Infrastructure tools to support an effective radiation oncology learning health system
Contents
-
(Top)
-
1 History
-
2 Laws and gameplay
-
3 Women's cricket
-
4 Governance
-
5 Forms of cricket
-
6 Competitions
-
7 Culture
-
8 See also
-
9 Footnotes
-
10 Citations
-
11 Sources
-
12 Further reading
-
13 External links
 Shaun Pollock of South Africa bowls to Michael Hussey of Australia during the 2005 Boxing Day Test match at the Melbourne Cricket Ground. | |
| Highest governing body | International Cricket Council |
|---|---|
| Nicknames | The Gentlemen's Game[1] |
| First played | 16th century; South East England |
| Characteristics | |
| Contact | No |
| Team members | 11 players per side (substitutes permitted in some circumstances) |
| Mixed-sex | No, separate competitions |
| Type | Team sport, Bat-and-Ball |
| Equipment | Cricket ball, Cricket bat, Wicket (Stumps, Bails), Protective equipment |
| Venue | Cricket field |
| Glossary | Glossary of cricket terms |
| Presence | |
| Country or region | Worldwide (most popular in the Commonwealth) |
| Olympic | 1900 |
| Part of a series on |
| Cricket |
|---|
| Women's cricket |
| Records |
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field, at the centre of which is a 22-yard (20-metre; 66-foot) pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails (small sticks) balanced on three stumps. Two players from the batting team, the striker and nonstriker, stand in front of either wicket holding bats, while one player from the fielding team, the bowler, bowls the ball toward the striker's wicket from the opposite end of the pitch. The striker's goal is to hit the bowled ball with the bat and then switch places with the nonstriker, with the batting team scoring one run for each of these exchanges. Runs are also scored when the ball reaches the boundary of the field or when the ball is bowled illegally.
The fielding team tries to prevent runs from being scored by dismissing batters (so they are "out"). Means of dismissal include being bowled, when the ball hits the striker's wicket and dislodges the bails, and by the fielding side either catching the ball after it is hit by the bat but before it hits the ground, or hitting a wicket with the ball before a batter can cross the crease line in front of the wicket. When ten batters have been dismissed, the innings (playing phase) ends and the teams swap roles. Forms of cricket range from traditional Test matches played over five days to the newer Twenty20 format (also known as T20), in which each team bats for a single innings of 20 overs (each "over" being a set of 6 fair opportunities for the batting team to score) and the game generally lasts three to four hours.
Traditionally, cricketers play in all-white kit, but in limited overs cricket, they wear club or team colours. In addition to the basic kit, some players wear protective gear to prevent injury caused by the ball, which is a hard, solid spheroid made of compressed leather with a slightly raised sewn seam enclosing a cork core layered with tightly wound string.
The earliest known definite reference to cricket is to it being played in South East England in the mid-16th century. It spread globally with the expansion of the British Empire, with the first international matches in the second half of the 19th century. The game's governing body is the International Cricket Council (ICC), which has over 100 members, twelve of which are full members who play Test matches. The game's rules, the Laws of Cricket, are maintained by Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) in London. The sport is followed primarily in South Asia, Australia, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Southern Africa, and the West Indies.[2]
Women's cricket, which is organised and played separately, has also achieved international standard.
The most successful side playing international cricket is Australia, which has won eight One Day International trophies, including six World Cups, more than any other country, and has been the top-rated Test side more than any other country.[citation needed]
History
Origins

Cricket is one of many games in the "club ball" sphere that involve hitting a ball with a hand-held implement. Others include baseball (which shares many similarities with cricket, both belonging in the more specific bat-and-ball games category[3]), golf, hockey, tennis, squash, badminton and table tennis.[4] In cricket's case, a key difference is the existence of a solid target structure, the wicket (originally, it is thought, a "wicket gate" through which sheep were herded), that the batter must defend.[5] The cricket historian Harry Altham identified three "groups" of "club ball" games: the "hockey group", in which the ball is driven to and from between two targets (the goals); the "golf group", in which the ball is driven towards an undefended target (the hole); and the "cricket group", in which "the ball is aimed at a mark (the wicket) and driven away from it".[6]
It is generally believed that cricket originated as a children's game in the south-eastern counties of England, sometime during the medieval period.[5] Although there are claims for prior dates, the earliest definite reference to cricket being played comes from evidence given at a court case in Guildford in January 1597 (Old Style, equating to January 1598 in the modern calendar). The case concerned ownership of a certain plot of land, and the court heard the testimony of a 59-year-old coroner, John Derrick, who gave witness that:[7][8][9]
Being a scholler in the ffree schoole of Guldeford hee and diverse of his fellows did runne and play there at creckett and other plaies.
Given Derrick's age, it was about half a century earlier when he was at school, and so it is certain that cricket was being played c. 1550 by boys in Surrey.[9] The view that it was originally a children's game is reinforced by Randle Cotgrave's 1611 English-French dictionary in which he defined the noun "crosse" as "the crooked staff wherewith boys play at cricket", and the verb form "crosser" as "to play at cricket".[10][11]
One possible source for the sport's name is the Old English word "cryce" (or "cricc") meaning a crutch or staff. In Samuel Johnson's Dictionary, he derived cricket from "cryce, Saxon, a stick".[7] In Old French, the word "criquet" seems to have meant a kind of club or stick.[12] Given the strong medieval trade connections between south-east England and the County of Flanders when the latter belonged to the Duchy of Burgundy, the name may have been derived from the Middle Dutch (in use in Flanders at the time) "krick"(-e), meaning a stick (crook).[12] Another possible source is the Middle Dutch word "krickstoel", meaning a long low stool used for kneeling in church that resembled the long low wicket with two stumps used in early cricket.[13] According to Heiner Gillmeister, a European language expert of Bonn University, "cricket" derives from the Middle Dutch phrase for hockey, "met de (krik ket)sen" ("with the stick chase").[14] Gillmeister has suggested that not only the name but also the sport itself may be of Flemish origin.[14]
Growth of amateur and professional cricket in England

Although the main object of the game has always been to score the most runs, the early form of cricket differed from the modern game in certain key technical aspects; the North American variant of cricket known as wicket retained many of these aspects.[15] The ball was bowled underarm by the bowler and along the ground towards a batter armed with a bat that in shape resembled a hockey stick; the batter defended a low, two-stump wicket; and runs were called notches because the scorers recorded them by notching tally sticks.[16][17][18]
In 1611, the year Cotgrave's dictionary was published, ecclesiastical court records at Sidlesham in Sussex state that two parishioners, Bartholomew Wyatt and Richard Latter, failed to attend church on Easter Sunday because they were playing cricket. They were fined 12d each and ordered to do penance.[19] This is the earliest mention of adult participation in cricket and it was around the same time that the earliest known organised inter-parish or village match was played, at Chevening, Kent.[7][20] In 1624, a player called Jasper Vinall died after he was accidentally struck on the head during a match between two parish teams in Sussex.[21]
Cricket remained a low-key local pursuit for much of the 17th century.[11] It is known, through numerous references found in the records of ecclesiastical court cases, to have been proscribed at times by the Puritans before and during the Commonwealth.[22][23] The problem was nearly always the issue of Sunday play, as the Puritans considered cricket to be "profane" if played on the Sabbath, especially if large crowds or gambling were involved.[24][25]
According to the social historian Derek Birley, there was a "great upsurge of sport after the Restoration" in 1660.[26] Several members of the court of King Charles II took a strong interest in cricket during that era.[27] Gambling on sport became a problem significant enough for Parliament to pass the 1664 Gambling Act, limiting stakes to £100, which was, in any case, a colossal sum exceeding the annual income of 99% of the population.[26] Along with horse racing, as well as prizefighting and other types of blood sport, cricket was perceived to be a gambling sport.[28] Rich patrons made matches for high stakes, forming teams in which they engaged the first professional players.[29] By the end of the century, cricket had developed into a major sport that was spreading throughout England and was already being taken abroad by English mariners and colonisers—the earliest reference to cricket overseas is dated 1676.[30] A 1697 newspaper report survives of "a great cricket match" played in Sussex "for fifty guineas apiece", the earliest known contest that is generally considered a First Class match.[31][32]
The patrons and other players from the gentry began to classify themselves as "amateurs"[fn 1] to establish a clear distinction from the professionals, who were invariably members of the working class, even to the point of having separate changing and dining facilities.[33] The gentry, including such high-ranking nobles as the Dukes of Richmond, exerted their honour code of noblesse oblige to claim rights of leadership in any sporting contests they took part in, especially as it was necessary for them to play alongside their "social inferiors" if they were to win their bets.[34] In time, a perception took hold that the typical amateur who played in first-class cricket, until 1962 when amateurism was abolished, was someone with a public school education who had then gone to one of Cambridge or Oxford University. Society insisted that such people were "officers and gentlemen" whose destiny was to provide leadership.[35] In a purely financial sense, the cricketing amateur would theoretically claim expenses for playing while his professional counterpart played under contract and was paid a wage or match fee; in practice, many amateurs claimed more than actual expenditure, and the derisive term "shamateur" was coined to describe the practice.[36][37]
English cricket in the 18th and 19th centuries

