Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
| Boreal woodland caribou | |
|---|---|

| |
| Boreal woodland caribou in the southern Selkirk Mountains of Idaho in 2007 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Cervidae |
| Subfamily: | Capreolinae |
| Genus: | Rangifer |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | R. t. caribou
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Rangifer tarandus caribou (Gmelin, 1788)
| |
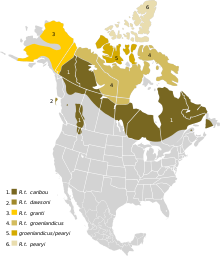
| |
| Approximate range of boreal woodland caribou in 2003. Overlap with other subspecies of caribou is possible for contiguous range. 1. Rangifer tarandus caribou, which is subdivided into ecotypes: woodland (boreal), woodland (migratory) and woodland (mountain), 2. R. t. dawsoni (extinct 1908), 3. R. t. groenlandicus, 4. R. t. groenlandicus, 5. R. t. groenlandicus, 6. R. t. pearyi | |
The boreal woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou; but subject to a recent taxonomic revision. See Reindeer: Taxonomy), also known as Eastern woodland caribou, boreal forest caribou and forest-dwelling caribou, is a North American subspecies of reindeer (or caribou in North America) found primarily in Canada with small populations in the United States. Unlike the Porcupine caribou and barren-ground caribou, boreal woodland caribou are primarily (but not always) sedentary.[Notes 1][2][3][4][5]
The boreal woodland caribou is the third largest of the caribou ecotypes [6][7] after the Selkirk Mountains caribou and Osborn's caribou (see Reindeer: Taxonomy) and is darker[8] in color than the barren-ground caribou.[9] Valerius Geist, specialist on large North American mammals, described the "true" woodland caribou as "the uniformly dark, small-maned type with the frontally emphasized, flat-beamed antlers" which is "scattered thinly along the southern rim of North American caribou distribution". Geist asserted that "the true woodland caribou is very rare, in very great difficulties and requires the most urgent of attention", but suggests that this urgency is compromised by the inclusion of the Newfoundland caribou, the Labrador caribou, and Osborn's caribou in the Rangifer tarandus caribou subspecies. In Geist's opinion, the inclusion of these additional populations obscures the precarious position of the "true" woodland caribou.[8] A recent revision,[10] recognizing Labrador and Newfoundland caribou as distinct subspecies of woodland caribou, partially rectifies this problem.
They prefer lichen-rich, mature forests,[11] and mainly live in marshes, bogs, lakes and river regions.[12][13]
The historic range of the woodland caribou covered over half of present-day Canada,[4] stretching from Yukon to Newfoundland and Labrador. The national meta-population of this sedentary boreal ecotype spans the boreal forest from the Northwest Territories to Labrador (but not Newfoundland). Their former range stretched south into the contiguous United States. By 2019, the last individual in the Lower 48 (a female) was captured and taken to a rehab center in British Columbia, thus marking the extirpation of the caribou in the contiguous U.S.[14]
The boreal woodland caribou was designated as Threatened in 2002 by the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada (COSEWIC).[15] Environment Canada reported in 2011 that there were approximately 34,000 boreal woodland caribou in 51 ranges remaining in Canada.(Environment Canada, 2011b).[16] In a joint report by the Canadian Parks and Wilderness Society (CPAWS) and the David Suzuki Foundation, on the status of boreal woodland caribou, it was claimed that "the biggest risk to caribou is industrial development, which fragments their habitat and exposes them to greater predation. Scientists consider only 30% (17 of 57) of Canada’s boreal woodland caribou populations to be self-sustaining."[3][4] Additionally, it was observed that the caribou “… are extremely sensitive to both natural (such as forest fires) and human disturbances, and to habitat damage and fragmentation brought about by resource exploration, road building, and other human activities. New forest growth (following destruction of vegetation) provides habitat and food for other ungulates, which in turn attracts more predators, putting pressure on woodland caribou."[11]
Compared to barren-ground caribou of mainland Canada and Alaska (see Barren-ground caribou), boreal woodland caribou do not form large aggregations and are more dispersed, particularly at calving time. Their seasonal movements are not as extensive.[17] Mallory and Hillis explained how, "In North America, populations of the woodland caribou subspecies typically form small, isolated herds in winter, but are relatively sedentary, and migrate only short distances (50 – 150 km) during the rest of the year."[18]
See Evolution in main page, Reindeer. Following are excerpts relating to boreal woodland caribou.
