Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
| Generation | IEEE standard |
Adopted | Maximum link rate (Mb/s) |
Radio frequency (GHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Wi-Fi 0*) | 802.11 | 1997 | 1–2 | 2.4 |
| (Wi-Fi 1*) | 802.11b | 1999 | 1–11 | 2.4 |
| (Wi-Fi 2*) | 802.11a | 1999 | 6–54 | 5 |
| (Wi-Fi 3*) | 802.11g | 2003 | 2.4 | |
| Wi-Fi 4 | 802.11n | 2009 | 6.5–600 | 2.4, 5 |
| Wi-Fi 5 | 802.11ac | 2013 | 6.5–6933 | 5[a] |
| Wi-Fi 6 | 802.11ax | 2021 | 0.4–9608[1] | 2.4, 5 |
| Wi-Fi 6E | 2.4, 5, 6[b] | |||
| Wi-Fi 7 | 802.11be | exp. 2024 | 0.4–23,059 | 2.4, 5, 6[2] |
| Wi-Fi 8 | 802.11bn | exp. 2028[3] | 100,000[4] | 2.4, 5, 6[5] |
| *Wi‑Fi 0, 1, 2, and 3 are named by retroactive inference. They do not exist in the official nomenclature.[6][7][8] | ||||
IEEE 802.11b-1999 or 802.11b is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 wireless networking specification that extends throughout up to 11 Mbit/s using the same 2.4 GHz band. A related amendment was incorporated into the IEEE 802.11-2007 standard.
802.11 is a set of IEEE standards that govern wireless networking transmission methods. They are commonly used today in their 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac and 802.11ax versions to provide wireless connectivity in the home, office and some commercial establishments.
802.11b has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s and uses the same CSMA/CA media access method defined in the original standard. Due to the CSMA/CA protocol overhead, in practice the maximum 802.11b throughput that an application can achieve is about 5.9 Mbit/s using TCP and 7.1 Mbit/s using UDP.
802.11b products appeared on the market in mid-1999, since 802.11b is a direct extension of the DSSS (Direct-sequence spread spectrum) modulation technique defined in the original standard. The Apple iBook was the first mainstream computer sold with optional 802.11b networking. Technically, the 802.11b standard uses complementary code keying (CCK) as its modulation technique, which uses a specific set of length 8 complementary codes that was originally designed for OFDM [9] but was also suitable for use in 802.11b because of its low autocorrelation properties.[10] The dramatic increase in throughput of 802.11b (compared to the original standard) along with simultaneous substantial price reductions led to the rapid acceptance of 802.11b as the definitive wireless LAN technology as well as to the formation of the Wi-Fi Alliance.
802.11b devices suffer interference from other products operating in the 2.4 GHz band. Devices operating in the 2.4 GHz range include: microwave ovens, Bluetooth devices, baby monitors and cordless telephones. Interference issues and user density problems within the 2.4 GHz band have become a major concern and frustration for users.
| Code Length bits | Modulation type |
Symbol Rate | Bit per Symbol | Data rate (Mbit/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11-bit Barker code | DBPSK | 11/11 = 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 11-bit Barker code | DQPSK | 11/11 = 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 8-bit CCK | QPSK | 11/8 = 1.375 | 4 | 5.5 |
| 8-bit CCK | QPSK | 11/8 = 1.375 | 8 | 11 |
802.11b is used in a point-to-multipoint configuration, wherein an access point communicates via an omnidirectional antenna with mobile clients within the range of the access point. Typical range depends on the radio frequency environment, output power and sensitivity of the receiver. Allowable bandwidth is shared across clients in discrete channels. A directional antenna focuses transmit and receive power into a smaller field which reduces interference and increases point-to-point range. Designers of such installations who wish to remain within the law must however be careful about legal limitations on effective radiated power.[11]
Some 802.11b cards operate at 11 Mbit/s, but scale back to 5.5, then to 2, then to 1 Mbit/s (also known as Adaptive Rate Selection) in order to decrease the rate of re-broadcasts that result from errors.