The game underwent major development in the 18th century to become England's national sport.[38] Its success was underwritten by the twin necessities of patronage and betting.[39] Cricket was prominent in London as early as 1707 and, in the middle years of the century, large crowds flocked to matches on the Artillery Ground in Finsbury.[citation needed] The single wicket form of the sport attracted huge crowds and wagers to match, its popularity peaking in the 1748 season.[40] Bowling underwent an evolution around 1760 when bowlers began to pitch (bounce) the ball instead of rolling or skimming it towards the batter. This caused a revolution in bat design because, to deal with the bouncing ball, it was necessary to introduce the modern straight bat in place of the old "hockey stick" shape.[41][citation needed]
The Hambledon Club was founded in the 1760s and, for the next twenty years until the formation of Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) and the opening of Lord's Old Ground in 1787, Hambledon was both the game's greatest club and its focal point.[citation needed] MCC quickly became the sport's premier club and the custodian of the Laws of Cricket. New Laws introduced in the latter part of the 18th century include the three-stump wicket and leg before wicket (lbw).[42]
The 19th century saw underarm bowling superseded by first roundarm and then overarm bowling. Both developments were controversial.[43] Organisation of the game at county level led to the creation of the county clubs, starting with Sussex in 1839.[44] In December 1889, the eight leading county clubs formed the official County Championship, which began in 1890.[45]

The most famous player of the 19th century was W. G. Grace, who started his long and influential career in 1865. It was especially during the career of Grace that the distinction between amateurs and professionals became blurred by the existence of players like him who were nominally amateur but, in terms of their financial gain, de facto professional. Grace himself was said to have been paid more money for playing cricket than any professional.[citation needed]
The last two decades before the First World War have been called the "Golden Age of cricket". It is a nostalgic name prompted by the collective sense of loss resulting from the war, but the period did produce some great players and memorable matches, especially as organised competition at county and Test level developed.[46]
Cricket becomes an international sport

In 1844, the first-ever international match took place between what were essentially club teams, from the United States and Canada, in Toronto; Canada won.[47][48] In 1859, a team of English players went to North America on the first overseas tour.[49] Meanwhile, the British Empire had been instrumental in spreading the game overseas, and by the middle of the 19th century it had become well established in Australia, the Caribbean, British India (which includes present-day Pakistan and Bangladesh), New Zealand, North America and South Africa.[50]
In 1862, an English team made the first tour of Australia.[51] The first Australian team to travel overseas consisted of Aboriginal stockmen who toured England in 1868.[52]
In 1876–77, an England team took part in what was retrospectively recognised as the first-ever Test match at the Melbourne Cricket Ground against Australia.[53] The rivalry between England and Australia gave birth to The Ashes in 1882, which remains Test cricket's most famous contest.[54] Test cricket began to expand in 1888–89 when South Africa played England.[55]
Cricket in the 20th century

The inter-war years were dominated by Australia's Don Bradman, statistically the greatest Test batter of all time. To curb his dominance, England employed bodyline tactics during the 1932–33 Ashes series. These involved bowling at the body of the batter and setting a field, resulting in batters having to choose between being hit or risk getting out. This series moved cricket from a game to a matter of national importance, with diplomatic cables being passed between the two countries over the incident.[56]
During this time, the number of Test nations continued to grow, with the West Indies, New Zealand and India being admitted as full Test members within a four-year period from 1928 to 1932.
An enforced break during the Second World War stopped Test Cricket for a time, although the Partition of India caused Pakistan to gain Test status in 1952. As teams began to travel more, the game quickly grew from 500 tests in 84 years to 1000 within the next 23.
Cricket entered a new era in 1963 when English counties introduced the limited overs variant.[57] As it was sure to produce a result, limited overs cricket was lucrative, and the number of matches increased.[58] The first Limited Overs International was played in 1971, and the governing International Cricket Council (ICC), seeing its potential, staged the first limited overs Cricket World Cup in 1975.[59]
Sri Lanka joined the ranks in 1982. Meanwhile, South Africa was banned by the ICC due to apartheid from 1970 until 1992. 1992 also brought about the introduction of the Zimbabwe team.[60]
Cricket in the 21st century

The 21st century brought with it the Bangladesh Team, who made their Test debut in 2000. The game itself also grew, with a new format made up of 20-over innings being created. This format, called T20 cricket, quickly became a highly popular format, putting the longer formats at risk. The new shorter format also introduced franchise cricket, with new tournaments like the Indian Premier League and the Australian Big Bash League. The ICC has selected the T20 format as cricket's growth format, and has introduced a T20 World Cup which is played every two years;[62] T20 cricket has also been increasingly accepted into major events such as the Asian Games.[63] The resultant growth has seen cricket's fanbase cross one billion people, with 90% of them in South Asia.[2] T20's success has also spawned even shorter formats, such as 10-over cricket (T10) and 100-ball cricket, though not without controversy.[64]
Outside factors have also taken their toll on cricket. For example, the 2008 Mumbai attacks led India and Pakistan to suspend their bilateral series indefinitely. The 2009 attack on the Sri Lankan team during their tour of Pakistan led to Pakistan being unable to host matches until 2019.[65][66][67][68]
In 2017, Afghanistan and Ireland became the 11th and 12th Test nations.[69][70]
Laws and gameplay
In cricket, the rules of the game are codified in The Laws of Cricket (hereinafter called "the Laws"), which has a global remit. There are 42 Laws (always written with a capital "L"). The earliest known version of the code was drafted in 1744, and since 1788, it has been owned and maintained by its custodian, the Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) in London.[71]
Playing area
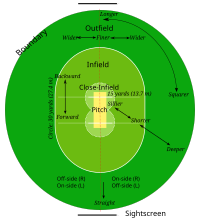
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played on a cricket field (see image of cricket pitch and creases) between two teams of eleven players each.[72] The field is usually circular or oval in shape, and the edge of the playing area is marked by a boundary, which may be a fence, part of the stands, a rope, a painted line, or a combination of these; the boundary must if possible be marked along its entire length.[73]
In the approximate centre of the field is a rectangular pitch (see image, below) on which a wooden target called a wicket is sited at each end; the wickets are placed 22 yards (20 m) apart.[74] The pitch is a flat surface 10 feet (3.0 m) wide, with very short grass that tends to be worn away as the game progresses (cricket can also be played on artificial surfaces, notably matting). Each wicket is made of three wooden stumps topped by two bails.[75]

