Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
 | |
 The readable surface of a compact disc includes a spiral track wound tightly enough to cause light to diffract into a full visible spectrum. | |
| Media type | Optical disc |
|---|---|
| Encoding | Various |
| Capacity | Typically up to 700 MiB (up to 80 minutes audio), 800 MiB (also up to 90 minutes audio), 870 MiB (and up to 99 minutes audio) |
| Read mechanism | 780 nm wavelength (infrared) semiconductor laser (early players used helium–neon lasers),[1] |
| Write mechanism | 780 nm wavelength (infrared) semiconductor laser in recordable formats CD-R and CD-RW, stamped in read-only formats |
| Standard | Rainbow Books |
| Developed by | Philips, Sony |
| Dimensions | Diameter: 120 mm (4.7 in) Thickness: 1.2 mm (0.047 in) |
| Usage | Audio and data storage |
| Extended from | LaserDisc |
| Extended to | |
| Released |
|
| Optical discs |
|---|
The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was co-developed by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. It uses the Compact Disc Digital Audio format which typically provides 74 minutes of audio on a disc. In later years, the compact disc was adapted for non-audio computer data storage purposes as CD-ROM and its derivatives. First released in Japan in October 1982, the CD was the second optical disc technology to be invented, after the much larger LaserDisc (LD). By 2007, 200 billion CDs (including audio CDs, CD-ROMs and CD-Rs) had been sold worldwide.
Standard CDs have a diameter of 120 mm (4.7 in), and are designed to hold up to 74 minutes of uncompressed stereo digital audio or about 650 MiB (681,574,400 bytes) of data. Capacity is routinely extended to 80 minutes and 700 MiB (734,003,200 bytes), 90 minutes 800 MiB (838,860,800 bytes), or 99 minutes 870 MiB (912,261,120 bytes) by arranging data more closely on the same-sized disc. The Mini CD has various diameters ranging from 60 to 80 millimetres (2.4 to 3.1 in); they have been used for CD singles or delivering device drivers.
The CD gained rapid popularity in the 1990s, quickly outselling all other audio formats in the United States by 1991, ending the market dominance of the phonograph record and the cassette tape. By 2000, the CD accounted for 92.3% of the entire market share in regard to US music sales.[3] The CD is considered the last dominant audio format of the album era, as the rise of MP3, iTunes, cellular ringtones, and other downloadable music formats in the mid-2000s ended the decade-long dominance of the CD.[4]
The format was later adapted (as CD-ROM) for general purpose data storage and initially could hold much more data than a personal computer hard disk drive. Several other formats were further derived, both pre-pressed and blank user writable, including write-once audio and data storage (CD-R), rewritable media (CD-RW), Video CD (VCD), Super Video CD (SVCD), Photo CD, Picture CD, Compact Disc-Interactive (CD-i), Enhanced Music CD, and Super Audio CD (SACD) which may have a CD-DA layer.
The optophone, first presented in 1931, was an early device that used light for both recording and playback of sound signals on a transparent photograph.[5] More than thirty years later, American inventor James T. Russell has been credited with inventing the first system to record digital media on a photosensitive plate. Russell's patent application was filed in 1966, and he was granted a patent in 1970.[6] Following litigation, Sony and Philips licensed Russell's patents for recording in 1988.[7][8] It is debatable whether Russell's concepts, patents, and prototypes instigated and in some measure influenced the compact disc's design.[9]
The compact disc is an evolution of LaserDisc technology,[10] where a focused laser beam is used that enables the high information density required for high-quality digital audio signals. Unlike the prior art by Optophonie and James Russell, the information on the disc is read from a reflective layer using a laser as a light source through a protective substrate. Prototypes were developed by Philips and Sony independently in the late 1970s.[11] Although originally dismissed by Philips Research management as a trivial pursuit,[12] the CD became the primary focus for Philips as the LaserDisc format struggled.[13] In 1979, Sony and Philips set up a joint task force of engineers to design a new digital audio disc. After a year of experimentation and discussion, the Red Book CD-DA standard was published in 1980. After their commercial release in 1982, compact discs and their players were extremely popular. Despite costing up to $1,000, over 400,000 CD players were sold in the United States between 1983 and 1984.[14] By 1988, CD sales in the United States surpassed those of vinyl LPs, and, by 1992, CD sales surpassed those of prerecorded music-cassette tapes.[15][16] The success of the compact disc has been credited to the cooperation between Philips and Sony, which together agreed upon and developed compatible hardware. The unified design of the compact disc allowed consumers to purchase any disc or player from any company and allowed the CD to dominate the at-home music market unchallenged.[17]