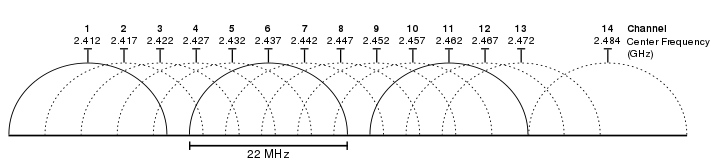
| Channel | Center frequency | Frequency delta | Channel width | Overlaps channels |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.412 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.401–2.423 GHz | 2-5 |
| 2 | 2.417 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.406–2.428 GHz | 1,3-6 |
| 3 | 2.422 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.411–2.433 GHz | 1–2,4-7 |
| 4 | 2.427 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.416–2.438 GHz | 1–3,5-8 |
| 5 | 2.432 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.421–2.443 GHz | 1–4,6-9 |
| 6 | 2.437 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.426–2.448 GHz | 2–5,7-10 |
| 7 | 2.442 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.431–2.453 GHz | 3–6,8-11 |
| 8 | 2.447 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.436–2.458 GHz | 4–7,9-12 |
| 9 | 2.452 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.441–2.463 GHz | 5–8,10-13 |
| 10 | 2.457 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.446–2.468 GHz | 6–9,11-13 |
| 11 | 2.462 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.451–2.473 GHz | 7-10,12-13 |
| 12 | 2.467 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.456–2.478 GHz | 8-11,13-14 |
| 13 | 2.472 GHz | 5 MHz | 2.461–2.483 GHz | 9-12, 14 |
| 14 | 2.484 GHz | 12 MHz | 2.473–2.495 GHz | 12-13 |
| Frequency range, or type |
PHY | Protocol | Release date[13] |
Frequency | Bandwidth | Stream data rate[14] |
Max. MIMO streams |
Modulation | Approx. range | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indoor | Outdoor | |||||||||||
| (GHz) | (MHz) | (Mbit/s) | ||||||||||
| 1–7 GHz | DSSS[15], |
802.11-1997 | June 1997 | 2.4 | 22 | 1, 2 | — | DSSS, |
20 m (66 ft) | 100 m (330 ft) | ||
| HR/DSSS[15] | 802.11b | September 1999 | 2.4 | 22 | 1, 2, 5.5, 11 | — | CCK, DSSS | 35 m (115 ft) | 140 m (460 ft) | |||
| OFDM | 802.11a | September 1999 | 5 | 5, 10, 20 | 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 (for 20 MHz bandwidth, divide by 2 and 4 for 10 and 5 MHz) |
— | OFDM | 35 m (115 ft) | 120 m (390 ft) | |||
| 802.11j | November 2004 | 4.9, 5.0 [B][16] |
? | ? | ||||||||
| 802.11y | November 2008 | 3.7[C] | ? | 5,000 m (16,000 ft)[C] | ||||||||
| 802.11p | July 2010 | 5.9 | 200 m | 1,000 m (3,300 ft)[17] | ||||||||
| 802.11bd | December 2022 | 5.9, 60 | 500 m | 1,000 m (3,300 ft) | ||||||||
| ERP-OFDM[18] | 802.11g | June 2003 | 2.4 | 38 m (125 ft) | 140 m (460 ft) | |||||||
| HT-OFDM[19] | 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) |
October 2009 | 2.4, 5 | 20 | Up to 288.8[D] | 4 | MIMO-OFDM (64-QAM) |
70 m (230 ft) | 250 m (820 ft)[20] | |||
| 40 | Up to 600[D] | |||||||||||