Reindeer originated in a Late Pliocene North American-Beringian radiation of New World deer [Geist 1998). A frontoparietal skull fragment of Rangifer sp. from the Early Pleistocene of Omsk, Russia dates back to 2.1-1.8 Ma and suggests northern Eurasia as a center of reindeer origin (Bondarev et al. 2017).[19] Its pedicles (antler bases), unlike modern reindeer, are inclined backward and set parallel to each other, demonstrating the primitive morphology for archaic cervids. The oldest North American Rangifer fossil is from the Yukon, 1.6 million years before present (BP).[20]
Rangifer “evolved as a mountain deer, ...exploiting the subalpine and alpine meadows...”.[21] Rangifer originated in the Early Pleistocene, a 2+ million-year period of multiple glacier advances and retreats. Several named Rangifer fossils in Eurasia and North America predate the evolution of modern tundra reindeer.[22]
Archaeologists distinguish “modern” tundra reindeer and barren-ground caribou from primitive forms — living and extinct — that did not have adaptations to extreme cold and to long-distance migration.[22] They include a broad, high muzzle to increase the volume of the nasal cavity to warm and moisten the air before it enters the throat and lungs, bez tines set close to the brow tines, distinctive coat patterns, short legs and other adaptations for running long distances, and multiple behaviors suited to tundra, but not to forest (such as synchronized calving and aggregation during rutting and post-calving). As well, many genes, including those for vitamin D metabolism, fat metabolism, retinal development, circadian rhythm, and tolerance to cold temperatures, are found in tundra caribou that are lacking or rudimentary in forest types. For this reason, forest-adapted reindeer and caribou could not survive in tundra or polar deserts. Genetic research confirms this, documenting almost no introgression (interbreeding) of woodland caribou into barren-ground caribou and very few the other way. This is evidence of reproductive isolation, a hallmark of species definitions.
In North America, DNA analysis shows that woodland caribou (originally Cervus tarandus caribou Gmelin 1788) diverged from primitive ancestors of tundra/barren-ground caribou not during the last glacial maximum, 26,000–19,000 years ago, as previously assumed, but in the Middle Pleistocene around 357,000 years ago.[23][24] At that time, modern tundra caribou had not even evolved. Woodland caribou are likely more related to extinct forest caribou subspecies than to barren-ground caribou. For example, the extinct caribou Torontoceros [Rangifer] hypogaeus, had features (robust and short pedicles, smooth antler surface, and high position of second tine) that relate it to forest caribou.[25] For this reason (in addition to molecular data showing lack of shared haplotypes and great genetic distance, as well as morphological and ecological differences) woodland caribou cannot be conspecific with barren-ground caribou because they do not share a direct common ancestor.
Molecular data also revealed that the four western Canadian montane ecotypes shared a common ancestor with modern barren-ground/tundra reindeer and caribou, but distantly, having diverged 120,000–130,000 years ago.[24] They are subspecies of the Arctic caribou (R. arcticus).
The name caribou was probably derived from the Mi'kmaq word xalibu or qalipu meaning "the one who paws".
The caribou design on the Royal Canadian Mint quarter was first used in 1937.[26]
The boreal woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou; but subject to a recent taxonomic revision. See Reindeer: Taxonomy) is also referred to as the woodland caribou, woodland caribou (boreal group) and forest-dwelling caribou.[27][28][a]
The Mi'kmaq people referred to caribou as xalibu or qalipu which means "the one who paws."[9] The word "caribous" was first published in print in the 1610 publication on the history of New France by Marc Lescarbot. Lescarbot partially based his writing on his expedition to 1606–1607 to Acadia where he encountered the Mi'kmaq people.[29] Silas Tertius Rand included the term kaleboo in his Mi'kmaq-English Dictionary in 1888.[30]
According to the 2019 Species at Risk Act (SARA), while caribou and reindeer were the same species — Rangifer tarandus — there are differences. The term "Caribou" refers to the "various subspecies present in North America" and the term "reindeer" is used to describe the "domesticated, semi-domesticated or wild subspecies found in Eurasia."[31][32][b] Some reindeer have been introduced to North America.[32] Woodland caribou, a rather large subspecies, is a medium-sized ungulate which inhabits boreal and subarctic environments and exhibits "tremendous variation in ecology, genetics, behavior and morphology." A distinctive characteristic of all caribou is large crescent-shaped hooves that change shape with the season and that are adapted to walking in snow-covered and soft ground such as swamps and peat lands and assist in digging through snow to forage on lichens and other ground vegetation.[12][33] The subspecies ecotype, boreal woodland caribou, have a shoulder height of approximately 1.0-1.2 m shoulder height and weigh 110–210 kg (242–462 lbs).[33]
Both male and female boreal woodland caribou have antlers[12] during part of the year, although some females may have only one antler or no antlers at all (Boreal Caribou ATK Reports, 2010–2011).[33] On the males these grow so quickly each year that velvety lumps in March can become a rack measuring more than a metre in length by August. Antlers of boreal woodland caribou are flattened, compact, and relatively dense.[34] Boreal woodland caribou antlers are thicker and broader than those of the barren-ground caribou and their legs and heads are longer.[34]
The boreal woodland caribou is well-adapted to cold environments, with a compact body covered with a thick and long coat (thicker in winter than in summer).[12] They have a large blunt muzzle, short wide ears and a small tail. Adults have a brown to dark-brown coat in summer,[12] becoming greyer in winter.[12] Adults have a distinctive creamy-white neck, mane, shoulder stripe, underbelly, underside of the tail and patch above each hoof.[35](Boreal Caribou ATK Reports, 2010–2011)[36]

Female boreal woodland caribou reach maturity at 16 months, and males at 18–20. Males usually do not breed before reaching three or four years of age, due to the hierarchical nature of the herd and competition with older males. Their reproduction rate is low. Breeding occurs at the end of September and the beginning of October. Calves are born in mid-June.[12] Precise dates may vary based on geographical region. For conservation and herd management purposes, migratory herds are often defined in terms of female natal philopatry or natal homing – the tendency to return to natal calving areas.[37] Female boreal woodland caribou and their newborn calves are more vulnerable to predation than migratory caribou, as they often calve separate from the rest of the herd and remain solitary until mid-winter.[18]
Previous classifications of Rangifer tarandus, either with prevailing taxonomy on subspecies, designations based on ecotypes, or natural population groupings, failed to capture "the variability of caribou across their range in Canada" needed for effective species conservation and management.[38] "Across the range of a species, individuals may display considerable morphological, genetic, and behavioral variability reflective of both plasticity and adaptation to local environments."[39] COSEWIC developed Designated Unit (DU) attribution to add to classifications already in use.[38] The recent revision[10] is consistent with COSEWIC's designations and gives them Latin names according to international rules of zoological nomenclature.
