Histopathology image classification: Highlighting the gap between manual analysis and AI automation
| Old Norse | |
|---|---|
| Old Nordic, Old Scandinavian | |
| dǫnsk tunga ('Danish tongue') norrǿnt mál ('Northern speech') | |
| Native to | Scandinavia, Iceland, Faroe Islands, Greenland and other Norse settlements |
| Region | Nordic countries, Great Britain, Ireland, Isle of Man, Normandy, Newfoundland, the Volga and places in-between |
| Ethnicity | Norsemen and their descendants |
| Era | Evolved from Proto-Norse in the 8th century, developed into the various North Germanic languages by the 15th century |
Indo-European
| |
Early form | Proto-Norse (attested)
|
| Runic, later Latin (Old Norse alphabet) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | non |
| ISO 639-3 | non |
| Glottolog | oldn1244 |
| Part of a series on |
| Old Norse |
|---|
 |
| WikiProject Norse history and culture |
| Part of a series on the |
| Norsemen |
|---|
 |
| WikiProject Norse history and culture |
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic,[1] or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia, and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 8th to the 15th centuries.[2]
The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid- to late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not absolute, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century.[3][better source needed]
Old Norse was divided into three dialects: Old West Norse (Old West Nordic, often referred to as Old Norse),[4] Old East Norse (Old East Nordic), and Old Gutnish. Old West Norse and Old East Norse formed a dialect continuum, with no clear geographical boundary between them. Old East Norse traits were found in eastern Norway, although Old Norwegian is classified as Old West Norse, and Old West Norse traits were found in western Sweden. In what is present-day Denmark and Sweden, most speakers spoke Old East Norse. Though Old Gutnish is sometimes included in the Old East Norse dialect due to geographical associations, it developed its own unique features and shared in changes to both other branches.[5]
The 12th-century Icelandic Gray Goose Laws state that Swedes, Norwegians, Icelanders, and Danes spoke the same language, dǫnsk tunga ("Danish tongue"; speakers of Old East Norse would have said dansk tunga). Another term was norrœnt mál ("northern speech"). Today Old Norse has developed into the modern North Germanic languages Icelandic, Faroese, Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, and other North Germanic varieties of which Norwegian, Danish and Swedish retain considerable mutual intelligibility. Icelandic remains the most conservative language, such that in present-day Iceland, schoolchildren are able to read the 12th-century Icelandic sagas in the original language (in editions with normalised spelling).[6]
Geographical distribution
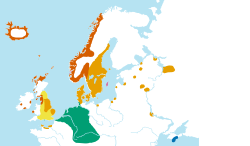
Old Icelandic was very close to Old Norwegian, and together they formed Old West Norse, which was also spoken in Norse settlements in Greenland, the Faroes, Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, northwest England, and in Normandy.[7] Old East Norse was spoken in Denmark, Sweden, Kievan Rus',[8] eastern England, and Danish settlements in Normandy. The Old Gutnish dialect was spoken in Gotland and in various settlements in the East.
In the 11th century, Old Norse was the most widely spoken European language, ranging from Vinland in the West to the Volga River in the East. In Kievan Rus', it survived the longest in Veliky Novgorod, probably lasting into the 13th century there.[8] The age of the Swedish-speaking population of Finland is strongly contested, but Swedish settlement had spread the language into the region by the time of the Second Swedish Crusade in the 13th century at the latest.[citation needed]
Modern descendants
The modern descendants of the Old West Norse dialect are the West Scandinavian languages of Icelandic, Faroese, Norwegian, and the extinct Norn language of Orkney and Shetland, although Norwegian was heavily influenced by the East dialect, and is today more similar to East Scandinavian (Danish and Swedish) than to Icelandic and Faroese. The descendants of the Old East Norse dialect are the East Scandinavian languages of Danish and Swedish.
Among these, the grammar of Icelandic and Faroese have changed the least from Old Norse in the last thousand years, though their pronunciations both have changed considerably from Old Norse. With Danish rule of the Faroe Islands, Faroese has also been influenced by Danish.