In 1974, Lou Ottens, director of the audio division of Philips, started a small group to develop an analog optical audio disc with a diameter of 20 cm (7.9 in) and a sound quality superior to that of the vinyl record.[18] However, due to the unsatisfactory performance of the analog format, two Philips research engineers recommended a digital format in March 1974. In 1977, Philips then established a laboratory with the mission of creating a digital audio disc. The diameter of Philips's prototype compact disc was set at 11.5 cm (4.5 in), the diagonal of an audio cassette.[10][19]
Heitaro Nakajima, who developed an early digital audio recorder within Japan's national public broadcasting organization, NHK, in 1970, became general manager of Sony's audio department in 1971. In 1973, his team developed a digital PCM adaptor that made audio recordings using a Betamax video recorder. After this, in 1974 the leap to storing digital audio on an optical disc was easily made.[20] Sony first publicly demonstrated an optical digital audio disc in September 1976. A year later, in September 1977, Sony showed the press a 30 cm (12 in) disc that could play an hour of digital audio (44,100 Hz sampling rate and 16-bit resolution) using modified frequency modulation encoding.[21] In September 1978, the company demonstrated an optical digital audio disc with a 150-minute playing time, 44,056 Hz sampling rate, 16-bit linear resolution, and cross-interleaved Reed-Solomon coding (CIRC) error correction code—specifications similar to those later settled upon for the standard compact disc format in 1980. Technical details of Sony's digital audio disc were presented during the 62nd AES Convention, held on 13–16 March 1979, in Brussels.[22] Sony's AES technical paper was published on 1 March 1979. A week later, on 8 March, Philips publicly demonstrated a prototype of an optical digital audio disc at a press conference called "Philips Introduce Compact Disc"[23] in Eindhoven, Netherlands.[24] Sony executive Norio Ohga, later CEO and chairman of Sony, and Heitaro Nakajima were convinced of the format's commercial potential and pushed further development despite widespread skepticism.[25]

In 1979, Sony and Philips set up a joint task force of engineers to design a new digital audio disc. Led by engineers Kees Schouhamer Immink and Toshitada Doi, the research pushed forward laser and optical disc technology.[26] After a year of experimentation and discussion, the task force produced the Red Book CD-DA standard. First published in 1980, the standard was formally adopted by the IEC as an international standard in 1987, with various amendments becoming part of the standard in 1996.[citation needed]
Philips coined the term compact disc in line with another audio product, the Compact Cassette,[27] and contributed the general manufacturing process, based on video LaserDisc technology. Philips also contributed eight-to-fourteen modulation (EFM), while Sony contributed the error-correction method, CIRC, which offers resilience to defects such as scratches and fingerprints.
The Compact Disc Story,[28] told by a former member of the task force, gives background information on the many technical decisions made, including the choice of the sampling frequency, playing time, and disc diameter. The task force consisted of around 6 persons,[12][29] though according to Philips, the compact disc was "invented collectively by a large group of people working as a team".[30]
Early milestones in the launch and adoption of the format included:
The first artist to sell a million copies on CD was Dire Straits, with their 1985 album Brothers in Arms.[39] One of the first CD markets was devoted to reissuing popular music whose commercial potential was already proven. The first major artist to have their entire catalog converted to CD was David Bowie, whose first fourteen studio albums of (then) sixteen were made available by RCA Records in February 1985, along with four greatest hits albums; his fifteenth and sixteenth albums had already been issued on CD by EMI Records in 1983 and 1984, respectively.[40] On 26 February 1987, the first four UK albums by the Beatles were released in mono on compact disc.[41]
The growing acceptance of the CD in 1983 marks the beginning of the popular digital audio revolution.[42] It was enthusiastically received, especially in the early-adopting classical music and audiophile communities, and its handling quality received particular praise. As the price of players gradually came down, and with the introduction of the portable Discman, the CD began to gain popularity in the larger popular and rock music markets. With the rise in CD sales, pre-recorded cassette tape sales began to decline in the late 1980s; CD sales overtook cassette sales in the early 1990s.[citation needed][43] In 1988, 400 million CDs were manufactured by 50 pressing plants around the world.[44]

Early CD players employed binary-weighted digital-to-analog converters (DAC), which contained individual electrical components for each bit of the DAC.[45] Even when using high-precision components, this approach was prone to decoding errors.[clarification needed][45] Another issue was jitter, a time-related defect. Confronted with the instability of DACs, manufacturers initially turned to increasing the number of bits in the DAC and using several DACs per audio channel, averaging their output.[45] This increased the cost of CD players but did not solve the core problem.