As illustrated, the pitch is marked at each end with four white painted lines: a bowling crease, a popping crease and two return creases. The three stumps are aligned centrally on the bowling crease, which is eight feet eight inches long. The popping crease is drawn four feet in front of the bowling crease and parallel to it; although it is drawn as a 12 ft (3.7 m) line (six feet on either side of the wicket), it is, in fact, unlimited in length. The return creases are drawn at right angles to the popping crease so that they intersect the ends of the bowling crease; each return crease is drawn as an 8 ft (2.4 m) line, so that it extends four feet behind the bowling crease, but is also, in fact, unlimited in length.[76]
Match structure
Before a match begins, the team captains (who are also players) toss a coin to decide which team will bat first and so take the first innings.[77] "Innings" is the term used for each phase of play in the match.[77] In each innings, one team bats, attempting to score runs, while the other team bowls and fields the ball, attempting to restrict the scoring and dismiss the batters.[78][79] When the first innings ends, the teams change roles; there can be two to four innings depending upon the type of match. A match with four scheduled innings is played over three to five days; a match with two scheduled innings is usually completed in a single day.[77] During an innings, all eleven members of the fielding team take the field, but usually only two members of the batting team are on the field at any given time.[a] The order of batters is usually announced just before the match, but it can be varied.[72]
The main objective of each team is to score more runs than their opponents, but in some forms of cricket, it is also necessary to dismiss all but one of the opposition batters (making their team 'all out') in their final innings in order to win the match, which would otherwise be drawn (not ending with a winner or tie.)[82]
Clothing and equipment

The wicket-keeper (a specialised fielder behind the batter) and the batters wear protective gear because of the hardness of the ball, which can be delivered at speeds of more than 145 kilometres per hour (90 mph) and presents a major health and safety concern. Protective clothing includes pads (designed to protect the knees and shins), batting gloves or wicket-keeper's gloves for the hands, a safety helmet for the head, and a box for male players inside the trousers (to protect the crotch area).[83] Some batters wear additional padding inside their shirts and trousers such as thigh pads, arm pads, rib protectors and shoulder pads. The only fielders allowed to wear protective gear are those in positions very close to the batter (i.e., if they are alongside or in front of him), but they cannot wear gloves or external leg guards.[84]
Subject to certain variations, on-field clothing generally includes a collared shirt with short or long sleeves; long trousers; woolen pullover (if needed); cricket cap (for fielding) or a safety helmet; and spiked shoes or boots to increase traction. The kit is traditionally all white, and this remains the case in Test and first-class cricket, but in limited overs cricket, team colours are now worn instead.[85]
Bat and ball
i) A used white ball. White balls are mainly used in limited overs cricket, especially in matches played at night, under floodlights (left).
The essence of the sport is that a bowler delivers (i.e., bowls) the ball from their end of the pitch towards the batter who, armed with a bat, is "on strike" at the other end (see next sub-section: Basic gameplay).
The bat is made of wood, usually Salix alba (white willow), and has the shape of a blade topped by a cylindrical handle. The blade must not be more than 4.25 inches (10.8 cm) wide and the total length of the bat not more than 38 inches (97 cm). There is no standard for the weight, which is usually between 2 lb 7 oz and 3 lb (1.1 and 1.4 kg).[86][87]
The ball is a hard leather-seamed spheroid, with a circumference of 9 inches (23 cm). The ball has a "seam": six rows of stitches attaching the leather shell of the ball to the string and cork interior. The seam on a new ball is prominent and helps the bowler propel it in a less predictable manner. During matches, the quality of the ball deteriorates to a point where it is no longer usable; during the course of this deterioration, its behaviour in flight will change and can influence the outcome of the match. Players will, therefore, attempt to modify the ball's behaviour by modifying its physical properties. Polishing the ball and wetting it with sweat or saliva was legal, even when the polishing was deliberately done on one side only to increase the ball's swing through the air. The use of saliva has since been made illegal due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[88] The acts of rubbing other substances into the ball, scratching the surface or picking at the seams constitute illegal ball tampering.[89]
Player roles
Basic gameplay: bowler to batter
During normal play, thirteen players and two umpires are on the field. Two of the players are batters and the rest are all eleven members of the fielding team. The other nine players in the batting team are off the field in the pavilion. The image with overlay below shows what is happening when a ball is being bowled and which of the personnel are on or close to the pitch.[90]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the photo, the two batters (3 and 8, wearing yellow) have taken position at each end of the pitch (6). Three members of the fielding team (4, 10 and 11, wearing dark blue) are in shot. One of the two umpires (1, wearing white hat) is stationed behind the wicket (2) at the bowler's (4) end of the pitch. The bowler (4) is bowling the ball (5) from his end of the pitch to the batter (8) at the other end who is called the "striker". The other batter (3) at the bowling end is called the "non-striker". The wicket-keeper (10), who is a specialist, is positioned behind the striker's wicket (9), and behind him stands one of the fielders in a position called "first slip" (11). While the bowler and the first slip are wearing conventional kit only, the two batters and the wicket-keeper are wearing protective gear, including safety helmets, padded gloves and leg guards (pads).
While the umpire (1) in shot stands at the bowler's end of the pitch, his colleague stands in the outfield, usually in or near the fielding position called "square leg", so that he is in line with the popping crease (7) at the striker's end of the pitch. The bowling crease (not numbered) is the one on which the wicket is located between the return creases (12). The bowler (4) intends to hit the wicket (9) with the ball (5) or at least prevent the striker (8) from scoring runs. The striker (8) intends, by using his bat, to defend his wicket and, if possible, hit the ball away from the pitch in order to score runs.
Some players are skilled in both batting and bowling, or either of these as well as wicket-keeping, so are termed all-rounders. Bowlers are classified according to their style, generally as fast bowlers, seam bowlers or spinners. Batters are classified according to whether they are right-handed or left-handed.
Overs
The Laws state that, throughout an innings, "the ball shall be bowled from each end alternately in overs of 6 balls".[91] The name "over" came about because the umpire calls "Over!" when six legal balls (deliveries) have been bowled. At this point, another bowler is deployed at the other end, and the fielding side changes ends while the batters do not. A bowler cannot bowl two successive overs, although a bowler can (and usually does) bowl alternate overs, from the same end, for several overs which are termed a "spell"; if the captain wants a bowler to "change ends", another bowler must temporarily fill in so that the change is not immediate. The batters do not change ends at the end of the over, and so the one who was non-striker is now the striker and vice versa. The umpires also change positions so that the one who was at "square leg" now stands behind the wicket at the nonstriker's end and vice versa.[91]
Fielding

Of the eleven fielders, three are in shot in the image above. The other eight are elsewhere on the field, their positions determined on a tactical basis by the captain or the bowler. Fielders often change position between deliveries, again as directed by the captain or bowler.[84]
If a fielder is injured or becomes ill during a match, a substitute is allowed to field instead of the aforementioned fielder, but the substitute cannot bowl or act as a captain, except in the case of concussion substitutes in international cricket.[81] The substitute leaves the field when the injured player is fit to return.[92] The Laws of Cricket were updated in 2017 to allow substitutes to act as wicket-keepers.[93]
Batting and scoring
Batters take turns to bat via a batting order which is decided beforehand by the team captain and presented to the umpires, though the order remains flexible when the captain officially nominates the team.[72] Substitute batters are generally not allowed,[92] except in the case of concussion substitutes in international cricket.[81]
In order to begin batting the batter first adopts a batting stance. Standardly, this involves adopting a slight crouch with the feet pointing across the front of the wicket, looking in the direction of the bowler, and holding the bat so it passes over the feet and so its tip can rest on the ground near to the toes of the back foot.[94]
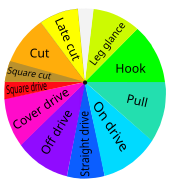
A skilled batter can use a wide array of "shots" or "strokes" in both defensive and attacking mode. The idea is to hit the ball to the best effect with the flat surface of the bat's blade. If the ball touches the side of the bat, it is called an "edge". The batter does not have to play a shot and can allow the ball to go through to the wicket-keeper. Equally, the batter does not have to attempt a run when hitting the ball with their bat. Batters do not always seek to hit the ball as hard as possible, and a good player can score runs by simply making a deft stroke with a turn of the wrists, or by simply "blocking" the ball but directing it away from fielders so that the player has time to take a run. A wide variety of shots are played, the batter's repertoire including strokes named according to the style of swing and the direction aimed: e.g., "cut", "drive", "hook", and "pull".[95]

The batter on strike (i.e., the "striker") must prevent the ball from hitting the wicket and try to score runs by hitting the ball with their bat so that the batter and their partner have time to switch places, with each of them running from one end of the pitch to the other before the fielding side can return the ball and attempt a run out (throwing the ball at one of the wickets before the run is scored.) To register a run, both runners must touch the ground behind the popping crease with either their bats or their bodies (the batters carry their bats as they run) before a fielder can throw the ball at the nearby wicket. Each completed run increments the score of both the team and the striker.[96]
The decision to attempt a run is ideally made by the batter who has the better view of the ball's progress, and this is communicated by calling, usually "yes", "no" or "wait". More than one run can be scored from a single hit. Hits worth one to three runs are common, but the size of the field is such that it is usually difficult to run four or more.[96] To compensate for this, hits that reach the boundary of the field are automatically awarded four runs if the ball touches the ground en route to the boundary or six runs if the ball clears the boundary without touching the ground within the boundary. In these cases the batters do not need to run.[97] Hits for five are unusual and generally rely on the help of "overthrows" by a fielder returning the ball.