Further information can be found in Reindeer: Taxonomy.
Until 1919, taxonomists had named 13 species of caribou in North America. As definitions of "species" evolved, taxonomists began to rein in this excess, for example, bringing the four western montane ecotypes under Arctic caribou, R. arcticus Richardson 1829, as subspecies.[40][41] By 1949, when Rudolph M. Anderson published the first compendium of Canadian mammals[42] (Anderson knew caribou: he had led biological expeditions from Point Barrow, Alaska to the Coronation Gulf in 1908-1912 and 1913-1916 and was then Chief of the Biology Division of the Canadian Natural History Museum), the woodland caribou was one of just four recognized species: Arctic caribou (R. arcticus), Peary caribou (R. pearyi), Ungava caribou (R. caboti), and Woodland caribou (R. caribou). Anderson left the Newfoundland caribou as a subspecies of woodland caribou, R. caribou terranovae.
By mid-century, the taxonomic pendulum was swinging the other way. Ellerman and Morrison-Scott had brought all reindeer and caribou in the world under one species, Rangifer tarandus. In 1961, A. W. F. "Frank" Banfield, who had succeeded Anderson as Chief of the CMNH Biology Division, published a revision of the genus Rangifer that was widely rejected by other caribou specialists. He reduced the number of living subspecies in Canada to two, renaming barren-ground caribou as R. t. groenlandicus and woodland caribou as R. t. caribou. McTaggart-Cowan published a scathing review.[43] Most other mammalogists accepted Banfield's classification for the species, R. tarandus, but continued to recognize the subspecies Labrador (Ungava) caribou (R. t. caboti), barren-ground caribou (R. t. groenlandicus), Newfoundland caribou (R. t. terranovae), Peary caribou (R. t. pearyi), and Osborn's caribou (R. t. osborni).[44][21][45][46][47][48] A recent revision [10] returns woodland caribou to species status with subspecies R. caribou terranovae, R. c. caboti and the nominate subspecies R. c. caribou.
Caribou herds are classified by ecotype depending on several behavioral factors – predominant habitat use (northern, tundra, mountain, forest, boreal forest, forest-dwelling), spacing (dispersed or aggregated) and migration patterns (sedentary or migratory). Caribou herds can be classified as a northern or mountain woodland ecotype.[49][50]
In eastern North America caribou are classified into three ecotypes – "the mountain caribou which is found south of the St. Lawrence River, the barren-ground caribou which calves in the tundra, and in between, the forest-dwelling ecotype which lives all year long in the boreal forest. In west-central Alberta there are two ecotypes – boreal and mountain. In Québec there are three ecotypes with specific habitats and behavior – migratory barren-ground ecotype, the mountain ecotype and the forest-dwelling ecotype (boreal woodland caribou). In British Columbia caribou are classified into three ecotypes – Mountain, Northern, and Boreal. In Ontario caribou are classified into two ecotypes – forest-dwelling woodland caribou and forest-tundra woodland caribou.[51] In Newfoundland and Labrador, woodland caribou are classified as part of the boreal population of caribou, which is subdivided into two ecotypes: the migratory forest-tundra and the sedentary forest-dwelling.[52] In the Northwest Territories, the Canadian Parks and Wilderness Society identified five types of caribou – boreal woodland caribou, northern mountain woodland caribou, barren-ground caribou, Peary caribou and the Dolphin-Union caribou herd. "The Boreal woodland caribou live in the forests east of the Mackenzie Mountains and tend to live in small groups. They prefer to stay within the forest for most of the year and do not migrate."[11] Ecotypes are useful descriptors in that they categorize populations by habitat on a broad scale, but they cannot substitute for taxonomic distinctions.[53]
In 2012 Environment Canada identified 51 Rangifer tarandus caribou (boreal woodland caribou) or boreal ecotype of forest-dwelling woodland caribou ranges in Canada.[54][Notes 2][54]
The northernmost range of boreal woodland caribou in Canada is in the Mackenzie River Delta area, the Northwest Territories.[55] In 2000, in the Northwest Territories, boreal woodland caribou had a very large range and the population was assessed and was not considered to be at risk.[12] The population is identified as NT1 for conservation purposes.[56] Caribou geneticists recently discovered that the "woodland" caribou between the Mackenzie River and Great Bear Lake were not genetically members of boreal woodland caribou (R. c. caribou); instead, they are of Beringian-Eurasian Lineage, distantly related to Arctic caribou (R. arcticus) as per the 2022 revision of the genus, and the best model showed that they likely descended from Osborn's caribou (R. a. osborni) and adopted woodland caribou-like behaviors and ecology.[57]
The southernmost populations of the boreal woodland caribou are isolated populations on Lake Superior in Ontario, Canada such as the Slate Islands and Michipicoten Island.