A breakthrough in the late 1980s culminated in development of the 1-bit DAC, which converts high-resolution low-frequency digital input signal into a lower-resolution high-frequency signal that is mapped to voltages and then smoothed with an analog filter. The temporary use of a lower-resolution signal simplified circuit design and improved efficiency, which is why it became dominant in CD players starting from the early 1990s. Philips used a variation of this technique called pulse-density modulation (PDM),[46] while Matsushita (now Panasonic) chose pulse-width modulation (PWM), advertising it as MASH, which is an acronym derived from their patented Multi-stAge noiSe-sHaping PWM topology.[45]
The CD was primarily planned as the successor to the vinyl record for playing music, rather than as a data storage medium. However, CDs have grown to encompass other applications. In 1983, following the CD's introduction, Immink and Joseph Braat presented the first experiments with erasable compact discs during the 73rd AES Convention.[47] In June 1985, the computer-readable CD-ROM (read-only memory) and, in 1990, recordable CD-R discs were introduced.[a] Recordable CDs became an alternative to tape for recording and distributing music and could be duplicated without degradation in sound quality.
Other newer video formats such as DVD and Blu-ray use the same physical geometry as CD, and most DVD and Blu-ray players are backward compatible with audio CDs.
CD sales in the United States peaked by 2000.[48] By the early 2000s, the CD player had largely replaced the audio cassette player as standard equipment in new automobiles, with 2010 being the final model year for any car in the United States to have a factory-equipped cassette player.[49]
Two new formats were marketed in the 2000s designed as successors to the CD: the Super Audio CD (SACD) and DVD-Audio. However neither of these were adopted partly due to increased relevance of digital (virtual) music and the apparent lack of audible improvements in audio quality to most human ears.[50] These effectively extended the CD's longevity in the music market.[51]
With the advent and popularity of Internet-based distribution of files in lossy-compressed audio formats such as MP3, sales of CDs began to decline in the 2000s. For example, between 2000 and 2008, despite overall growth in music sales and one anomalous year of increase, major-label CD sales declined overall by 20%.[52] Despite rapidly declining sales year-over-year, the pervasiveness of the technology lingered for a time, with companies placing CDs in pharmacies, supermarkets, and filling station convenience stores to target buyers less likely to be able to use Internet-based distribution.[13] In 2012, CDs and DVDs made up only 34% of music sales in the United States.[53] By 2015, only 24% of music in the United States was purchased on physical media, two thirds of this consisting of CDs;[54] however, in the same year in Japan, over 80% of music was bought on CDs and other physical formats.[55] In 2018, U.S. CD sales were 52 million units—less than 6% of the peak sales volume in 2000.[48] In the UK, 32 million units were sold, almost 100 million fewer than in 2008.[56] In 2018, Best Buy announced plans to decrease their focus on CD sales, however, while continuing to sell records, sales of which are growing during the vinyl revival.[57][58][59]
During the 2010s, the increasing popularity of solid-state media and music streaming services caused automakers to remove automotive CD players in favor of minijack auxiliary inputs, wired connections to USB devices and wireless Bluetooth connections.[60] Automakers viewed CD players as using up valuable space and taking up weight which could be reallocated to more popular features, like large touchscreens.[61] By 2021, only Lexus and General Motors were still including CD players as standard equipment with certain vehicles.[61]
CDs continued to be strong in some markets such as Japan where 132 million units were produced in 2019.[62]
The decline in CD sales has slowed in recent years; in 2021, CD sales increased in the US for the first time since 2004,[63] with Axios citing its rise to "young people who are finding they like hard copies of music in the digital age".[64] It came at the same time as both vinyl and cassette reached sales levels not seen in 30 years.[65] The RIAA reported that CD revenue made a dip in 2022, before increasing again in 2023 and overtook downloading for the first time in over a decade.[66]
In the US, 33.4 million CD albums were sold in the year 2022.[67] In France in 2023, 10.5 million CDs were sold, almost double that of vinyl, but both of them represented generated 12% each of the French music industry revenues.[68]
Sony and Philips received praise for the development of the compact disc from professional organizations. These awards include:

A CD is made from 1.2-millimetre (0.047 in) thick, polycarbonate plastic, and weighs 14–33 grams.[71] From the center outward, components are: the center spindle hole (15 mm), the first-transition area (clamping ring), the clamping area (stacking ring), the second-transition area (mirror band), the program (data) area, and the rim. The inner program area occupies a radius from 25 to 58 mm.
