Infrastructure tools to support an effective radiation oncology learning health system
Contents

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1H-Indene-1,3(2H)-dione | |
| Other names
Indandione; 1,3-Diketohydrindene; 1,3-Dioxoindane; 1,3-Hydrindendione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.191 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 146.145 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.37 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 129 to 132 °C (264 to 270 °F; 402 to 405 K)[1][2] |
| slight | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1,3-Indandione (sometimes simply indanedione) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4(CO)2CH2. It is a β-diketone with indane as its structural nucleus. It is a colorless or white solid, but old samples can appear yellowish[3] or even green. It is a popular chemical scaffold (building block of various useful chemical compounds).[4][5]
Structural properties
Solid 1,3-indandione is a diketone, As a solution in water, it is partially (~2%) enolized. The enolate anion exhibits significant delocalization, and the highest electron density is on the second carbon. This acid-base behavior explains many properties of the compound.[citation needed]
Preparation
1,3-Indandione can be prepared by decarboxylation of the sodium salt of 2-ethoxycarbonyl-1,3-indandione, which itself is obtained by Claisen condensation of ethyl acetate and dimethyl phthalate.[citation needed]
Chemical properties
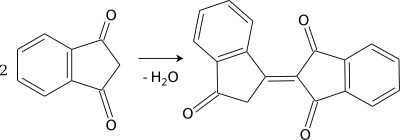
The carbon at the C-2 position is alpha to both carbonyls, and thus can act as a nucleophile. It undergoes self-aldol condensation quite easily, resulting in bindone.
Bromination occurs at the 2-position:
One or both carbonyl groups can be reduced to alcohol groups or methylene groups, depending on the method used.
See also
References
- ^ 1,3-Indandione at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ MSDS at Acros Organics, retrieved on June 16, 2011
- ^ (in Russian) Нейланд О. Я. Органическая химия: Учеб. для хим. спец. вузов. Москва: Высшая школа, 1990.— с. 481—490.
- ^ Dumur, Frédéric (2021). "Recent advances on visible light photoinitiators of polymerization based on Indane-1,3-dione and related derivatives". European Polymer Journal. 143: 110178. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.110178. S2CID 229445473.
- ^ Pluskota, Robert; Koba, Marcin (2018). "Indandione and Its Derivatives - Chemical Compounds with High Biological Potential". Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry. 18 (15): 1321–1330. doi:10.2174/1389557518666180330101809. PMID 29600759. S2CID 4516564.
External links
 Media related to 1,3-Indandione at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 1,3-Indandione at Wikimedia Commons