Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
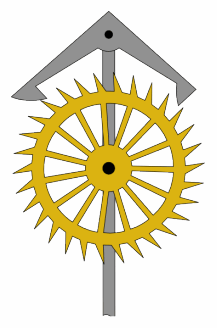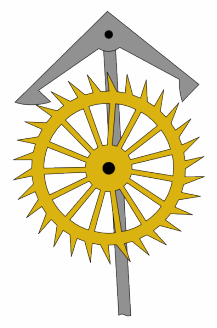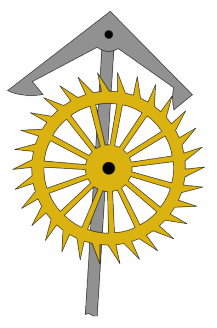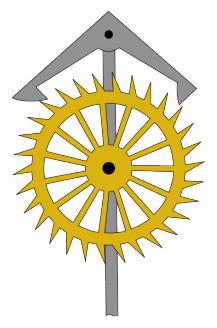

In horology, the anchor escapement is a type of escapement used in pendulum clocks. The escapement is a mechanism in a mechanical clock that maintains the swing of the pendulum by giving it a small push each swing, and allows the clock's wheels to advance a fixed amount with each swing, moving the clock's hands forward. The anchor escapement was so named because one of its principal parts is shaped vaguely like a ship's anchor.
The anchor escapement was invented by clockmaker William Clement,[1] [2][3] who popularized the anchor in his invention of the longcase or grandfather clock around 1680. Clement's invention was a substantial improvement on Robert Hooke's constant force escapement of 1671.[4] The oldest known anchor clock is Wadham College Clock, a tower clock built at Wadham College, Oxford, in 1670, probably by clockmaker Joseph Knibb.[5][6] The anchor became the standard escapement used in almost all pendulum clocks.
A more accurate variation without recoil called the deadbeat escapement was invented by Richard Towneley around 1675 and introduced by British clockmaker George Graham around 1715. This gradually superseded the ordinary anchor escapement and is used in most modern pendulum clocks.
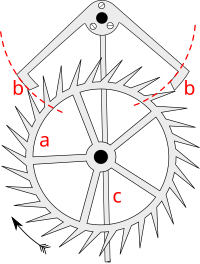
The anchor escapement consists of two parts: the escape wheel, which is a vertical wheel with pointed teeth on it rather like saw teeth, and the anchor, shaped vaguely like a ship's anchor, which swings back and forth on a pivot just above the escape wheel. On the two arms of the anchor are curved faces which the teeth of the escape wheel push against, called pallets. The central shaft of the anchor is attached to a fork pushed by the pendulum, so the anchor swings back and forth, with the pallets alternately catching and releasing an escape wheel tooth on each side.
Each time one pallet moves away from the escape wheel, releasing a tooth, the wheel turns and a tooth on the other side catches on the other pallet, which is moving toward the wheel. The momentum of the pendulum continues to move the second pallet toward the wheel, pushing the escape wheel backward for a distance, until the pendulum reverses direction and the pallet begins to move away from the wheel, with the tooth sliding along its surface, pushing it. Then the tooth slides off the end of the pallet, beginning the cycle again.
Neither the anchor escapement nor the deadbeat form, below, are self-starting. The pendulum must be given a swing to get them going.

The backward motion of the escape wheel during part of the cycle, called recoil, is one of the disadvantages of the anchor escapement. It results in a temporary reversal of the entire wheel train back to the driving weight with each tick of the clock, causing extra wear in the wheel train, excessive wear to the gear teeth, and inaccuracy. It can also cause the points of the escape wheel teeth to dig into the pallet surface. The teeth are slanted backward, opposite the direction of rotation, and the surface of the pallets is slightly convex, to prevent this.[7]
Another reason the escape wheel teeth are slanted backward is as a safety measure. If the clock is moved without immobilising the pendulum, the uncontrolled swinging of the pendulum can cause the anchor pallets to collide violently with the escape wheel. The slanted teeth ensure that the flat faces of the anchor pallets hit the sides of the teeth first, protecting the delicate points from being broken.[7]
The deadbeat escapement (below) doesn't have recoil. One way to determine whether an antique pendulum clock has an anchor or deadbeat escapement is to observe the second hand. If it moves backward slightly after every tick, showing recoil, the clock has an anchor escapement.