The Species at Risk Committee's (SARC) assessed the biological status of the boreal woodland caribou (formerly Rangifer tarandus caribou) in the NWT as Threatened, in their completed assessment and status report dated 5 December 2012, submitted in compliance with the Species at Risk (NWT) Act. The SARC 2012 report provided the following reasons for its assessment:[58]
"Boreal caribou need large tracts of undisturbed habitat so they can spread out to minimize predation risk. This adaptation results in naturally low densities across a large area, making them more vulnerable to systematic habitat fragmentation. Population size is small: about 5,300 mature individuals, 6,500 total population. While there is uncertainty in the estimate (e.g. in the eastern Sahtu region), it is unlikely the total population size is larger than 10,000 in the NWT. Currently, there is variation across the NWT in rates and population declines in parts of the southern NWT where the majority of boreal caribou occur. Current and future threats leading to habitat fragmentation are expected to increase. A continuing decline in the amount of secure habitat and population size is projected."
— SARC 2012
Based on this 2012 SARC report, the NWT Conference of Management Authorities (CMA) undertook further studies and in October 2013, reached a consensus to add boreal woodland caribou to the Northwest Territories List of Species at Risk as a threatened species.[59]
Management authorities include NWT Conference of Management Authorities (CMA) for boreal woodland caribou are the Government of the NWT, the Tłįchǫ Government, the Wildlife Management Advisory Council (NWT), the Gwich'in Renewable Resources Board, the Sahtu Renewable Resources Board and the Wek'eezhii Renewable Resources Board.[59]
There is a stable population of boreal woodland caribou throughout a large portion of the Gwich’in Settlement Area that are an important food source for the Gwich’in, although they harvest them less than other caribou. Gwich’in living in Inuvik, Aklavik, Fort McPherson, and Tsiigehtchic harvest boreal woodland caribou, but not as much as other caribou.[7] The Gwich'in prefer to hunt the Porcupine caribou or the barren-ground Bluenose caribou herd, who travel in large herds, when they are available. Many hunters claimed that boreal woodland caribou that form very small groups, are wilder and are both hard to see and hard to hunt. They are very smart, cunning and elusive. However, at times due to their natural curiosity, they may freeze, standing as if they were trying to hide, unlike the Porcupine or Bluenose caribou that will outrun a hunter.[7]
In British Columbia, from 2000 to 2011, woodland caribou were classified into three ecotypes – mountain, northern and boreal.[60] In 2011 they were given "Designatable Unit" (DU) status corresponding to Osborn's caribou (R. a. osborni) DU7, Rocky Mountain caribou (R. a. fortidens) DU8 and Selkirk Mountains caribou (R. a. montanus) DU9 in the recent revision.[10] The boreal woodland caribou DU6 is now only found in "the lowlands of the Boreal Plains and Taiga Plains ecoprovinces of the Alberta Plateau physiographic region, in the northeastern corner." This population was in an area with a high density of wolves and there was concern that the caribou herd was not self-sustaining.[13]
Density and population of boreal woodland caribou in British Columbia was not well known prior to 2000. In British Columbia the conservation status of caribou "is important from both federal and provincial perspectives because declining populations have been recognized globally (Vors and Boyce 2009), nationally (Sleep 2007), and provincially (Wittmer et al. 2005)."[61] Following a 2006 survey of mountain and boreal caribou populations in 2006, they were blue-listed within British Columbia.
The 15 northern caribou herds of the Southern Mountains National Ecological Area (SMNEA) were federally listed as "Threatened" by the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada (COSEWIC).[62] The 16 northern caribou herds of the Northern Mountains Ecological Area (NMNEA) are listed as of "Special Concern" federally.[62] This includes the Pink Mountain Herd which is locally, provincially and federally of concern. In 1996 there were 1,300 animals.[63] The population declined from 1,300 in 1996 to 850 animals in 2002 and continues to decline.[64][c][d] In 2014, COSEWIC classified Selkirk Mountain caribou and Rocky Mountain caribou as Endangered and Osborn's caribou as Threatened.[67]
The name of the Cariboo district of central British Columbia relates to their once-large numbers there, but they have almost vanished from that area in the last century. There are a number of populations in British Columbia that are currently being monitored. In 2006 there were approximately 200 to 340 individual boreal woodland caribou in the BC1 Maxhamish DU, north of Fort Nelson,[68] BC2 Calendar. The BC3 Snake-Sahtahneh boreal woodland caribou are non-migratory.[60] In BC4 Parker DU, there was a small local population of 20 individuals in 2006.[68][Notes 3][56] BC5 Prophet (small local population).[69] According to Forest and Wildlife Ecologist, R. Scott McNay,[61][63]
"The northern ecotype of woodland caribou is a classification based on regional location and behaviour rather than taxonomy and refers to woodland caribou of northern British Columbia. Northern caribou forage primarily on terrestrial lichens (Cladina spp. and Cladonia spp.) in winter and, in comparison to other woodland caribou, also generally have distinct horizontal as well as vertical change in location when migrating from low-elevation winter ranges in early winter to higher-elevation ranges in late winter (Heard & Vagt 1998). Northern caribou occur in the mountainous and lowland plateau areas of west-central and northern British Columbia, from the Williston Lake area in the north-central part of the province north to the Yukon and northwest to Atlin, and southeast along the east side of the Rocky Mountains near Kakwa Park and the Alberta border."