If an odd number of runs is scored by the striker, the two batters have changed ends, and the one who was non-striker is now the striker. Only the striker can score individual runs, but all runs are added to the team's total.[96]
Additional runs can be gained by the batting team as extras (called "sundries" in Australia) due to errors made by the fielding side. This is achieved in four ways: no-ball, a penalty of one extra conceded by the bowler if they break the rules (often by failing to bowl the ball before their front foot passes the popping crease at their end);[98] wide, a penalty of one extra conceded by the bowler if they bowl so that the ball is out of the batter's reach;[99] bye, an extra awarded if the batter misses the ball and it goes past the wicket-keeper and gives the batters time to run in the conventional way;[100] and leg bye, as for a bye except that the ball has hit the batter's body, though not their bat.[100] If the bowler has bowled an illegal delivery (i.e., a no-ball or a wide), the bowler's team incurs an additional penalty because that ball (i.e., delivery) has to be bowled again, and hence the batting side has the opportunity to score more runs from this extra ball. In addition, the ways in which the batters can be dismissed on an illegal delivery greatly narrow down; in the case of a no-ball, which is the more egregious type of illegal delivery, the only common way in which the batters can be dismissed is by being run out.[98][99]
Dismissals
There are nine ways in which a batter can be dismissed: five relatively common and four extremely rare. When a batter is dismissed, they are said to have 'lost their wicket', and are barred from batting again in that innings; their team is also said to have 'lost a wicket'. Once a team has lost 10 wickets, its innings is over. The common forms of dismissal are bowled (when the striker fails to prevent a delivery from hitting their wicket),[101] caught (when a ball struck by the bat is caught by a fielder before it hits the ground),[102] leg before wicket (lbw - when the striker's body 'unfairly' prevents a delivery from hitting the wicket),[103] run out (generally when the ball is thrown at a wicket by a fielder while the batters are running between the wickets),[104] and stumped (a special type of run out).[105] Rare methods are hit wicket (a striker hitting their own wicket),[106] hit the ball twice,[107] obstructing the field,[108] and timed out (a batter failing to enter the field in a timely manner).[109] The Laws state that the fielding team, usually the bowler in practice, must appeal for a dismissal before the umpire can give their decision. If the batter is out, the umpire raises a forefinger and says "Out!"; otherwise, the umpire will shake their head and say "Not out".[110] There is, effectively, a tenth method of dismissal, retired out (self-dismissal - generally permanent except in cases of injury), which is not an on-field dismissal as such but rather a retrospective one for which no fielder is credited.[111]
Bowling

| Part of a series on |
| Bowling techniques |
|---|
Most bowlers are considered specialists in that they are selected for the team because of their skill as a bowler, although some are all-rounders, and even specialist batters bowl occasionally. These specialists bowl "spells" that are generally 4 to 8 overs long in order not to physically exhaust the bowler, cause muscle strain and stress the skeleton. The rules prevent a single bowler from bowling consecutive overs, resulting in at least two bowlers alternating each over. If the captain wants a bowler to "change ends", another bowler must temporarily fill in so that the change is not immediate.[91] The action of bowling the ball is akin to throwing, with the caveat that a bowler's elbow extension is almost entirely restricted, resulting in most bowlers maintaining a straight arm when releasing the ball during their delivery stride. Additionally, while the bowler is not required to pitch (bounce) the ball, a full toss (non-bouncing) delivery that reaches the striker above waist height is penalised as a no-ball.
A bowler reaches their delivery stride by means of a "run-up", and an over is deemed to have begun when the bowler starts their run-up for the first delivery of that over, the ball then being "in play".[91] Fast bowlers, or pacemen, need momentum, taking a lengthy run up, while bowlers with a slow delivery take no more than a couple of steps before bowling. The fastest bowlers can deliver the ball at a speed of over 145 kilometres per hour (90 mph), and they sometimes rely on sheer speed to try to defeat the batter, who is forced to react very quickly.[112] Other fast bowlers rely on a mixture of speed and guile by making the ball seam or swing (i.e., curve) in flight. This type of delivery can deceive a batter into miscuing their shot, for example, so that the ball just touches the edge of the bat and can then be "caught behind" by the wicket-keeper or a slip fielder.[112] At the other end of the bowling scale is the spin bowler, who bowls at a relatively slow pace and relies entirely on guile to deceive the batter. A spinner will often "buy their wicket" by "tossing one up" (in a slower, steeper parabolic path) to lure the batter into making a poor shot. The batter has to be very wary of such deliveries, as the batter is often "flighted" or spun so that the ball will not behave quite as the batter expects it to, and the batter could be "trapped" into getting themself out. Accidental full toss deliveries can also get wickets, as the failure of the ball to bounce can surprise a batsman or induce a poor stroke in an effort to punish the poor delivery with a boundary hit.[113] In between the pacemen and the spinners are the medium-paced seamers, who rely on persistent accuracy to try to contain the rate of scoring and wear down the batter's concentration.[112]
Specialist roles
The captain is often the most experienced player in the team, certainly the most tactically astute, and can possess any of the main skillsets as a batter, a bowler or a wicket-keeper. Within the Laws, the captain has certain responsibilities in terms of nominating their players to the umpires before the match and ensuring that the captain's players conduct themselves "within the spirit and traditions of the game as well as within the Laws".[72]
The wicket-keeper (sometimes called simply the "keeper") is a specialist fielder subject to various rules within the Laws about their equipment and demeanour. The wicket-keeper is the only member of the fielding side who can effect a stumping and is the only one permitted to wear gloves and external leg guards.[114]
Depending on their primary skills, the other ten players in the team tend to be classified as specialist batters or specialist bowlers. Generally, a team will include five or six specialist batters, and four or five specialist bowlers, plus the wicket-keeper.[115][116]
Match closure

There are a number of ways that a cricket match can end and its result be described, depending on whether the team batting first or last wins as well as the format of the game.
If the team batting last is 'all out' having scored fewer runs than their opponents, they are said to have "lost by n runs" (where n is the difference between the aggregate number of runs scored by the teams). If the team that bats last scores enough runs to win, it is said to have "won by n wickets", where n is the number of wickets left to fall (batters yet to be dismissed) until the team would have been all out. For example, a team that passes its opponents' total having lost six wickets (i.e., six of their batters have been dismissed) wins the match "by four wickets", since the team would only have been prevented from scoring the winning runs if four more of its batters had been dismissed, which would have resulted in all but one of its eleven batters being dismissed.[82]
In a two-innings-a-side match, one team's combined first and second innings total may be less than the other side's first innings total. The team with the greater score is then said to have "won by an innings and n runs" and does not need to bat again: n is the difference between the two teams' aggregate scores. If the team batting last is all out and both sides have scored the same number of runs, then the match is a tie; this result is quite rare in matches of two innings a side with only 62 happening in first-class matches from the earliest known instance in 1741 until January 2017. In the traditional form of the game, if the time allotted for the match expires before either side can win, then the game is declared a draw.[82]
If the match has only a single innings per side, then usually a maximum number of overs applies to each innings. Such a match is called a "limited overs" or "one-day" match, and the side scoring more runs wins regardless of the number of wickets lost, so that a draw cannot occur. In some cases, ties are broken by having each team bat for a one-over innings known as a Super Over; subsequent Super Overs may be played if the first Super Over ends in a tie. If this kind of match is temporarily interrupted by bad weather, then a complex mathematical formula, known as the Duckworth–Lewis–Stern method after its developers, is often used to recalculate a new target score. A one-day match can also be declared a "no-result" if fewer than a previously agreed number of overs have been bowled by either team, in circumstances that make normal resumption of play impossible, for example, wet weather.[82]
In all forms of cricket, the umpires can abandon the match if bad light or rain makes it impossible to continue.[117] There have been instances of entire matches, even Test matches scheduled to be played over five days, being lost to bad weather without a ball being bowled, for example, the third Test of the 1970/71 series in Australia.[118]
Innings