Both Middle English (especially northern English dialects within the area of the Danelaw) and Early Scots (including Lowland Scots) were strongly influenced by Norse and contained many Old Norse loanwords. Consequently, Modern English (including Scottish English), inherited a significant proportion of its vocabulary directly from Norse.
The development of Norman French was also influenced by Norse. Through Norman, to a smaller extent, so was modern French.
Written modern Icelandic derives from the Old Norse phonemic writing system. Contemporary Icelandic-speakers can read Old Norse, which varies slightly in spelling as well as semantics and word order. However, pronunciation, particularly of the vowel phonemes, has changed at least as much in Icelandic as in the other North Germanic languages.
Faroese retains many similarities but is influenced by Danish, Norwegian, and Gaelic (Scottish and/or Irish).[9] Although Swedish, Danish and Norwegian have diverged the most, they still retain considerable mutual intelligibility.[10] Speakers of modern Swedish, Norwegian and Danish can mostly understand each other without studying their neighboring languages, particularly if speaking slowly. The languages are also sufficiently similar in writing that they can mostly be understood across borders. This could be because these languages have been mutually affected by each other, as well as having a similar development influenced by Middle Low German.[11]
Other influenced languages
Various languages unrelated to Old Norse and others not closely related have been heavily influenced by Norse, particularly the Norman language; to a lesser extent, Finnish and Estonian. Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Lithuanian and Latvian also have a few Norse loanwords. The words Rus and Russia, according to one theory, may be named after the Rus' people, a Norse tribe, probably from present-day east-central Sweden. The current Finnish and Estonian words for Sweden are Ruotsi and Rootsi, respectively.
A number of loanwords have been introduced into Irish, many associated with fishing and sailing.[12][13][14][15] A similar influence is found in Scottish Gaelic, with over one hundred loanwords estimated to be in the language, many of which are related to fishing and sailing.[16][17][18]
Phonology
Vowels
Old Norse vowel phonemes mostly come in pairs of long and short. The standardized orthography marks the long vowels with an acute accent. In medieval manuscripts, it is often unmarked but sometimes marked with an accent or through gemination.
Old Norse had nasalized versions of all ten vowel places.[cv 1][obsolete source] These occurred as allophones of the vowels before nasal consonants and in places where a nasal had followed it in an older form of the word, before it was absorbed into a neighboring sound. If the nasal was absorbed by a stressed vowel, it would also lengthen the vowel. This nasalization also occurred in the other Germanic languages, but were not retained long. They were noted in the First Grammatical Treatise, and otherwise might have remained unknown. The First Grammarian marked these with a dot above the letter.[cv 1] This notation did not catch on, and would soon be obsolete. Nasal and oral vowels probably merged around the 11th century in most of Old East Norse.[19] However, the distinction still holds in Dalecarlian dialects.[20] The dots in the following vowel table separate the oral from nasal phonemes.
| Front vowels | Back vowels | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unrounded | Rounded | Unrounded | Rounded | |||||
| Close | i • ĩ | iː • ĩː | y • ỹ | yː • ỹː | u • ũ | uː • ũː | ||
| Mid | e • ẽ | eː • ẽː | ø • ø̃ | øː • ø̃ː | o • õ | oː • õː | ||
| Open, open-mid | ɛ • ɛ̃ | ɛː • ɛ̃ː | œ • œ̃ | a • ã | aː • ãː | ɔ • ɔ̃ | ɔː • ɔ̃ː | |
Note: The open or open-mid vowels may be transcribed differently:
- /æ/ = /ɛ/
- /ɒ/ = /ɔ/
- /ɑ/ = /a/
Sometime around the 13th century, /ɔ/ (spelled ⟨ǫ⟩) merged with /ø/ or /o/ in most dialects except Old Danish, and Icelandic where /ɔ/ (ǫ) merged with /ø/. This can be determined by their distinction within the 12th-century First Grammatical Treatise but not within the early 13th-century Prose Edda. The nasal vowels, also noted in the First Grammatical Treatise, are assumed to have been lost in most dialects by this time (but notably they are retained in Elfdalian and other dialects of Ovansiljan). See Old Icelandic for the mergers of /øː/ (spelled ⟨œ⟩) with /ɛː/ (spelled ⟨æ⟩) and /ɛ/ (spelled ⟨ę⟩) with /e/ (spelled ⟨e⟩).