— McNay

There are 16 woodland caribou herds in Alberta and their ranges are all on Crown land.[70] In west-central Alberta there are two ecotypes – boreal and mountain. "Seven of the ten most-at-risk herds are in Alberta and are generally well-known to be under severe threat." There are 12 designated units for conservation purposes[71] including the most-at-risk herds, AB2 Bistcho, Little Smoky, a small isolated local population at risk of extirpation, AB1 Chinchaga in Alberta and British Columbia, AB8 Richardson, AB6 Red Earth, AB11 Nipisi, a small local population, and AB7 West Side Athabasca River.[72] The remaining herds are AB3 Yates, AB4 Caribou Mountains,[73] AB9 East Side Athabasca River, AB10 Cold Lake and AB12 Slave Lake (a small, local population).[71] The Banff National Park population of Central Mountain DU8 caribou was extirpated in 2009 when the last five were killed by an avalanche.[74]
A herd is protected in the Caribou Mountains Wildland Park in Alberta.[73] The Redrock-Prairie Creek (RPC) herd, located north of Jasper, in northwestern Alberta is also endangered. Land use practices in their range includes "timber harvesting, extensive oil and gas exploration and production, coal mining, roads, recreational off-road vehicle use, recreational hunting, and commercial trapping."[75]
"The Park contains relatively undisturbed and lichen-rich forests, favoured habitat for woodland caribou. About 80 percent of the range of an important population of woodland caribou is contained within the Park, and about a third of Alberta’s population of this threatened species is dependent on the Park."
— Alberta Wilderness
The AB5 Little Smoky Herd "is the most critically disturbed boreal caribou habitat in the country" with "only five per cent of intact forest left in the Little Smoky Range."[70] By 2012 there were only 80 animals left in this herd. Since 2005 the Alberta government has been culling wolves, up to a hundred a year.[70]
In June 2014, an Alberta Biodiversity Monitoring Institute (ABMI) report funded by the Canadian government revealed dwindling numbers between 1994 through 2014 in all populations of all six herds — including the threatened boreal woodland and the endangered mountain woodland caribou — with ranges in the oil sands region (OSR) of the northern Alberta boreal forests. This represented "annual rates of decline ranging from 4.6% to 15.2% from 1999 to 2012" in the OSR.[76] The ABMI report concluded that it is unlikely these herds would gain new members from other Alberta caribou herds as the OSR herds are "genetically distinct" from other boreal woodland caribou populations. According to a June 2014 article in The Wall Street Journal, the ABMI report was released during a period of "controversy over Alberta's recent sales of oil and gas development leases in areas populated by both boreal and mountain caribou."[76] The OSR "comprises about 20%" of the province's land area.[76]
By November 2014 it was apparent that the recovery plan adopted by the Alberta government had not been implemented as development expanded in the oil sands.[77] However Carolyn Campbell, a conservation specialist with the Alberta Wilderness Association in a radio interview[78] was hopeful that the new Premier of Alberta Jim Prentice would work towards a new recovery plan. Campbell described the caribou as an "umbrella species." Caribou are leading indicators of old growth forest core areas. By protecting their ecosystem, water quality is protected and other native fish and bird species also benefit. Dave Hervieux, Alberta's caribou specialist, confirmed the 2013 report findings that "woodland caribou are declining rapidly across Alberta."[77] "The report suggests the population viability of caribou is compromised and supports recovery-based actions to reverse the trend."[77]
Canadian Press correspondent Bob Weber revealed in March 2015 that the government of Alberta had planned to sell energy leases on 21,000 hectares in the habitat in northwestern Alberta of the endangered Redrock-Prairie Creek[75] boreal woodland caribou herd which both the Alberta provincial government and the Canadian federal government had promised to protect.[79] However, on 5 March the government announced it would postpone the oil and gas lease auction in this endangered caribou range.[80]
In Saskatchewan the boreal woodland caribou are in what is called the SK1 Boreal Shield, an area with very low anthropogenic disturbance, but very high fire disturbance.[71]
In Manitoba there are several small populations including the MB1 The Bog (a small, local population), MB2 Kississing (a small, local population), MB3 Naosap, MB4 Reed, MB5 North Interlake (a small, local population), MB6 William Lake (a small, local population), MB7 Wabowden, MB8 Wapisu, MB9 Manitoba North, MB10 Manitoba South, MB11 Manitoba East, MB12 Atikaki-Berens and MB13 Owl-Flinstone (a small local population).[71]
In their Annual Report 2006–2007,[81] the Office of the Environmental Commissioner of Ontario argued that, "Woodland caribou represent the "hard-to-perceive, slow-motion crisis"[82][83] that faces many species at risk."[84] "Woodland caribou are a sensitive indicator of the ecological effects of development in northern Ontario. The success or failure of conservation efforts for this species also may serve as a benchmark to measure the sustainability of policy choices made by the Ontario government."[81]
