Infrastructure tools to support an effective radiation oncology learning health system
Contents
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
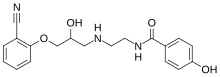
| IUPAC name
(RS)-N-[2-([3-(2-cyanophenoxy)-2-hydroxypropyl]amino)ethyl]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H23N3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 369.41432 |
| Pharmacology | |
| C07AB10 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Epanolol is a beta blocker.[1] developed by Imperial Chemical Industries.[2]
Synthesis
The ester methyl 4-benzyloxyphenylacetate (1) is treated with ethylenediamine to give the amide (3). Separately, 2-cyanophenol (4) is reacted with epichlorohydrin and sodium hydroxide to produce the benzonitrile derivative (5). Combination of (3) and (5) by heating in propanol gives (6). Lastly, catalytic hydrogenation removes the benzyl protecting group and yields epanolol.[2][3]
See also
References
- ^ Hosie, J.; Scott, A. K.; Petrie, J. C.; Cockshott, I. D. (1990). "Pharmacokinetics of epanolol after acute and chronic oral dosing in elderly patients with stable angina pectoris". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 29 (3): 333–337. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03644.x. PMC 1380134. PMID 1968755.
- ^ a b Large, M. S.; Smith, L. H. (1982). ".beta.-Adrenergic blocking agents. 22. 1-Phenoxy-3-[[(substituted-amido)alkyl]amino]-2-propanols". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 25 (11): 1286–1292. doi:10.1021/jm00353a004. PMID 6128420.
- ^ "Epanolol". Thieme. Retrieved 2024-06-30.


