| Front vowels | Back vowels | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unrounded | Rounded | Unrounded | Rounded | |||||
| High | i | iː | y | yː | u | uː | ||
| Mid | e | eː | ø | øː | o | oː | ||
| Low/Low-mid | ɛ | ɛː | a | aː | ||||
Old Norse had three diphthong phonemes: /ɛi/, /ɔu/, /øy ~ ɛy/ (spelled ⟨ei⟩, ⟨au⟩, ⟨ey⟩ respectively). In East Norse these would monophthongize and merge with /eː/ and /øː/, whereas in West Norse and its descendants the diphthongs remained.
| Proto-Germanic | Northwest Germanic | Primitive Old West Norse | Old Icelandic (1st Grammarian) |
Later Old Icelandic | Example (Old Norse) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | a | a ⟨a⟩ | a | a | land "land" < *landą |
| a | a (+i-mut) | ɛ ⟨ę⟩ | e ⟨e⟩ | e | menn "men" < *manniz |
| a | a (+u/w-mut) | ɔ ⟨ǫ⟩ | ɔ | ø ⟨ö⟩ | lǫnd "lands" < *landu < *landō; sǫngr "song" < sǫngr < *sangwaz |
| a | a (+i-mut +w-mut) | œ ⟨ø₂⟩ | ø | ø ⟨ö⟩ | gøra "to make" < *garwijaną |
| æː ⟨ē⟩ | aː | aː ⟨á⟩ | aː | aː | láta "to let" < *lētaną |
| æː ⟨ē⟩ | aː (+i-mut) | ɛː ⟨æ⟩ | ɛː | ɛː | mæla "to speak" < *mālijan < *mēlijaną |
| æː ⟨ē⟩ | aː (+u-mut) | ɔː ⟨ǫ́⟩ | ɔː | aː ⟨á⟩ | mǫ́l "meals" < '*mālu < *mēlō |
| e | e | e ⟨e⟩ | e | e | sex "six" < *seks; bresta "to burst" < *brestaną |
| e | e (+u/w-mut) | ø ⟨ø₁⟩ | ø | ø ⟨ö⟩ | tøgr "ten" < *teguz |
| e | e (broken) | ea ⟨ea⟩ | ja ⟨ja⟩ | ja | gjalda "to repay" < *geldaną |
| e | e (broken +u/w-mut) | eo/io ⟨eo⟩/⟨io⟩ | jo > jɔ ⟨jǫ⟩ | jø ⟨jö⟩ | skjǫldr "shield" < *skelduz |
| eː ⟨ē₂⟩ | eː | eː ⟨é⟩ | eː | eː | lét "let (past tense)" < *lē₂t |
| i | i | i ⟨i⟩ | i | i | mikill "great" < *mikilaz |
| i | i (+w-mut) | y ⟨y⟩ | y | y(ː) | slyngva "to sling" < *slingwaną |
| iː | iː | iː ⟨í⟩ | iː | iː | líta "to look" < *lītaną |
| oː | oː | oː ⟨ó⟩ | oː | oː | fór "went" < *fōr; mót "meeting" < *mōtą |
| oː | oː (+i-mut) | øː ⟨œ⟩ | øː | ɛː ⟨æ⟩ | mœðr "mothers" < *mōdriz |
| u | u | u ⟨u⟩ | u | u | una "to be content" < *unaną |
| u | u (+i-mut) | y ⟨y⟩ | y | y | kyn "race" < *kunją |
| u | u (+a-mut) | o ⟨o⟩ | o | o | fogl/fugl "bird" < *fuglaz; morginn "morning" < *murganaz |
| uː | uː | uː ⟨ú⟩ | uː | uː | drúpa "to droop" < *drūpaną |
| uː | uː (+i-mut) | yː ⟨ý⟩ | yː | yː | mýss "mice" < *mūsiz |
| ai | ai | ai > ɛi ⟨ei⟩ | ɛi | ɛi | bein, Gut. bain "bone" < *bainą |
| ai | ai (+w-mut) | øy ⟨ey⟩, ⟨øy⟩ | øy ⟨ey⟩[21] | ɛy | kveykva "to kindle" < *kwaikwaną |
| au | au | au > ɔu ⟨au⟩ | ɔu ⟨au⟩ | au | lauss "loose" < *lausaz |
| au | au (+i-mut) | øy ⟨ey⟩, ⟨øy⟩ | øy ⟨ey⟩ | ɛy | leysa "to loosen" < *lausijaną |