Since the 1940s the decline of Rangifer caribou caribou range occupancy in Ontario has been recognized.[85] There are two populations of woodland caribou, the forest-tundra migratory ecotype, DU4,[86] Labrador caribou R. c. caboti, and the sedentary forest-dwelling ecotype DU6,[86] boreal woodland caribou R. c. caribou. The boreal woodland caribou population (forest-dwelling), estimated at approximately 3,000, make up approximately one-quarter of Ontario's woodland caribou, was designated as threatened in 2000 (and likely to become endangered if limiting factors are not reversed) by the Federal Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada and by the Province of Ontario.[85] The migratory forest-tundra woodland caribou, numbering about 20,000 in 2007[81] is found in northern Ontario, on the coastal plains south of Hudson Bay was not considered to be endangered.[81]
In 1985, the Ontario government established the Slate Islands in Lake Superior as a natural environment provincial park. The islands are notable for having Ontario's largest herd of boreal woodland caribou.[87] Slate Island, where there were no wolves or other predators, had the highest density of boreal woodland caribou in the world with a population peaking at 660.[88] Because of a food shortage in 1990, their numbers were reduced to less than 100.[89]
There are six designated units in Ontario – ON1 Sydney, ON2 Berens, ON3 Churchill, ON4 Brightsand, ON5 Nipigon, ON6 Coastal (a small, isolated local population), ON7 Pagwachuan, ON8 Kesagami and ON9 Far North (a very large range).[71]
Québec: QC1 Val d'Or (a small, isolated local population), QC2 Charlevoix (a small, isolated local population), QC3 Pipmuacan, QC4 Manouane, QC5 Manicouagan and QC6 Quebec (a very large range).[71]
Newfoundland: NL1 Lac Joseph, NL2 Red Wine Mountain (a small, local population) and NL3 Mealy Mountain.[71]
In 1961 in Banfield's often-cited A Revision of the Reindeer and Caribou, Genus Rangifer (1961),[90] R. t. caboti (Labrador caribou) and R. t. terraenovae (Newfoundland caribou) were considered invalid and included in R. t. caribou. This was never accepted by the scientific community, however, and they continue to be recognized subspecies.[44][21][45][91][92][48] The recent revision[10] places them both under R. caribou, as genetic lineage data show: R. c. caboti and R. c. terranovae, respectively.
In insular Newfoundland, in Gros Morne National Park, for example, boreal woodland caribou (formerly R. t. terranovae) are "usually seen on the Long Range traverse and sometimes on Gros Morne Mountain. In recent winters, they have been seen in large numbers on the coastal lowlands north of Berry Hill and St. Paul's." An adult male R. t. terranovae can weigh up to 270 kilograms (600 lb) and females are about a quarter smaller. The caribou is much smaller than the moose.[93]
According to Bergerud in the 1800s and early 1900s, woodland caribou numbers declined following settlement.[94][Notes 4] The decline continued along the southern edge of woodland caribou distribution throughout the 1960s, 70s and 80s with the direct loss of habitat to logging, mines and dams. The increase of roads led to increased hunting and poaching and increased predator/prey densities.[17]
According to the Canadian Wildlife Federation in Canada, "Despite its vast range, the boreal population of woodland caribou [boreal ecotype of forest-dwelling woodland caribou] has been listed as threatened by the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada (COSEWIC) since 2002 and endangered in British Columbia. One of the main reasons numbers are dropping is that fewer calves are surviving their first year of life. The main cause is predation. More calves are being preyed on by wolves and black bears than ever before." However, this is caused by habitat fragmentation, due to forestry, agriculture, and mining, which reduce the mother's ability to shelter calves from predators.[6]
In 1991 Edmonds identified 44 herds of woodland caribou in seven jurisdictions in western North America (west of the Ontario/Manitoba border) with an estimated total maximum population of 61,090 caribou.[17] She noted that by 1991 caribou were a threatened species in Alberta and an endangered species in Washington/Idaho.

All caribou of the province of Québec were assigned to the same subspecies (R. t. caribou) in 1961. Banfield classified the caribou of Ungava as woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou) based on skull measurements.[90][95] But there are three ecotypes with specific habitats and behaviour.[96] Bergerud et al. compared the sedentary ecotype caribou (Bergerud 1988b) in southern Ungava (south of 55°N) to those farther north, the migratory ecotype Leaf River Caribou Herd (LRH) and the George River Caribou Herd (GRCH). In southern Ungava caribou females disperse from other females to avoid predators.[97] Genetic research has shown the migratory herds of northern Ungava, originally described as Labrador caribou (Rangifer arcticus caboti) Allen, 1914, and Newfoundland caribou (Rangifer tarandus terrænovæ) Allen, 1896, are both clades of woodland caribou (see Reindeer: taxonomy and migratory woodland caribou).
The boreal woodland caribou (forest-dwelling) ecotype is found discontinuously, mainly between the 49th and 55th parallels. In 2003 its distribution covered 235 000 km2,mainly east of the 72nd meridian. This sedentary ecotype is found almost exclusively in the boreal forest, principally in areas with long forest fire cycles. Its abundance has also decreased over the years. Large forest-dwelling populations still persisted during the 1950s and 1960s, but they apparently disappeared. The current abundance is not known precisely, but based on density estimates and considering the current distribution, it probably does not exceed 3000 individuals. Current data are insufficient to identify precisely the causes of the population decline, although hunting seems to be an important proximal cause."[96]
COSEWIC [86] designated the Labrador (Ungava) caribou, R. t. caboti, as the Eastern Migratory population, DU4. It consists of several herds. See Canadian Caribou Populations and migratory woodland caribou.