A thin layer of aluminum or, more rarely, gold is applied to the surface, making it reflective. The metal is protected by a film of lacquer normally spin coated directly on the reflective layer. The label is printed on the lacquer layer, usually by screen printing or offset printing.
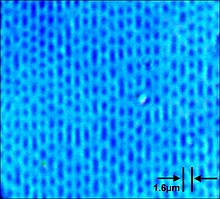
CD data is represented as tiny indentations known as pits, encoded in a spiral track molded into the top of the polycarbonate layer. The areas between pits are known as lands. Each pit is approximately 100 nm deep by 500 nm wide, and varies from 850 nm to 3.5 μm in length.[72] The distance between the windings (the pitch) is 1.6 μm (measured center-to-center, not between the edges).[73][74][75]
When playing an audio CD, a motor within the CD player spins the disc to a scanning velocity of 1.2–1.4 m/s (constant linear velocity, CLV)—equivalent to approximately 500 RPM at the inside of the disc, and approximately 200 RPM at the outside edge.[76] The track on the CD begins at the inside and spirals outward so a disc played from beginning to end slows its rotation rate during playback.

The program area is 86.05 cm2 and the length of the recordable spiral is 86.05 cm2 / 1.6 μm = 5.38 km. With a scanning speed of 1.2 m/s, the playing time is 74 minutes or 650 MiB of data on a CD-ROM. A disc with data packed slightly more densely is tolerated by most players (though some old ones fail). Using a linear velocity of 1.2 m/s and a narrower track pitch of 1.5 μm increases the playing time to 80 minutes, and data capacity to 700 MiB. Even denser tracks are possible, with semi-standard 90 minute/800 MiB discs having 1.33 μm, and 99 minute/870 MiB having 1.26 μm,[77] but compatibility suffers as density increases.
A CD is read by focusing a 780 nm wavelength (near infrared) semiconductor laser through the bottom of the polycarbonate layer. The change in height between pits and lands results in a difference in the way the light is reflected. Because the pits are indented into the top layer of the disc and are read through the transparent polycarbonate base, the pits form bumps when read.[78] The laser hits the disc, casting a circle of light wider than the modulated spiral track reflecting partially from the lands and partially from the top of any bumps where they are present. As the laser passes over a pit (bump), its height means that the round trip path of the light reflected from its peak is 1/2 wavelength out of phase with the light reflected from the land around it. This is because the height of a bump is around 1/4 of the wavelength of the light used, so the light falls 1/4 out of phase before reflection and another 1/4 wavelength out of phase after reflection. This causes partial cancellation of the laser's reflection from the surface. By measuring the reflected intensity change with a photodiode, a modulated signal is read back from the disc.[76]
To accommodate the spiral pattern of data, the laser is placed on a mobile mechanism within the disc tray of any CD player. This mechanism typically takes the form of a sled that moves along a rail. The sled can be driven by a worm gear or linear motor. Where a worm gear is used, a second shorter-throw linear motor, in the form of a coil and magnet, makes fine position adjustments to track eccentricities in the disk at high speed. Some CD drives (particularly those manufactured by Philips during the 1980s and early 1990s) use a swing arm similar to that seen on a gramophone.

The pits and lands do not directly represent the 0s and 1s of binary data. Instead, non-return-to-zero, inverted encoding is used: a change from either pit to land or land to pit indicates a 1, while no change indicates a series of 0s. There must be at least two, and no more than ten 0s between each 1, which is defined by the length of the pit. This, in turn, is decoded by reversing the eight-to-fourteen modulation used in mastering the disc, and then reversing the cross-interleaved Reed–Solomon coding, finally revealing the raw data stored on the disc. These encoding techniques (defined in the Red Book) were originally designed for CD Digital Audio, but they later became a standard for almost all CD formats (such as CD-ROM).
