Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
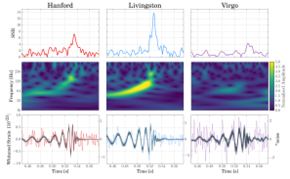 The signal of GW170814 measured by Hanford, Livingston and Virgo | |
| Right ascension | 3h 11m |
|---|---|
| Declination | −44° 57′ |
| Total energy output | ≈ 3 M☉ × c2 |
| Other designations | GW170814 |
| | |
GW170814 was a gravitational wave signal from two merging black holes, detected by the LIGO and Virgo observatories on 14 August 2017.[1] On 27 September 2017, the LIGO and Virgo collaborations announced the observation of the signal, the fourth confirmed event after GW150914, GW151226 and GW170104. It was the first binary black hole merger detected by LIGO and Virgo together.[2]

The signal was detected at 10:30:43 UTC. The Livingston detector was the first to receive the signal, followed by the Hanford detector 8 milliseconds later and Virgo received the signal 14 milliseconds after Livingston. The detection in all three detectors lead to a very accurate estimate of the position of the source, with a 90% credible region of just 60 deg2, a factor 20 times more accurate than before.[3]
Analysis indicated the signal resulted from the inspiral and merger of a pair of black holes (BBH) with 30.5+5.7
−3.0 and 25.3+2.8
−4.2 times the mass of the Sun, at a distance of 540+130
−210 megaparsecs (1.8+0.4
−0.7 billion light years) from Earth.[4] The resulting black hole had a mass of 53.2+3.2
−2.5 solar masses, 2.7+0.4
−0.3 solar masses having been radiated away as gravitational energy. The peak luminosity of GW170814 was 3.7+0.5
−0.5×1049 W.
General relativity predicts that gravitational waves have a tensor-like (spin-2) polarization. The detection in all three detectors led to strong experimental evidence for pure tensor polarization over pure scalar or pure vector polarizations.[2][5]