Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
A delta ray is a secondary electron with enough energy to escape a significant distance away from the primary radiation beam and produce further ionization.[1]: 25 The term is sometimes used to describe any recoil particle caused by secondary ionization. The term was coined by J. J. Thomson.
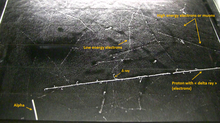
A delta ray is characterized by very fast electrons produced in quantity by alpha particles or other fast energetic charged particles knocking orbiting electrons out of atoms. Collectively, these electrons are defined as delta radiation when they have sufficient energy to ionize further atoms through subsequent interactions on their own. Delta rays appear as branches in the main track of a cloud chamber (See Figs. 1,2). These branches will appear nearer the start of the track of a heavy charged particle, where more energy is imparted to the ionized electrons.

Otherwise called a knock-on electron, the term "delta ray" is also used in high energy physics to describe single electrons in particle accelerators that are exhibiting characteristic deceleration. In a bubble chamber, electrons will lose their energy more quickly than other particles through Bremsstrahlung and will create a spiral track due to their small mass and the magnetic field. The Bremsstrahlung rate is proportional to the square of the acceleration of the electron.
An Epsilon ray or Epsilon radiation is a type of tertiary radiation.[2] Epsilon rays are a form of particle radiation and are composed of electrons. The term was coined by J. J. Thomson, but is very rarely used as of 2019.