CDs are susceptible to damage during handling and from environmental exposure. Pits are much closer to the label side of a disc, enabling defects and contaminants on the clear side to be out of focus during playback. Consequently, CDs are more likely to suffer damage on the label side of the disc. Scratches on the clear side can be repaired by refilling them with similar refractive plastic or by careful polishing. The edges of CDs are sometimes incompletely sealed, allowing gases and liquids to enter the CD and corrode the metal reflective layer and/or interfere with the focus of the laser on the pits, a condition known as disc rot.[79] The fungus Geotrichum candidum has been found—under conditions of high heat and humidity—to consume the polycarbonate plastic and aluminium found in CDs.[80][81]
The data integrity of compact discs can be measured using surface error scanning, which can measure the rates of different types of data errors, known as C1, C2, CU and extended (finer-grain) error measurements known as E11, E12, E21, E22, E31 and E32, of which higher rates indicate a possibly damaged or unclean data surface, low media quality, deteriorating media and recordable media written to by a malfunctioning CD writer.
Error scanning can reliably predict data losses caused by media deterioration. Support of error scanning differs between vendors and models of optical disc drives, and extended error scanning (known as "advanced error scanning" in Nero DiscSpeed) has only been available on Plextor and some BenQ optical drives so far, as of 2020.[82][83]

The digital data on a CD begins at the center of the disc and proceeds toward the edge, which allows adaptation to the different sizes available. Standard CDs are available in two sizes. By far, the most common is 120 millimetres (4.7 in) in diameter, with a 74-, 80, 90, or 99-minute audio capacity and a 650, 700, 800, or 870 MiB (737,280,000-byte) data capacity. Discs are 1.2 millimetres (0.047 in) thick, with a 15 millimetres (0.59 in) center hole. The size of the hole was chosen by Joop Sinjou and based on a Dutch 10-cent coin: a dubbeltje.[84] Philips/Sony patented the physical dimensions.[85]
The official Philips history says the capacity was specified by Sony executive Norio Ohga to be able to contain the entirety of Beethoven's Ninth Symphony on one disc.[86] This is a myth[87] according to Kees Immink, as the EFM code format had not yet been decided in December 1979, when the 120 mm size was adopted. The adoption of EFM in June 1980 allowed 30 percent more playing time that would have resulted in 97 minutes for 120 mm diameter or 74 minutes for a disc as small as 100 millimetres (3.9 in). Instead, the information density was lowered by 30 percent to keep the playing time at 74 minutes.[88][89] The 120 mm diameter has been adopted by subsequent formats, including Super Audio CD, DVD, HD DVD, and Blu-ray Disc. The 80-millimetre (3.1 in) diameter discs ("Mini CDs") can hold up to 24 minutes of music or 210 MiB.
| Physical size | Audio capacity | CD-ROM data capacity | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 120 mm | 74–80 min | 650–700 MB | Standard size |
| 80 mm | 21–24 min | 185–210 MB | Mini-CD size |
| 80×54 mm – 80×64 mm | ~6 min | 10–65 MB | "Business card" size |


The logical format of an audio CD (officially Compact Disc Digital Audio or CD-DA) is described in a document produced in 1980 by the format's joint creators, Sony and Philips.[90] The document is known colloquially as the Red Book CD-DA after the color of its cover. The format is a two-channel 16-bit PCM encoding at a 44.1 kHz sampling rate per channel. Four-channel sound was to be an allowable option within the Red Book format, but has never been implemented. Monaural audio has no existing standard on a Red Book CD; thus, the mono source material is usually presented as two identical channels in a standard Red Book stereo track (i.e., mirrored mono); an MP3 CD, can have audio file formats with mono sound.
CD-Text is an extension of the Red Book specification for an audio CD that allows for the storage of additional text information (e.g., album name, song name, artist) on a standards-compliant audio CD. The information is stored either in the lead-in area of the CD, where there are roughly five kilobytes of space available or in the subcode channels R to W on the disc, which can store about 31 megabytes.
Compact Disc + Graphics is a special audio compact disc that contains graphics data in addition to the audio data on the disc. The disc can be played on a regular audio CD player, but when played on a special CD+G player, it can output a graphics signal (typically, the CD+G player is hooked up to a television set or a computer monitor); these graphics are almost exclusively used to display lyrics on a television set for karaoke performers to sing along with. The CD+G format takes advantage of the channels R through W. These six bits store the graphics information.
