ISO/IEC 17025: History and introduction of concepts
Inhoud
FOXL2 is een gen dat transcriptiefactor FOXL2 codeert. Het gen bevindt zich bij de mens op locus 3q22.3 van chromosoom 3 en behoort tot de genfamilie FOX. Het FOXL2-eiwit heeft een DNA-bindingsdomein en van belang voor de vrouwelijk vruchtbaarheid en de vrouwelijke geslachtsdifferentiatie, vooral bij de vorming van de eierstokken.[1]
Aandoeningen
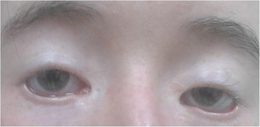
Mutaties in FOXL2 kunnen de oorzaak zijn van het blefarofimose, ptose en epicanthus inversus-syndroom (BPES) met als symptomen blefarofimose – onderontwikkelde oogleden – ptose – het afhangen van de bovenste oogleden – epicanthus inversus – omgekeerde amandelogen en telecanthus – een grotere afstand tussen de binnenste ooghoeken. Bij type I is er ook sprake van primair ovariumfalen (POI), bij type II niet.[2]
Noten
- ↑ Benayoun, B.A.; Caburet, S.; Dipietromaria, A.; Bailly-Bechet, M.; Batista, F.; Fellous, M.; Vaiman, D.; Veitia, R.A. (2008): 'The identification and characterization of a FOXL2 response element provides insights into the pathogenesis of mutant alleles' in Human Molecular Genetics, Volume 17, Issue 20, p. 3118-3127
- ↑ Crisponi, L.; Deiana, M.; Loi, A.; Chiappe, F.; Uda, M.; Amati, P.; Bisceglia, L.; Zelante, L.; Nagaraja, R.; Porcu, S.; Ristaldi, M.S.; Marzella, R.; Rocchi, M.; Nicolino, M.; Lienhardt-Roussie, A.; Nivelon, A.; Verloes, A.; Schlessinger, D.; Gasparini, P.; Bonneau, D.; Cao, A.; Pilia, G. (2001): 'The putative forkhead transcription factor FOXL2 is mutated in blepharophimosis/ptosis/epicanthus inversus syndrome' in Nature Genetics, Volume 27, Issue 2, p. 159-166

