The innings (ending with 's' in both singular and plural form) is the term used for each phase of play during a match. Depending on the type of match being played, each team has either one or two innings. Sometimes all eleven members of the batting side take a turn to bat but, for various reasons, an innings can end before they have all done so. The innings terminates if the batting team is "all out", a term defined by the Laws: "At the fall of a wicket or the retirement of a batter, further balls remain to be bowled but no further batter is available to come in".[77] In this situation, one of the batters has not been dismissed and is termed not out; this is because he has no partners left and there must always be two active batters while the innings is in progress.
An innings may end early while there are still two not out batters:[77]
- the batting team's captain may declare the innings closed, even though some of the captain's players have not had a turn to bat: this is a tactical decision by the captain, usually because the captain believes that their team have scored sufficient runs and need time to dismiss the opposition in their innings
- the set number of overs (i.e., in a limited overs match) have been bowled
- the match has ended prematurely due to bad weather or running out of time
- in the final innings of the match, the batting side has reached its target (i.e., scored more runs than the opposition) and won the game.
Umpires and scorers


The game on the field is regulated by the two umpires, one of whom stands behind the wicket at the bowler's end and the other in a position called "square leg", which is about 15–20 m (49–66 ft) away from the batter on strike and in line with the popping crease on which that umpire is taking guard. The umpires have several responsibilities, including adjudication on whether a ball has been correctly bowled (i.e., not a no-ball or a wide); when a run is scored; whether a batter is out (the fielding side must first appeal to the umpire, usually with the phrase "How's that?" or "Howzat?"); when intervals start and end; and the suitability of the pitch, field and weather for playing the game. The umpires are authorised to interrupt or even abandon a match due to circumstances likely to endanger the players, such as a damp pitch or deterioration of the light.[117]
Off the field in televised matches, there is usually a third umpire who can make decisions on certain incidents with the aid of video evidence. The third umpire is mandatory under the playing conditions for Test and Limited Overs International matches played between two ICC full member countries. These matches also have a match referee whose job is to ensure that play is within the Laws and the spirit of the game.[117]
The match details, including runs and dismissals, are recorded by two official scorers, one representing each team. The scorers are directed by the hand signals of an umpire (see image, right). For example, the umpire raises a forefinger to signal that the batter is out (has been dismissed); the umpire raises both arms above their head if the batter has hit the ball for six runs. The scorers are required by the Laws to record all runs scored, wickets taken, and overs bowled; in practice, they also note significant amounts of additional data relating to the game.[119]
A match's statistics are summarised on a scorecard. Prior to the popularisation of scorecards, most scoring was done by men sitting on vantage points cuttings notches on tally sticks, and runs were originally called notches.[120] According to historian Rowland Bowen, the earliest known scorecard templates were introduced in 1776 by T. Pratt of Sevenoaks and soon came into general use.[121] It is believed that scorecards were printed and sold at Lord's for the first time in 1846.[122]
Scores are displayed differently depending on location, although it is standard to show how many wickets have been lost and how many runs a team has made. Within Australia, the format is Wickets/Runs, while in the rest of the world, the format is Runs/Wickets. For example, a score of 125 runs with 4 wickets lost would be displayed as 4/125 or 125/4, respectively.[123]
Spirit of the Game
Besides observing the Laws, cricketers must respect the "Spirit of Cricket", a concept encompassing sportsmanship, fair play and mutual respect. This spirit has long been considered an integral part of the sport but is only nebulously defined. Amidst concern that the spirit was weakening, in 2000, a Preamble was added to the Laws instructing all participants to play within the spirit of the game. The Preamble was last updated in 2017, now opening with the line:[124]
Cricket owes much of its appeal and enjoyment to the fact that it should be played not only according to the Laws, but also within the Spirit of Cricket.
The Preamble is a short statement intended to emphasise the "positive behaviours that make cricket an exciting game that encourages leadership, friendship, and teamwork".[125] Its second line states that, "the major responsibility for ensuring fair play rests with the captains, but extends to all players, match officials and, especially in junior cricket, teachers, coaches and parents".[124]
The umpires are the sole judges of fair and unfair play. They are required under the Laws to intervene in case of dangerous or unfair play or in cases of unacceptable conduct by a player.
Previous versions of the Spirit identified actions that were deemed contrary (for example, appealing knowing that the batter is not out), but all specifics are now covered in the Laws of Cricket, the relevant governing playing regulations and disciplinary codes, or left to the judgement of the umpires, captains, their clubs and governing bodies. The terse expression of the Spirit of Cricket now avoids trying to enumerate the diverse cultural conventions that exist in the detail of sportsmanship, or its absence.
Women's cricket

Women's cricket was first recorded in Surrey in 1745.[126] International development began at the start of the 20th century, and the first Test match was played between Australia and England in December 1934.[127] The following year, New Zealand joined them, and in 2007 Netherland became the tenth women's Test nation when they made their debut against South Africa. In 1958, the International Women's Cricket Council was founded (it merged with the ICC in 2005).[127] In 1973, the first Cricket World Cup of any kind took place when a Women's World Cup was held in England.[127] In 2005, the International Women's Cricket Council was merged with the International Cricket Council (ICC) to form one unified body to help manage and develop cricket. The ICC Women's Rankings were launched on 1 October 2015 covering all three formats of women's cricket. In October 2018 following the ICC's decision to award T20 International status to all members, the Women's rankings were split into separate ODI (for Full Members) and T20I lists.[128]
Governance

The International Cricket Council (ICC), which has its headquarters in Dubai, is the global governing body of cricket. It was founded as the Imperial Cricket Conference in 1909 by representatives from England, Australia and South Africa, renamed the International Cricket Conference in 1965 and took up its current name in 1989.[127] The ICC in 2017 has 105 member nations, twelve of which hold full membership and can play Test cricket.[129] The ICC is responsible for the organisation and governance of cricket's major international tournaments, notably the men's and women's versions of the Cricket World Cup. It also appoints the umpires and referees that officiate at all sanctioned Test matches, Limited Overs Internationals and Twenty20 Internationals.
Each member nation has a national cricket board which regulates cricket matches played in its country, selects the national squad, and organises home and away tours for the national team.[130] In the West Indies, which for cricket purposes is a federation of nations, these matters are addressed by Cricket West Indies.[131]
The table below lists the ICC full members and their national cricket boards:[132]
| Nation | Governing body | Full Member since[133] |
|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Afghanistan Cricket Board | 22 June 2017 |
| Australia | Cricket Australia | 15 July 1909 |
| Bangladesh | Bangladesh Cricket Board | 26 June 2000 |
| England | England and Wales Cricket Board | 15 July 1909 |
| India | Board of Control for Cricket in India | 31 May 1926 |
| Ireland | Cricket Ireland | 22 June 2017 |
| New Zealand | New Zealand Cricket | 31 May 1926 |
| Pakistan | Pakistan Cricket Board | 28 July 1952 |
| South Africa | Cricket South Africa | 15 July 1909 |
| Sri Lanka | Sri Lanka Cricket | 21 July 1981 |
| West Indies | Cricket West Indies | 31 May 1926 |
| Zimbabwe | Zimbabwe Cricket | 6 July 1992 |
Forms of cricket