Although they are included as boreal woodland caribou, the George River and Leaf River caribou herds are migratory, covering thousands of miles each year to and from their birthing grounds. They travel north and south of their birthing grounds near these rivers crossing from Nunavik in the Ungava region to Quebec and insular Newfoundland.
The George River caribou herd (GRCH) is a migratory forest-tundra ecotype of the boreal woodland caribou. "Since the mid-1990s, the George River Herd has declined catastrophically. A 2018 survey confirms a continuing decline of the George River migratory caribou herd population, as reported by the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, it is estimated to be fewer than 9,000 animals,[98] down from 385,000 in 2001, 74,131 in 2010,[99][100][101] and 27,600 in 2012.[102]


The Leaf River caribou herd (LRCH) is a migratory forest-tundra ecotype of the boreal woodland caribou.[52] The Leaf Herd in the west, near the coast of Hudson Bay, increased from 270 000 individuals in 1991 to 628 000 in 2001.[103] According to the Quebec's Natural Resources and Wildlife survey, the Leaf River Herd (LRH) (Rivière-aux-Feuilles) had decreased to 430 000 caribou in 2011.[99][101][104] According to an international study on caribou populations, the Leaf River herd and other herds that migrate from Nunavik, Quebec and insular Newfoundland, could be threatened with extinction by 2080.[100]
The southern end of the Selkirk Mountains was home to the only extant woodland caribou population in the contiguous United States by the 2000s.[105] In the United States, the woodland caribou was one of the most critically endangered mammals, with only a few woodland caribou found south of the Canada border each year. The mountain woodland caribou are known as grey ghosts because they are "only rarely glimpsed." In the U.S. there was only one naturally occurring herd of woodland caribou in extreme northern Idaho, eastern Washington, and British Columbia, Canada, of about 40 animals. By April 2018, only three remained.[106] By 2019, this population had been extirpated.
Though the boreal forest ecotype has been considered mostly extirpated in the lower 48 states, at the turn of the 20th century this ecotype ranged as far south as northern Wisconsin, Michigan, New York, Vermont, New Hampshire, Minnesota and Maine.
There was, however, a concerted effort on the part of the North Central Caribou Corporation and the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness to reintroduce a herd of around 75 animals from the Slate Islands in Lake Superior to northern Minnesota though this effort has since lost steam due to reluctance on the part of the Minnesota DNR and the death of the NCCC spokesperson.
Another location for reintroduction by the NCCC was [Isle Royale] National Park, Michigan on Lake Superior off the coast of Minnesota and Ontario not far from the Slate Islands. This idea appears to be gaining public support, as evident in the public scoping comments on the National Park Service website in regards to the wolf and moose situation on [Isle Royale].
In his article entitled "Woodland Caribou: A Conservation Dilemma", Idaho Department of Fish and Game biologist Peter Zager described how the range of the boreal woodland caribou had dramatically declined.[107][94][108]
"At the time of European settlement of North America, caribou (Rangifer tarandus) were found over most of Canada and Alaska. Woodland caribou (R. t. caribou) extended south to 42 degrees N, and were found in parts of New England, New York, the Upper Great Lakes states, Montana, Idaho, and Washington. By the 1970s, woodland caribou had been eliminated from the eastern United States and most of eastern Canada, extending only to approximately 48 degrees N. The decline extended to the west as well, and by 1980 only 25-30 animals persisted in north Idaho and northeast Washington; caribou had been extirpated elsewhere in the contiguous 48 states. This population was listed as endangered in 1984 under the Endangered Species Act (ESA). At that time, the entire woodland caribou population in the Selkirks consisted of one herd of 20-25 animals that occurred in extreme northeast Washington, northern Idaho, and the Stagleap Park area of British Columbia (B.C.)."
— Zager et al. citing Bergerud
There is also a small population of boreal woodland caribou in Pukaskwa National Park, but their numbers declined from 30 caribou in the 1970s to about four in 2012, mainly due to human activity and its associated changes with predator and prey abundance, which caused excessive wolf predation. Abundance of moose population may be lowering caribou populations, however more study is needed. Harvest rates north of the park are also confirmed to reduce caribou migrations into the park.[109][110]: 46
According to the 2019 Recovery Strategy for the Woodland Caribou, the "primary threat to most boreal caribou local populations is unnaturally high predation rates."[32] Caribou habitat fragmentation, loss, and degradation—as a result of by both human activities and natural causes—supports an increase in populations of the caribou's natural predator, the wolf (Canis lupus)[32] In areas where there has been extensive fragmentation of the forest, often with the crisscrossing of seismic lines. efforts are being made to restore these disturbed area to decrease wolves' access to the woodland caribou's preferred habitat, the peatlands. Caribou mortality increased and populations declined as the hunting success of wolves that followed seismic lines, increased.[111]
Boreal woodland caribou were once found throughout much of Ontario's boreal forest; at the turn of the 20th century they ranged as far south as northern Wisconsin. The last permanent residents were killed in Minnesota in 1962. Despite periodic sightings of individuals south of the border the caribou range has receded approximately 34 km/decade, the manifestation of widespread range collapse and population decline. Although boreal woodland caribou have been protected from sport hunting since 1929, the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada listed them in Canada as threatened (likely to become endangered if limiting factors are not reversed) in 2000. Boreal woodland caribou may be extinct before the year 2100 if the rate of range loss continues. "Destruction of habitat, hunting and disturbances by humans during the construction of roads and pipelines are all factors that have contributed to the decline of Woodland Caribou."[12]
David Suzuki explained that,[4]
BLCN lands cover an area the size of Switzerland and overlap the oil sands. The territory now yields 560,000 barrels of oil a day. Industry wants to raise that to 1.6 million. BLCN land already has 35,000 oil and gas sites, 21,700 kilometres of seismic lines, 4,028 kilometres of pipelines and 948 kilometres of road. Traditional territory has been carved into a patchwork quilt, with wild land reduced to small pieces between roads, pipes and wires, threatening animals like woodland caribou that can't adapt to these intrusions.