| eu | eu | eu ⟨eu⟩ | juː ⟨jú⟩ | juː | djúpr "deep" < *deupaz |
| eu | eu (+dental) | eo ⟨eo⟩ | joː ⟨jó⟩ | juː | bjóða/bjúða "to offer" < *beudaną |
| Ṽ | Ṽ | Ṽ | Ṽ | V | komȧ < *kwemaną "to come, arrive"; OWN vėtr/vėttr < vintr < *wintruz "winter" |
| Ṽː | Ṽː | Ṽː | Ṽː | Vː | hȧ́r "shark" < *hanhaz; ȯ́rar "our" (pl.) < *unseraz; ø̇́rȧ "younger" (acc. neut. wk.[cv 1]) < *junhizą [22] |
Consonants
Old Norse has six plosive phonemes, /p/ being rare word-initially and /d/ and /b/ pronounced as voiced fricative allophones between vowels except in compound words (e.g. veðrabati), already in the Proto-Germanic language (e.g. *b *[β] > [v] between vowels). The /ɡ/ phoneme was pronounced as [ɡ] after an /n/ or another /ɡ/ and as [k] before /s/ and /t/. Some accounts have it a voiced velar fricative [ɣ] in all cases, and others have that realisation only in the middle of words and between vowels (with it otherwise being realised [ɡ]).[23][24][clarification needed] The Old East Norse /ʀ/ was an apical consonant, with its precise position unknown; it is reconstructed as a palatal sibilant.[25][26] It descended from Proto-Germanic /z/ and eventually developed into /r/, as had already occurred in Old West Norse.
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Labiovelar | Glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosive | p b | t d | k ɡ | ||||
| Nasal | m | n | (ŋ) | ||||
| Fricative | f (v) | θ (ð) | s | ʀ[a] | (ɣ) | h | |
| Trill | r | ||||||
| Approximant | j | w | |||||
| Lateral approximant | l |
- ^ Reconstructed as [ɹ̝] when part of the stem of a word with a voiceless allophone [ɹ̝̊] word-finally when not part of the stem.[citation needed]
The consonant digraphs ⟨hl⟩, ⟨hr⟩, and ⟨hn⟩ occurred word-initially. It is unclear whether they were sequences of two consonants (with the first element realised as /h/ or perhaps /x/) or as single voiceless sonorants /l̥/, /r̥/ and /n̥/ respectively. In Old Norwegian, Old Danish and later Old Swedish, the groups ⟨hl⟩, ⟨hr⟩, and ⟨hn⟩ were reduced to plain ⟨l⟩, ⟨r⟩, ⟨n⟩, which suggests that they had most likely already been pronounced as voiceless sonorants by Old Norse times.
The pronunciation of ⟨hv⟩ is unclear, but it may have been /xʷ/ (the Proto-Germanic pronunciation), /hʷ/ or the similar phoneme /ʍ/. Unlike the three other digraphs, it was retained much longer in all dialects. Without ever developing into a voiceless sonorant in Icelandic, it instead underwent fortition to a plosive /kv/, which suggests that instead of being a voiceless sonorant, it retained a stronger frication.
