earth, or 496 light-years (ly) away;[11] an updated parallax measurement from Floor van Leeuwen in 2007, however, puts the distance at 455 ly with a much tighter error factor of only 8 ly.[5]
Iota Herculis is a multiple star system. It is a spectroscopic binary having a 113.8-day period, indicating that its closest component is separated by about 1 AU.[10] Another companion can be found at approximately 30 AU from the main star, giving it an orbital period of about 60 years. Still another star has been identified with a common proper motion at an angular separation of 116 arcseconds and a visual magnitude of 12.1.[12] This would place it approximately 18,000 AU away, giving it an orbit of about 1 million years.[10]
In Chinese, 天棓 (Tiān Bàng), meaning Celestial Flail, refers to an asterism consisting of ι Herculis, ξ Draconis, ν Draconis, β Draconis and γ Draconis.[13] Consequently, ι Herculis itself is known as 天棓五 (Tiān Bàng wu, English: the Fifth Star of Celestial Flail).
origin: SIMBAD