The shaft of the anchor, called the crutch ends in a fork which embraces the shaft of the pendulum, giving it transverse impulses. The pendulum rod is hung from a short straight suspension spring attached to a sturdy support directly behind the anchor. The pivot of the anchor is aligned with the bending point of the spring. This arrangement results in a more stable pendulum support than simply suspending the pendulum directly from the anchor.
The anchor is very tolerant of variations in its geometry, so its shape varied widely.[7] In the late 19th century, in Britain, the usual design[7] was a 90° angle between the pallets, which meant locating the anchor pivot a distance of √2 ≈ 1.4 times the escape wheel radius from the escape wheel pivot. In a grandfather clock, which had a pendulum which swung once per second, the escape wheel often had 30 teeth, which made the escape wheel rotate once per minute so the second hand could be attached to its shaft. In a 30-tooth escape wheel the pallets span about 7½ teeth. The impulse angle of the pallets, which determined the swing of the pendulum, was 3–4°.
The anchor was the second widely used escapement in Europe, replacing the primitive 400-year-old verge escapement in pendulum clocks. The pendulums in verge escapement clocks had very wide swings of 80° to 100°. In 1673, seventeen years after he invented the pendulum clock, Christiaan Huygens published his mathematical analysis of pendulums, Horologium Oscillatorium. In it he showed that the wide pendulum swings of verge clocks caused them to be inaccurate, because the period of oscillation of the pendulum was not isochronous but varied to a small degree due to circular error with changes in the amplitude of the pendulum's swing, which occurred with unavoidable changes in drive force. The realization that only small pendulum swings were nearly isochronous motivated clockmakers to design escapements with small swings.
The chief advantage of the anchor was that by locating the pallets farther from the pivot, the swing of the pendulum was reduced from around 100° in verge clocks to only 4°-6°.[8] In addition to the improved accuracy due to isochronism, this allowed clocks to use longer pendulums, which had a slower 'beat'. Lower air drag (aerodynamic drag rises with the square of speed, so a faster pendulum experiences greatly-increased drag) meant they needed less power to keep swinging, and caused less wear on the clock's movement. The anchor also allowed the use of a heavier pendulum bob for a given drive force, making the pendulum more independent of the escapement (higher Q), and thus more accurate. These long pendulums required long narrow clock cases. Around 1680 British clockmaker William Clement began selling the first commercial clocks to use the anchor escapement, tall freestanding clocks with 1 meter (39 inch) seconds pendulums contained inside a long narrow clock case that came to be called longcase or 'grandfather' clocks.[9] The anchor increased the accuracy of clocks so much that around 1680–1690 the use of the minute hand, formerly the exception in clocks, became the rule.[10]
The anchor escapement replaced the verge in pendulum clocks within about fifty years, although French clockmakers continued to use verges until about 1800. Many verge clocks were rebuilt with anchors. In the 18th century the more accurate deadbeat form of the escapement replaced the anchor in precision regulators, but the anchor remained the workhorse in home pendulum clocks. During the 19th century the deadbeat form gradually took over in most quality clocks, but the anchor form is still used in a few pendulum clocks today.[8]
Tower clocks are one of the few types of pendulum clock which the anchor escapement did not dominate. The varying force applied to the wheel train by the large exterior hands, exposed to wind, snow, and ice loads, was better handled by gravity escapements.