CD + Extended Graphics (CD+EG, also known as CD+XG) is an improved variant of the Compact Disc + Graphics (CD+G) format. Like CD+G, CD+EG uses basic CD-ROM features to display text and video information in addition to the music being played. This extra data is stored in subcode channels R-W. Very few CD+EG discs have been published.
Super Audio CD (SACD) is a high-resolution, read-only optical audio disc format that was designed to provide higher-fidelity digital audio reproduction than the Red Book. Introduced in 1999, it was developed by Sony and Philips, the same companies that created the Red Book. SACD was in a format war with DVD-Audio, but neither has replaced audio CDs. The SACD standard is referred to as the Scarlet Book standard.
Titles in the SACD format can be issued as hybrid discs; these discs contain the SACD audio stream as well as a standard audio CD layer which is playable in standard CD players, thus making them backward compatible.
CD-MIDI is a format used to store music-performance data, which upon playback is performed by electronic instruments that synthesize the audio. Hence, unlike the original Red Book CD-DA, these recordings are not digitally sampled audio recordings. The CD-MIDI format is defined as an extension of the original Red Book.
For the first few years of its existence, the CD was a medium used purely for audio. In 1988, the Yellow Book CD-ROM standard was established by Sony and Philips, which defined a non-volatile optical data computer data storage medium using the same physical format as audio compact discs, readable by a computer with a CD-ROM drive.
Video CD (VCD, View CD, and Compact Disc digital video) is a standard digital format for storing video media on a CD. VCDs are playable in dedicated VCD players, most modern DVD-Video players, personal computers, and some video game consoles. The VCD standard was created in 1993 by Sony, Philips, Matsushita, and JVC and is referred to as the White Book standard.
Overall picture quality is intended to be comparable to VHS video. Poorly compressed VCD video can sometimes be of lower quality than VHS video, but VCD exhibits block artifacts rather than analog noise and does not deteriorate further with each use. 352×240 (or SIF) resolution was chosen because it is half the vertical and half the horizontal resolution of the NTSC video. 352×288 is a similarly one-quarter PAL/SECAM resolution. This approximates the (overall) resolution of an analog VHS tape, which, although it has double the number of (vertical) scan lines, has a much lower horizontal resolution.
Super Video CD (Super Video Compact Disc or SVCD) is a format used for storing video media on standard compact discs. SVCD was intended as a successor to VCD and an alternative to DVD-Video and falls somewhere between both in terms of technical capability and picture quality.
SVCD has two-thirds the resolution of DVD, and over 2.7 times the resolution of VCD. One CD-R disc can hold up to 60 minutes of standard-quality SVCD-format video. While no specific limit on SVCD video length is mandated by the specification, one must lower the video bit rate, and therefore quality, to accommodate very long videos. It is usually difficult to fit much more than 100 minutes of video onto one SVCD without incurring a significant quality loss, and many hardware players are unable to play a video with an instantaneous bit rate lower than 300 to 600 kilobits per second.
Photo CD is a system designed by Kodak for digitizing and storing photos on a CD. Launched in 1992, the discs were designed to hold nearly 100 high-quality images, scanned prints, and slides using special proprietary encoding. Photo CDs are defined in the Beige Book and conform to the CD-ROM XA and CD-i Bridge specifications as well. They are intended to play on CD-i players, Photo CD players, and any computer with suitable software (irrespective of operating system). The images can also be printed out on photographic paper with a special Kodak machine. This format is not to be confused with Kodak Picture CD, which is a consumer product in CD-ROM format.
The Philips Green Book specifies a standard for interactive multimedia compact discs designed for CD-i players (1993). CD-i discs can contain audio tracks that can be played on regular CD players, but CD-i discs are not compatible with most CD-ROM drives and software. The CD-i Ready specification was later created to improve compatibility with audio CD players, and the CD-i Bridge specification was added to create CD-i-compatible discs that can be accessed by regular CD-ROM drives.
Philips defined a format similar to CD-i called CD-i Ready, which puts CD-i software and data into the pregap of track 1. This format was supposed to be more compatible with older audio CD players.
Enhanced Music CD, also known as CD Extra or CD Plus, is a format that combines audio tracks and data tracks on the same disc by putting audio tracks in a first session and data in a second session. It was developed by Philips and Sony, and it is defined in the Blue Book.