Cricket is a multifaceted sport with multiple formats that can effectively be divided into first-class cricket, limited overs cricket, and historically, single wicket cricket.
The highest standard is Test cricket (always written with a capital "T") which is in effect the international version of first-class cricket and is restricted to teams representing the twelve countries that are full members of the ICC (see above). Although the term "Test match" was not coined until much later, Test cricket is deemed to have begun with two matches between Australia and England in the 1876–77 Australian season; since 1882, most Test series between England and Australia have been played for a trophy known as The Ashes. The term "first-class", in general usage, is applied to top-level domestic cricket. Test matches are played over five days and first-class over three to four days; in all of these matches, the teams are allotted two innings each and the draw is a valid result.[134]
Limited overs cricket is always scheduled for completion in a single day, and the teams are allotted one innings each. There are two main types: List A which normally allows fifty overs per team; and Twenty20 in which the teams have twenty overs each. Both of the limited overs forms are played internationally as Limited Overs Internationals (LOI) and Twenty20 Internationals (T20I). List A was introduced in England in the 1963 season as a knockout cup contested by the first-class county clubs. In 1969, a national league competition was established. The concept was gradually introduced to the other leading cricket countries and the first limited overs international was played in 1971. In 1975, the first Cricket World Cup took place in England. Twenty20 is a new variant of limited overs itself with the purpose being to complete the match within about three to four hours, usually in an evening session. The first Twenty20 World Championship was held in 2007. In addition, a few full-member cricket boards have decided to start leagues that are played in the T10 format,[135][136][137][138] in which games are intended to last approximately 90 minutes.[139][140] Most recently, in 2021, the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB) introduced a new league featuring a hundred-ball tournament, known as The Hundred.[141] Limited overs matches cannot be drawn, although a tie is possible and an unfinished match is a "no result".[142][143]
Single wicket was popular in the 18th and 19th centuries, and its matches were generally considered top-class. In this form, although each team may have from one to six players, there is only one batter in at a time, and that batter must face every delivery bowled while their innings lasts. Single wicket has rarely been played since limited overs cricket began. Matches tended to have two innings per team like a full first-class one and they could end in a draw.[144]
Competitions
Cricket is played at both the international and domestic level. There is one major international championship per format, and top-level domestic competitions mirror the three main international formats. There are now a number of T20 leagues, which have spawned a "T20 freelancer" phenomenon.[145]
International competitions
Most international matches are played as parts of 'tours', when one nation travels to another for a number of weeks or months, and plays a number of matches of various sorts against the host nation. Sometimes a perpetual trophy is awarded to the winner of the Test series, the most famous of which is The Ashes.
The ICC also organises competitions that are for several countries at once, including the ICC Men's Cricket World Cup, ICC T20 World Cup and ICC Champions Trophy. A league competition for Test matches played as part of normal tours, the ICC World Test Championship, had been proposed several times, and its first instance began in 2019. A league competition for ODIs, the ICC Cricket World Cup Super League, began in August 2020 and lasted only for one edition. The ICC maintains Test rankings, ODI rankings and T20 rankings systems for the countries which play these forms of cricket.
Competitions for member nations of the ICC with Associate status include the ICC Intercontinental Cup, for first-class cricket matches, and the World Cricket League for one-day matches, the final matches of which now also serve as the ICC World Cup Qualifier.
The game's only appearance in an Olympic Games was the 1900 Olympics.[146] However, it is scheduled to make a return, with the T20 format of the game, in the 2028 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles.[147][148]
National competitions

First-class
First-class cricket in England is played for the most part by the 18 county clubs which contest the County Championship. The concept of a champion county has existed since the 18th century but the official competition was not established until 1890.[45] The most successful club has been Yorkshire, who had won 32 official titles (plus one shared) as of 2019.[149]
Australia established its national first-class championship in 1892–93 when the Sheffield Shield was introduced. In Australia, the first-class teams represent the various states.[150] New South Wales has the highest number of titles.
The other ICC full members have national championship trophies called the Ahmad Shah Abdali 4-day Tournament (Afghanistan); the National Cricket League (Bangladesh); the Ranji Trophy (India); the Inter-Provincial Championship (Ireland); the Plunket Shield (New Zealand); the Quaid-e-Azam Trophy (Pakistan); the Currie Cup (South Africa); the Premier Trophy (Sri Lanka); the Shell Shield (West Indies); and the Logan Cup (Zimbabwe).
Limited overs
Other
Club and school cricket


The world's earliest known cricket match was a village cricket meeting in Kent which has been deduced from a 1640 court case recording a "cricketing" of "the Weald and the Upland" versus "the Chalk Hill" at Chevening "about thirty years since" (i.e., c. 1611). Inter-parish contests became popular in the first half of the 17th century and continued to develop through the 18th with the first local leagues being founded in the second half of the 19th.[20]
At the grassroots level, local club cricket is essentially an amateur pastime for those involved but still usually involves teams playing in competitions at weekends or in the evening. Schools cricket, first known in southern England in the 17th century, has a similar scenario and both are widely played in the countries where cricket is popular.[151] Although there can be variations in game format, compared with professional cricket, the Laws are always observed and club/school matches are therefore formal and competitive events.[152] The sport has numerous informal variants such as French cricket.[153]
Rivalries
Culture
Influence on everyday life
Cricket has had a broad impact on popular culture, both in the Commonwealth of Nations and elsewhere. It has, for example, influenced the lexicon of these nations, especially the English language, with various phrases such as "that's not cricket" (that's unfair), "had a good innings" (lived a long life), and "sticky wicket". "On a sticky wicket" (aka "sticky dog" or "glue pot")[154] is a metaphor[155] used to describe a difficult circumstance. It originated as a term for difficult batting conditions in cricket, caused by a damp and soft pitch.[156]
In the arts and popular culture
Cricket is the subject of works by noted English poets, including William Blake and Lord Byron.[157] Beyond a Boundary (1963), written by Trinidadian C. L. R. James, is often named the best book on any sport ever written.[158]
In the visual arts, notable cricket paintings include Albert Chevallier Tayler's Kent vs Lancashire at Canterbury (1907) and Russell Drysdale's The Cricketers (1948), which has been called "possibly the most famous Australian painting of the 20th century."[159] French impressionist Camille Pissarro painted cricket on a visit to England in the 1890s.[157] Francis Bacon, an avid cricket fan, captured a batter in motion.[157] Caribbean artist Wendy Nanan's cricket images[160] are featured in a limited edition first day cover for Royal Mail's "World of Invention" stamp issue, which celebrated the London Cricket Conference 1–3 March 2007, first international workshop of its kind and part of the celebrations leading up to the 2007 Cricket World Cup.[161]
In music, many calypsos make reference to the Sport of Cricket.
Influence on other sports