The anchor escapement is reliable and tolerant of large geometrical errors in its construction, but its operation is similar to the old verge escapement, and retains two of the major disadvantages of the verge:
The above two disadvantages were removed with the invention of an improved version of the anchor escapement: the deadbeat or Graham escapement. This is often erroneously credited to English clockmaker George Graham who introduced it around 1715 in his precision regulator clocks.[11][12][13][14] However it was actually invented around 1675 by astronomer Richard Towneley, and first used by Graham's mentor Thomas Tompion in a clock built for Sir Jonas Moore, and in the two precision regulators he made for the new Greenwich Observatory in 1676,[15] mentioned in correspondence between Astronomer Royal John Flamsteed and Towneley.[16][17]
The deadbeat form of the anchor escapement is less tolerant to inaccuracy in its manufacture or wear during operation and was initially used only in precision clocks, but its use spread during the 19th century to most quality pendulum clocks. Almost all pendulum clocks made today use it.
The deadbeat escapement has two faces to the pallets: a "locking", or "dead", face, with a curved surface concentric with the axis on which the anchor rotates, and a sloping "impulse" face.[8] When an escape wheel tooth is resting against one of the dead faces, its force is directed through the anchor's pivot axis, so it gives no impulse to the pendulum, allowing it to swing freely. When the pallet on the other side releases the escape wheel, a tooth lands on this "dead" face first, and remains resting against it for most of the pendulum's outward swing and return. For this period the escape wheel is "locked" and unable to turn. Near the bottom of the pendulum's swing the tooth slides off the dead face onto the slanted "impulse" face of the pallet, allowing the escape wheel to turn and give the pendulum a push, before dropping off the pallet. It is still a frictional rest escapement because the sliding of the escape tooth on the dead face adds friction to the pendulum's swing, but it has less friction than the recoil escapement because there is no recoil force.
In contrast to the backward slant of the anchor escape wheel teeth, the deadbeat escape wheel teeth are radial or slant forward to ensure that the tooth makes contact with the "dead" face of the pallet, preventing recoil.[8]
Clockmakers discovered in the 1700s that for accuracy, the best place to apply the impulse to keep the pendulum swinging was at the bottom of its swing, as it passes through its equilibrium position. If the impulse is applied during the pendulum's downswing, before it reaches the bottom, the impulse force tends to decrease the period of the swing, so an increase in drive force causes the clock to gain time. If the impulse is applied during the pendulum's upswing, after it reaches the bottom, the impulse force tends to increase the period of the swing, so an increase in drive force causes the clock to lose time. If the impulse is applied at the bottom, changes in the impulse force theoretically should have no effect on the period.
In 1826 British astronomer George Airy proved this; specifically, he proved that a pendulum that is driven by a drive impulse that is symmetrical about its bottom equilibrium position is isochronous for different drive forces, ignoring friction, and that the deadbeat escapement approximately satisfies this condition.[18][19] It would be exactly satisfied if the escape wheel teeth were made to fall exactly on the corner between the two pallet faces, but for the escapement to operate reliably, the teeth must be made to fall above the corner, on the "dead" face.[20]
A major cause of error in clocks is changes in the drive force applied to the escapement, caused by small changes in the friction of the gears or the pallets, or the diminishing force of the mainspring as it unwinds. An escapement in which changes in drive force do not affect the rate is called isochronous. The superior performance of the deadbeat over the recoil is due to improved isochronism. This is due to the different ways changes in drive force affect the swing of the pendulum in the two escapements:[21]
When the deadbeat was invented, clockmakers initially believed it had inferior isochronism to the anchor, because of the greater effect of changes in force on the pendulum's amplitude.[21] Recent analyses point out that the nonisochronism of the anchor escapement can cancel the circular error of the pendulum. That is, an increase in amplitude of swing in the anchor causes a slight increase in period of a pendulum due to circular error, and that this can compensate for the decreased period due to isochronism. Due to this effect, a carefully adjusted anchor escapement with polished pallets might be more accurate than a deadbeat.[22] This has been confirmed by at least one modern experiment.[23][24]
the oft-repeated claim that Hooke invented the anchor escapement originated in William Derham's The artificial clock-maker (1696), not with Hooke, and is now regarded as untrue.
Escapements.—....Anchor escapement..&..Dead escapements