Accent
Primary stress in Old Norse falls on the word stem, so that hyrjar would be pronounced /ˈhyr.jar/. In compound words, secondary stress falls on the second stem (e.g. lærisveinn, /ˈlɛːɾ.iˌswɛinː/).[27]
Orthography
Unlike Proto-Norse, which was written with the Elder Futhark, runic Old Norse was originally written with the Younger Futhark, which had only 16 letters. Because of the limited number of runes, several runes were used for different sounds, and long and short vowels were not distinguished in writing. Medieval runes came into use some time later.
As for the Latin alphabet, there was no standardized orthography in use in the Middle Ages. A modified version of the letter wynn called vend was used briefly for the sounds /u/, /v/, and /w/. Long vowels were sometimes marked with acutes but also sometimes left unmarked or geminated. The standardized Old Norse spelling was created in the 19th century and is, for the most part, phonemic. The most notable deviation is that the nonphonemic difference between the voiced and the voiceless dental fricative is marked. The oldest texts and runic inscriptions use þ exclusively. Long vowels are denoted with acutes. Most other letters are written with the same glyph as the IPA phoneme, except as shown in the table below.
Phonological processes
Ablaut
Ablaut patterns are groups of vowels which are swapped, or ablauted, in the nucleus of a word. Strong verbs ablaut the lemma's nucleus to derive the past forms of the verb. This parallels English conjugation, where, e.g., the nucleus of sing becomes sang in the past tense and sung in the past participle. Some verbs are derived by ablaut, as the present-in-past verbs do by consequence of being derived from the past tense forms of strong verbs.
Umlaut
Umlaut or mutation is an assimilatory process acting on vowels preceding a vowel or semivowel of a different vowel backness. In the case of i-umlaut and ʀ-umlaut, this entails a fronting of back vowels, with retention of lip rounding. In the case of u-umlaut, this entails labialization of unrounded vowels. Umlaut is phonemic and in many situations grammatically significant as a side effect of losing the Proto-Germanic morphological suffixes whose vowels created the umlaut allophones.
Some /y/, /yː/, /ø/, /øː/, /ɛ/, /ɛː/, /øy/,[21] and all /ɛi/ were obtained by i-umlaut from /u/, /uː/, /o/, /oː/, /a/, /aː/, /au/, and /ai/ respectively. Others were formed via ʀ-umlaut from /u/, /uː/, /a/, /aː/, and /au/.[7]
Some /y/, /yː/, /ø/, /øː/, and all /ɔ/, /ɔː/ were obtained by u-umlaut from /i/, /iː/, /e/, /eː/, and /a/, /aː/ respectively. See Old Icelandic for information on /ɔː/.
/œ/ was obtained through a simultaneous u- and i-umlaut of /a/. It appears in words like gøra (gjǫra, geyra), from Proto-Germanic *garwijaną, and commonly in verbs with a velar consonant before the suffix like søkkva < *sankwijaną.[cv 2]
OEN often preserves the original value of the vowel directly preceding runic ʀ while OWN receives ʀ-umlaut. Compare runic OEN glaʀ, haʀi, hrauʀ with OWN gler, heri (later héri), hrøyrr/hreyrr ("glass", "hare", "pile of rocks").
U-umlaut
U-umlaut is more common in Old West Norse in both phonemic and allophonic positions, while it only occurs sparsely in post-runic Old East Norse and even in runic Old East Norse.
| Meaning | West Old Norse | Old Swedish[1] | Modern Swedish | Icelandic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transcription | IPA | Transcription | IPA | |||
| Guardian / Caretaker | vǫrðr | varþer | vård | [voːɖ] | vörður | [ˈvœrðʏr] |
| Eagle | ǫrn | ørn | örn | [œːɳ] | örn | [œrtn] |
| Earth | jǫrð | iorþ | jord [2] | [juːɖ] | jörð | [jœrð] |
| Milk | mjǫlk | miolk | mjölk [2] | [mjœlk] | mjólk | [mjoul̥k] |
- ^ Old Swedish orthography uses ⟨þ⟩ to represent both /ð/ and /θ/. The change from Norse ⟨ð⟩ to Old Swedish ⟨þ⟩ represents only a change in orthography rather than a change in sound. Similarly ⟨i⟩ is used in place of ⟨j⟩. And thus changes from Norse ⟨j⟩ to Old Swedish ⟨i⟩ to Swedish ⟨j⟩ should be viewed as a change in orthography.