Cricket has close historical ties with Australian rules football and many players have competed at top levels in both sports.[162] In 1858, prominent Australian cricketer Tom Wills called for the formation of a "foot-ball club" with "a code of laws" to keep cricketers fit during the off-season. The Melbourne Football Club was founded the following year, and Wills and three other members codified the first laws of the game.[163] It is typically played on modified cricket fields.[164]
In England, a number of association football clubs owe their origins to cricketers who sought to play football as a means of keeping fit during the winter months. Derby County was founded as a branch of the Derbyshire County Cricket Club in 1884;[165] Aston Villa (1874) and Everton (1876) were both founded by members of church cricket teams.[166] Sheffield United's Bramall Lane ground was, from 1854, the home of the Sheffield Cricket Club, and then of Yorkshire; it was not used for football until 1862 and was shared by Yorkshire and Sheffield United from 1889 to 1973.[167]
In the late 19th century, a former cricketer, English-born Henry Chadwick of Brooklyn, New York, was credited with devising the baseball box score[168] (which he adapted from the cricket scorecard) for reporting game events. The first box score appeared in an 1859 issue of the Clipper.[169] The statistical record is so central to the game's "historical essence" that Chadwick is sometimes referred to as "the Father of Baseball" because he facilitated the popularity of the sport in its early days.[170]
The influence of English sports such as cricket in British India resulted in the local sports becoming standardised by the 1920s.[171] The 21st century success of the Indian Premier League also inspired the growth of other sports leagues in India,[172] with some of the native sports being further modernised, as with the popular Pro Kabaddi League.[173]
See also
Related sports
Footnotes
- ^ The term "amateur" in this context does not mean someone who played cricket in his spare time. Many amateurs in first-class cricket were full-time players during the cricket season. Some of the game's greatest players, including W. G. Grace, held amateur status.
Citations
- ^ Sensharma, Agastya (4 January 2024). "Cricket: A Gentleman's Game". The AVM Theory. Retrieved 11 September 2024.
- ^ a b "ICC survey reveals over a billion fans – 90% in subcontinent". ESPNcricinfo. 27 June 2018.
- ^ "Cricket, baseball, rounders and softball: What's the difference?". BBC. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ Major (2007), p. 17.
- ^ a b Barclays (1986), p. 1.
- ^ Altham (1962), pp. 19–20.
- ^ a b c Altham (1962), p. 21.
- ^ Underdown (2000), p. 3.
- ^ a b Major (2007), p. 19.
- ^ Altham (1962), p. 22.
- ^ a b Major (2007), p. 31.
- ^ a b Birley (1999), p. 3.
- ^ Bowen (1970), p. 33.
- ^ a b Terry, David (2000). "The Seventeenth Century Game of Cricket: A Reconstruction of the Game" (PDF). The Sports Historian, No. 20. London: The British Society of Sports History. pp. 33–43. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 June 2009. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- ^ Hardman, Ray (31 October 2013). "Before There Was Baseball, There Was Wicket". www.wnpr.org. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ Birley (1999), p. 9.
- ^ Barclays (1986), pp. 1–2.
- ^ Major (2007), pp. 21–22.
- ^ McCann (2004), p. xxxi.
- ^ a b Underdown (2000), p. 4.
- ^ McCann (2004), pp. xxxiii–xxxiv.
- ^ McCann (2004), pp. xxxi–xli.
- ^ Underdown (2000), pp. 11–15.
- ^ Birley (1999), pp. 7–8.
- ^ Major (2007), p. 23.
- ^ a b Birley (1999), p. 11.
- ^ "A Pictorial History of Cricket", by Brown, Bison Books, London, 1988
- ^ Birley (1999), pp. 11–13.
- ^ Webber (1960), p. 10.
- ^ Haygarth (1862), p. vi.
- ^ McCann (2004), p. xli.
- ^ Major (2007), page 36.
- ^ Major (2007), pp. 268–269.
- ^ Birley (1999), p. 19.
- ^ Williams (2012), p. 23.
- ^ Williams (2012), pp. 94–95.
- ^ Birley (1999), p. 146.
- ^ "The Pictorial History of Cricket", by Ashley Brown, Bison Books, London, 1988
- ^ Birley (1999), pp. 14–16.
- ^ Ashley-Cooper, F. S. (1900). "At the Sign of the Wicket: Cricket 1742–1751". Cricket: A Weekly Record of the Game. Cardiff: ACS. pp. 4–85. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017. Retrieved 8 September 2017.
- ^ Nyren (1833), pp. 153–154.
- ^ Wisden. "Evolution of the Laws of Cricket". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack, 100th edition (1963 ed.). London: Sporting Handbooks Ltd. pp. 184–187.
- ^ Birley (1999), pp. 64–67, 97–101.
- ^ Barclays (1986), p. 456.
- ^ a b "Annual Meeting of County Secretaries – the programme for 1890". Cricket: A Weekly Record of the Game. Cardiff: ACS. 1889. pp. 478–479. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- ^ Frith, David (1978). The Golden Age of Cricket: 1890–1914. Guildford: Lutterworth Press. ISBN 0-7188-7022-0.
- ^ Das, Deb (n.d.). "Cricinfo – Cricket in the USA". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 9 March 2007.
- ^ "The Pictorial History of Cricket", by Ashley Brown, 1988, London, Bison Books
- ^ Birley (1999), pp. 96–97.
- ^ Barclays (1986), pp. 62, 78, 87, 99, 113, 127 & 131.
- ^ Birley (1999), p. 97.
- ^ "The Australian Eleven: The first Australian team". National Museum of Australia. Archived from the original on 8 September 2018. Retrieved 30 December 2014.
- ^ Reg Hayter, "The Centenary Test Match", Wisden 1978, pp. 130–32.
- ^ Lewis, Wendy; Simon Balderstone & John Bowan (2006). Events That Shaped Australia. New Holland. p. 75. ISBN 978-1-74110-492-9.
- ^ Brown, 1988
- ^ "Bodyline: 80 years of cricket's greatest controversy". BBC. 16 January 2013. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ Wisden. "One-Day Knockout Competition, 1963". Wisden Cricketers' Almanack, 100th edition (1963 ed.). London: Sporting Handbooks Ltd. pp. 1074–1076.
- ^ Barclays (1986), pp. 495–496.
- ^ Barclays (1986), pp. 496–497.
- ^ "Test Cricket". Britannica. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ Ronay, Barney (8 April 2023). "The Indian Premier League is a brilliant thing – but is killing Test cricket". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "Two-year T20 World Cup cycle important for growth of cricket: ICC". The Indian Express. 22 November 2021. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "T20 cricket confirmed as one of five new sports at LA28". ESPNcricinfo. 16 October 2023. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "Thirty-two predictions for the future of Twenty20 cricket". The Independent.
- ^ Ben Morse, for (14 November 2019). "Pakistan to play first Test at home since 2009 terror attack". CNN. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- ^ "T20 Cricket". Britannica. 8 March 2024. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ "Mumbai fallout: India cancels cricket tour". NBC. 18 December 2008. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ "When Bangladesh made their Test cricket debut". Cricket County. 10 November 2012. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ "Afghanistan, Ireland get Test status". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- ^ "Ireland & Afghanistan awarded Test status by International Cricket Council". BBC Sport. 2017. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- ^ "Laws". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Law 1 – Players". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 19 – Boundaries". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 7 – The pitch". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 8 – The wickets". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 9 – The bowling, popping and return creases". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- ^ a b c d e "Law 12 – Innings". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 18 – Scoring runs". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 27 – Appeals". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- ^ "LAW 25 BATTER'S INNINGS; RUNNERS | MCC". www.lords.org. Archived from the original on 8 June 2019. Retrieved 5 January 2020.
- ^ a b c "ICC Test Match Playing Conditions" (PDF). ICC. 1 September 2019.
- ^ a b c d "Law 21 – The result". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 15 January 2017. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- ^ "Appendix D". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Law 41 – The fielder". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ Birley (1999), p. 343.
- ^ "Law 6 – The bat". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ^ "Appendix E – The bat". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ^ PTI (20 September 2022). "Saliva ban made permanent as ICC announces changes to playing conditions". The Hindu. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- ^ "Law 5 – The ball". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ^ The photo was taken during an international match between Australia and Sri Lanka; Muttiah Muralitharan of Sri Lanka is bowling to Australian batter Adam Gilchrist.
- ^ a b c d "Law 22 – The over". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Law 2 – Substitutes, etc". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ Marylebone Cricket Club. "Summary of changes to the Laws of Cricket 2017 Code" (PDF). Lords the Home of Cricket. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