VinylDisc is the hybrid of a standard audio CD and the vinyl record. The vinyl layer on the disc's label side can hold approximately three minutes of music.

In 1995, material costs were 30 cents for the jewel case and 10 to 15 cents for the CD. The wholesale cost of CDs was $0.75 to $1.15, while the typical retail price of a prerecorded music CD was $16.98.[91] On average, the store received 35 percent of the retail price, the record company 27 percent, the artist 16 percent, the manufacturer 13 percent, and the distributor 9 percent.[91] When 8-track cartridges, compact cassettes, and CDs were introduced, each was marketed at a higher price than the format they succeeded, even though the cost to produce the media was reduced. This was done because the perceived value increased. This continued from phonograph records to CDs, but was broken when Apple marketed MP3s for $0.99, and albums for $9.99. The incremental cost, though, to produce an MP3 is negligible.[92]

Recordable Compact Discs, CD-Rs, are injection-molded with a "blank" data spiral. A photosensitive dye is then applied, after which the discs are metalized and lacquer-coated. The write laser of the CD recorder changes the color of the dye to allow the read laser of a standard CD player to see the data, just as it would with a standard stamped disc. The resulting discs can be read by most CD-ROM drives and played in most audio CD players. CD-Rs follow the Orange Book standard.
CD-R recordings are designed to be permanent. Over time, the dye's physical characteristics may change causing read errors and data loss until the reading device cannot recover with error correction methods. Errors can be predicted using surface error scanning. The design life is from 20 to 100 years, depending on the quality of the discs, the quality of the writing drive, and storage conditions.[93] Testing has demonstrated such degradation of some discs in as little as 18 months under normal storage conditions.[94][95] This failure is known as disc rot, for which there are several, mostly environmental, reasons.[96]
The recordable audio CD is designed to be used in a consumer audio CD recorder. These consumer audio CD recorders use SCMS (Serial Copy Management System), an early form of digital rights management (DRM), to conform to the AHRA (Audio Home Recording Act). The Recordable Audio CD is typically somewhat more expensive than CD-R due to lower production volume and a 3 percent AHRA royalty used to compensate the music industry for the making of a copy.[97]
High-capacity recordable CD is a higher-density recording format that can hold 20% more data than conventional discs.[98] The higher capacity is incompatible with some recorders and recording software.[99]
CD-RW is a re-recordable medium that uses a metallic alloy instead of a dye. The write laser, in this case, is used to heat and alter the properties (amorphous vs. crystalline) of the alloy, and hence change its reflectivity. A CD-RW does not have as great a difference in reflectivity as a pressed CD or a CD-R, and so many earlier CD audio players cannot read CD-RW discs, although most later CD audio players and stand-alone DVD players can. CD-RWs follow the Orange Book standard.
The ReWritable Audio CD is designed to be used in a consumer audio CD recorder, which will not (without modification) accept standard CD-RW discs. These consumer audio CD recorders use the Serial Copy Management System (SCMS), an early form of digital rights management (DRM), to conform to the United States' Audio Home Recording Act (AHRA). The ReWritable Audio CD is typically somewhat more expensive than CD-R due to (a) lower volume and (b) a 3 percent AHRA royalty used to compensate the music industry for the making of a copy.[97]
The Red Book audio specification, except for a simple "anti-copy" statement in the subcode, does not include any copy protection mechanism. Known at least as early as 2001,[100] attempts were made by record companies to market "copy-protected" non-standard compact discs, which cannot be ripped, or copied, to hard drives or easily converted to other formats (like FLAC, MP3 or Vorbis). One major drawback to these copy-protected discs is that most will not play on either computer CD-ROM drives or some standalone CD players that use CD-ROM mechanisms. Philips has stated that such discs are not permitted to bear the trademarked Compact Disc Digital Audio logo because they violate the Red Book specifications. Numerous copy-protection systems have been countered by readily available, often free, software, or even by simply turning off automatic AutoPlay to prevent the running of the DRM executable program.
The first test CD was Richard Strauss's Eine Alpensinfonie, and the first CD actually pressed at a factory was ABBA's The Visitors, but that disc wasn't released commercially until later.
Small quantities of 90-minute and 99-minute blanks have appeared [...] Indications are that many recorders and some software don't work with the longer discs.