| VHT-OFDM[19] | 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) |
December 2013 | 5 | 20 | Up to 693[D] | 8 | DL MU-MIMO OFDM (256-QAM) |
35 m (115 ft)[21] | ? | |||
| 40 | Up to 1600[D] | |||||||||||
| 80 | Up to 3467[D] | |||||||||||
| 160 | Up to 6933[D] | |||||||||||
| HE-OFDMA | 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E) |
May 2021 | 2.4, 5, 6 | 20 | Up to 1147[E] | 8 | UL/DL MU-MIMO OFDMA (1024-QAM) |
30 m (98 ft) | 120 m (390 ft)[F] | |||
| 40 | Up to 2294[E] | |||||||||||
| 80 | Up to 5.5 Gbit/s[E] | |||||||||||
| 80+80 | Up to 11.0 Gbit/s[E] | |||||||||||
| EHT-OFDMA | 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) |
Sep 2024 (est.) |
2.4, 5, 6 | 80 | Up to 11.5 Gbit/s[E] | 16 | UL/DL MU-MIMO OFDMA (4096-QAM) |
30 m (98 ft) | 120 m (390 ft)[F] | |||
| 160 (80+80) |
Up to 23 Gbit/s[E] | |||||||||||
| 240 (160+80) |
Up to 35 Gbit/s[E] | |||||||||||
| 320 (160+160) |
Up to 46.1 Gbit/s[E] | |||||||||||
| UHR | 802.11bn (Wi-Fi 8) |
May 2028 (est.) |
2.4, 5, 6, 42, 60, 71 |
320 | Up to 100000 (100 Gbit/s) |
16 | Multi-link MU-MIMO OFDM (8192-QAM) |
? | ? | |||
| WUR[G] | 802.11ba | October 2021 | 2.4, 5 | 4, 20 | 0.0625, 0.25 (62.5 kbit/s, 250 kbit/s) |
— | OOK (multi-carrier OOK) | ? | ? | |||
| mmWave (WiGig) |
DMG[22] | 802.11ad | December 2012 | 60 | 2160 (2.16 GHz) |
Up to 8085[23] (8 Gbit/s) |
— | 3.3 m (11 ft)[24] | ? | |||
| 802.11aj | April 2018 | 60[H] | 1080[25] | Up to 3754 (3.75 Gbit/s) |
— | single carrier, low-power single carrier[A] | ? | ? | ||||
| CMMG | 802.11aj | April 2018 | 45[H] | 540, 1080 |
Up to 15015[26] (15 Gbit/s) |
4[27] | OFDM, single carrier | ? | ? | |||
| EDMG[28] | 802.11ay | July 2021 | 60 | Up to 8640 (8.64 GHz) |
Up to 303336[29] (303 Gbit/s) |
8 | OFDM, single carrier | 10 m (33 ft) | 100 m (328 ft) | |||
| Sub 1 GHz (IoT) | TVHT[30] | 802.11af | February 2014 | 0.054– 0.79 |
6, 7, 8 | Up to 568.9[31] | 4 | MIMO-OFDM | ? | ? | ||
| S1G[30] | 802.11ah | May 2017 | 0.7, 0.8, 0.9 |
1–16 | Up to 8.67[32] (@2 MHz) |
4 | ? | ? | ||||
| Light (Li-Fi) |
LC (VLC/OWC) |
802.11bb | December 2023 (est.) |
800–1000 nm | 20 | Up to 9.6 Gbit/s | — | O-OFDM | ? | ? | ||
(IrDA) |
802.11-1997 | June 1997 | 850–900 nm | ? | 1, 2 | — | ? | ? | ||||
| 802.11 Standard rollups | ||||||||||||
| 802.11-2007 (802.11ma) | March 2007 | 2.4, 5 | Up to 54 | DSSS, OFDM | ||||||||
| 802.11-2012 (802.11mb) | March 2012 | 2.4, 5 | Up to 150[D] | DSSS, OFDM | ||||||||
| 802.11-2016 (802.11mc) | December 2016 | 2.4, 5, 60 | Up to 866.7 or 6757[D] | DSSS, OFDM | ||||||||
| 802.11-2020 (802.11md) | December 2020 | 2.4, 5, 60 | Up to 866.7 or 6757[D] | DSSS, OFDM | ||||||||
| 802.11me | September 2024 (est.) |
2.4, 5, 6, 60 | Up to 9608 or 303336 | DSSS, OFDM | ||||||||
| ||||||||||||