- ^ "Grip, Stance, Back-Lift". Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- ^ "Batting". TalkCricket. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ a b c "Law 18 – Scoring runs". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 19 – Boundaries". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Law 24 – No ball". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Law 25 – Wide ball". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Law 26 – Bye and Leg bye". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 30 – Bowled". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 32 – Caught". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 36 – Leg before wicket". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 38 – Run out". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 39 – Stumped". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 35 – Hit wicket". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 34 – Hit the ball twice". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 37 – Obstructing the field". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 31 – Timed out". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 27 – Appeals". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 2 – Section 9: Batsman retiring". MCC. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 18 July 2017.
- ^ a b c "Types of fast bowling". TalkCricket. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Spin bowling". TalkCricket. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 40 – The wicket-keeper". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 16 April 2017. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ^ "Bowling Strategy". TalkCricket. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ "Batting Strategy". TalkCricket. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ a b c "Law 3 – The umpires". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ^ "Australia v England, 3rd Test, 1970/71". CricketArchive. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ^ "Law 4 – The scorers". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original on 2 July 2017. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ^ Bowen (1970), p. 57.
- ^ Bowen (1970), p. 266.
- ^ Bowen (1970), p. 274.
- ^ "Why Cricket is the Greatest Sport, : Australian reverse-score antics". Cricket365. 24 January 2019. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ a b "Preamble to the Laws". Laws of Cricket. MCC. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ "Summary of changes to the Laws of Cricket 2017 Code" (PDF). Laws of Cricket. MCC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2017. Retrieved 10 September 2018.
- ^ "ICC History of Cricket (pre-1799)". ICC. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ a b c d "ICC History of Cricket (20th century)". ICC. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ "ICC Launches Global Women's T20I Team Rankings". Retrieved 12 October 2018.
- ^ "About the ICC". ICC. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ "About the England and Wales Cricket Board". ECB. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ "Cricket West Indies". Cricket West Indies. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- ^ "ICC Rankings". International Cricket Council. ICC Development (International) Limited. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- ^ "A brief history ..." Cricinfo. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ Rundell, Michael (2006). Dictionary of Cricket. London: A&C Black Publishers Ltd. p. 336. ISBN 978-0-7136-7915-1. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "CPL to launch inaugural T10 tournament 'The 6ixty' in August". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ Desk, SportsCafe (21 November 2022). "Sri Lanka becomes first full-member cricket nation to introduce T10 League". SportsCafe.in. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "ZC to launch six-team T10 tournament in March 2023". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ "T10 League Plans Expansion To Five Locations After Thumbs Up From 2 ICC Full Members | Cricket News". NDTVSports.com. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ Quint, The (25 January 2021). "Explained: Everything You Need to Know About Cricket's T10 League". TheQuint. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ "Abu Dhabi T10 cricket league eyes global expansion". www.gulftoday.ae. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ "The Hundred timeline: How the ECB's new format came about". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ "ICC clarification of limited overs". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- ^ "The first official T20". ESPNcricinfo. 12 March 2016. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- ^ Major (2007), pp. 155–167 & 404–410.
- ^ "The T20 Revolution – The Freelancers". Cricbuzz. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ^ "The ignorant Olympians". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 11 July 2023.
- ^ "IOC approves Cricket for 2028 Los Angeles Olympics". The Economic Times. 13 October 2023. Retrieved 14 October 2023.
- ^ "International Olympic Committee approves cricket and four other sports for 2028 Games in Los Angeles". Sky Sports. 16 October 2023.
- ^ Playfair. Marshall, Ian (ed.). Playfair Cricket Annual (70th edition) (2017 ed.). London: Headline. p. 216.
- ^ Harte, p. 175.
- ^ Birley (1999), pp. 9–10.
- ^ Birley (1999), pp. 151–152.
- ^ "Rules of French Cricket". topend sports. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- ^ Green, Jonathon (1987). Dictionary of Jargon. Routledge. p. 528. ISBN 9780710099198.
- ^ Marcus Callies; Wolfram R. Keller; Astrid Lohöfer (2011). Bi-directionality in the Cognitive Sciences: Avenues, Challenges, and Limitations. John Benjamins Publishing. pp. 73–. ISBN 978-90-272-2384-5.
- ^ Robert Hendrickson (2001). World English: From Aloha to Zed. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-34518-3.
- ^ a b c Smart, Alastair (20 July 2013). "The art of cricket: Enough to leave you stumped", The Telegraph. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- ^ Rosengarten, Frank (2007). Urbane Revolutionary: C. L. R. James and the Struggle for a New Society. University Press of Mississippi, ISBN 87-7289-096-7 p. 134
- ^ Meacham, Steve (6 June 2009). "Montmartre, with eucalypts". Sydney Morning Herald. Fairfax. Retrieved 31 August 2009.
- ^ "Caribbean cricket art, in the middle". BBC News. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- ^ "Cricket: Dawn of a New World". Bletchley Park Post Office. March 2007. Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- ^ Blainey, Geoffrey (2010). A Game of Our Own: The Origins of Australian Football. Black Inc. p. 186. ISBN 978-1-86395-347-4.
- ^ de Moore, Greg (2008). Tom Wills: His Spectacular Rise and Tragic Fall. Allen & Unwin. pp. 77, 93–94. ISBN 978-1-74175-499-5.
- ^ Hess, Rob (2008). A National Game: The History of Australian Rules Football. Viking. p. 44. ISBN 978-0-670-07089-3.
- ^ Goldstein, p. 184.
- ^ Goldstein, pp. 15 & 184.
- ^ Goldstein, p. 458.
- ^ His Hall of Fame plaque states, in part: "Inventor of the box score. Author of the first rule-book ... Chairman of rules committee in first nationwide baseball organization." Lederer, Rich. By the Numbers: Computer technology has deepened fans' passion with the game's statistics. Memories and Dreams (Vol. 33, No. 6; Winter 2011[–2012], pp. 32–34). National Baseball Hall of Fame official magazine.
- ^ Pesca, Mike (30 July 2009). "The Man Who Made Baseball's Box Score a Hit". National Public Radio. Retrieved 8 March 2014.
- ^ Arango, Tim (12 November 2010). "Myth of baseball's creation endures, with a prominent fan". The New York Times. Retrieved 8 November 2014.
- ^ Love, Adam; Dzikus, Lars (26 February 2020). "How India came to love cricket, favored sport of its colonial British rulers". The Conversation. Retrieved 1 October 2024.
- ^ "From Handball To Panja, Why Sports Leagues Are Taking Off In India". Forbes India. Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- ^ "The end of cricket's Indian monopoly". The Economist. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 30 September 2024.
Sources
- Altham, H. S. (1962). A History of Cricket, Volume 1 (to 1914). London: George Allen & Unwin.
- Ashley-Cooper, F. S. (1900). At the Sign of the Wicket: Cricket 1742–1751. Cricket: A Weekly Record of the Game. London: Cricket Magazine. OCLC 28863559.
- Barclays (1986). Swanton, E. W. (ed.). Barclays World of Cricket. London: Willow Books. ISBN 0-00-218193-2.
- Birley, Derek (1999). A Social History of English Cricket. London: Aurum Press Ltd. ISBN 1-85410-710-0.
- Bowen, Rowland (1970). Cricket: A History of its Growth and Development. London: Eyre & Spottiswoode. ISBN 0-413-27860-3.
- Goldstein, Dan (2000). The Rough Guide to English Football (2000–2001). London: Rough Guides. ISBN 1-85828-557-7.
- Harte, Chris (1993). A History of Australian Cricket. London: Andre Deutsch. p. 175. ISBN 0-233-98825-4.
- Haygarth, Arthur (1862). Frederick Lillywhite's Cricket Scores & Biographies, Volume 1 (1744–1826). London: Frederick Lillywhite.
- Major, John (2007). More Than A Game. London: HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-00-718364-7.
- McCann, Tim (2004). Sussex Cricket in the Eighteenth Century. Lewes: Sussex Record Society. ISBN 0-85445-055-6.
- Nyren, John (1998) [First published 1833]. Ashley Mote (ed.). The Cricketers of my Time. London: Robson Books. ISBN 1-86105-168-9.
- Underdown, David (2000). Start of Play. London: Allen Lane. ISBN 0-713-99330-8.
- Webber, Roy (1960). The Phoenix History of Cricket. London: Phoenix House Ltd.
- Williams, Charles (2012). Gentlemen & Players – The Death of Amateurism in Cricket. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 978-0-7538-2927-1.
Further reading
- Guha, Ramachandra (2002). A Corner of a Foreign Field: The Indian History of a British Sport. London: Picador. ISBN 0-330-49117-2. OCLC 255899689.
