— David Suzuki 28 August 2013
When Environment Canada (EC) introduced the new South Athabaska Sub-regional Strategic Environmental Assessment, it was partly in response to the cumulative effect of oil sands development on the habitat loss of the boreal woodland caribou, also known as woodland caribou (boreal), Rangifer tarandus caribou.[26] Ecosystem degradation of the "stands of old growth forest", for example, are caused by "mining, logging, oil and gas exploration and even excessive motorized recreation" which result in "a fragmented and altered landscape often leading to increased populations of deer, moose, elk, and their predators. Caribou require large areas of land with low densities of predators. The cumulative effect of oil sands development,[112] was one of the topics discussed.[113] It was noted that,[113]
The science is clear – all Alberta's boreal caribou are at elevated risk of becoming extirpated (locally extinct), including those in the oil sands region.
— DM-153229, 2012
In June 2007, a national recovery strategy for boreal caribou was to be posted on the Species at Risk Public Registry.[114]
Since the fall of 2010, the Alberta government has been working closely with the federal government, through the Major Projects Management Office (MPMO) on system-wide improvements in regulatory activities to align with the Canadian Environmental Assessment Act (CEAA) and to engage Alberta on energy and environment issues.
On 3 February 2013, a joint Canada-Alberta world-class, comprehensive and integrated monitoring system of the oil sands was announced. Through the South Athabaska Sub-regional Strategic Environmental Assessment, the Government of Canada and Alberta will "further align regulatory processes, while addressing cumulative effects by employing an ecosystem-based approach."[115]
On 11 May 2012, the briefing notes for the meeting with Suncor VP and Environment Canada included EC's concerns for the cumulative effects of oil sands development.[114][116][117]
"Environment Canada is not only concerned with the environmental impacts of individual oil and gas projects, it is concerned with the cumulative effects of development, especially in the oil sands and urban centers. Impacts are not limited to air emissions. Terrain disturbance, disruption of groundwater regimes, and contamination of surface waters are all concerns, particularly with the accelerated pace of development."
— DM 156431, 2012
By February 2013, Suncor's March report reflects their concerns with the Species at Risk Act (SARA), in particular on the implications of the Proposed Recovery Strategy for Woodland Caribou.[118] Suncor reported that,[119]
A number of statutes, regulations and frameworks are under development or have been issued by various provincial regulators that oversee oil sands development, including the recently announced Joint Canada-Alberta Implementation Plan for Oil Sands Monitoring, and the Lower Athabasca Regional Plan (LARP) that implements a cumulative efforts management regime in the Athabaskca oil sands region. These statutes, regulations and frameworks relate to such issues as tailings management, water use, air emissions and land use. While the financial implications of statutes, regulations and frameworks under development are not yet known, the company is committed to working with the appropriate regulatory bodies as they develop new policies, and to fully complying with all existing and new statutes, regulations and frameworks as they apply to the company’s operations.
— Suncor, 2013
Caribou are monitored through a capture and collaring with VHF or Global Positioning System (GPS)[120] tracking collars. The satellite tracking Argos system[120] collects, processes and disseminates the data from caribou tracking collars, clearly locating exact geographic coordinates. Satellite networks have tracked the migration and territorial movements of caribou.[120] Electronic tags are giving scientists a complete, accurate picture of migration patterns. Using radio transmitters to track one herd of caribou, scientists learned that the herd moves much more than previously thought and they learned that each year the herd returns to about the same place to give birth. Environment Canada uses Landsat satellite imagery, for example, to identify anthropogenic disturbance (human-caused disturbance) to the natural landscape. This includes roads, seismic lines, pipe lines, well sites, and cutblocks that accompany industrial activities such as oil and gas exploration and development and forestry. British Columbia uses telemetry and computer modelling.[121]
Experts in Finland are also concerned about their R. tarandus subspecies, R. fennicus fennicus or the Finnish forest reindeer, where an increasing, returning wolf population may be partially responsible for slowing the recovery.[122]
des colonies en diverses places de ces quartiers là, comme à Tadoussac, Gachepé, Campseau, La Héve, Ougoudi, Saincte Croix, Pemptegoet, Kinibeki, & autres endroits... Car venant le Printemps ils se divisent par troupes sur les rives de mer jusques à l'Hiver, lequel venant, par ce que le poisson se retire au fond des grandes eaux salées, ilz cherchent les lacs & ombres des bois, où ilz pechent les Castors, dont ilz vivent, & d'autres chasses, comme Ellan, Caribous, Cerfs, & autres animaux moindres que ceux-là. Et neantmoins quelquefois en eté méme ilz ne saissent point de chasser; & d'ailleurs ont infinie quantité d'oyseaux en certaines iles dés mois de May, Juin, Juillet & Aoust.
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)