- ^ Represents the u-umlaut found in Swedish.
This is still a major difference between Swedish and Faroese and Icelandic today. Plurals of neuters do not have u-umlaut at all in Swedish, but in Faroese and Icelandic they do, for example the Faroese and Icelandic plurals of the word land, lond and lönd respectively, in contrast to the Swedish plural land and numerous other examples. That also applies to almost all feminine nouns, for example the largest feminine noun group, the o-stem nouns (except the Swedish noun jord mentioned above), and even i-stem nouns and root nouns, such as Old West Norse mǫrk (mörk in Icelandic) in comparison with Modern and Old Swedish mark.[29]
Breaking
Vowel breaking, or fracture, caused a front vowel to be split into a semivowel-vowel sequence before a back vowel in the following syllable.[7] While West Norse only broke /e/, East Norse also broke /i/. The change was blocked by a /w/, /l/, or /ʀ/ preceding the potentially-broken vowel.[7][30]
Some /ja/ or /jɔ/ and /jaː/ or /jɔː/ result from breaking of /e/ and /eː/ respectively.[cv 3]
Assimilation or elision of inflectional ʀ
When a noun, pronoun, adjective, or verb has a long vowel or diphthong in the accented syllable and its stem ends in a single l, n, or s, the r (or the elder r- or z-variant ʀ) in an ending is assimilated.[cv 4] When the accented vowel is short, the ending is dropped.
The nominative of the strong masculine declension and some i-stem feminine nouns uses one such -r (ʀ). Óðin-r (Óðin-ʀ) becomes Óðinn instead of *Óðinr (*Óðinʀ).
The verb blása ('to blow'), has third person present tense blæss ('[he] blows') rather than *blæsr (*blæsʀ).[31] Similarly, the verb skína ('to shine') had present tense third person skínn (rather than *skínr, *skínʀ); while kala ('to cool down') had present tense third person kell (rather than *kelr, *kelʀ).
The rule is not absolute, with certain counter-examples such as vinr ('friend'), which has the synonym vin, yet retains the unabsorbed version, and jǫtunn ('giant'), where assimilation takes place even though the root vowel, ǫ, is short.
The clusters */Clʀ, Csʀ, Cnʀ, Crʀ/ cannot yield */Clː, Csː, Cnː, Crː/ respectively, instead /Cl, Cs, Cn, Cr/.[32] The effect of this shortening can result in the lack of distinction between some forms of the noun. In the case of vetr ('winter'), the nominative and accusative singular and plural forms are identical. The nominative singular and nominative and accusative plural would otherwise have been OWN *vetrr, OEN *wintrʀ. These forms are impossible because the cluster */Crʀ/ cannot be realized as /Crː/, nor as */Crʀ/, nor as */Cʀː/. The same shortening as in vetr also occurs in lax = laks ('salmon') (as opposed to *lakss, *laksʀ), botn ('bottom') (as opposed to *botnn, *botnʀ), and jarl (as opposed to *jarll, *jarlʀ).
Furthermore, wherever the cluster */rʀ/ is expected to exist, such as in the male names Ragnarr, Steinarr (supposedly *Ragnarʀ, *Steinarʀ), the result is apparently always /rː/ rather than */rʀ/ or */ʀː/. This is observable in the Runic corpus.
Phonotactics
Blocking of ii, uu
In Old Norse, i/j adjacent to i, e, their u-umlauts, and æ was not possible, nor u/v adjacent to u, o, their i-umlauts, and ǫ.[7] At the beginning of words, this manifested as a dropping of the initial /j/ (which was general, independent of the following vowel) or /v/. Compare ON orð, úlfr, ár with English word, wolf, year. In inflections, this manifested as the dropping of the inflectional vowels. Thus, klæði + dat -i remains klæði, and sjáum in Icelandic progressed to sjǫ́um > sjǫ́m > sjám.[33] The *jj and *ww of Proto-Germanic became ggj and ggv respectively in Old Norse, a change known as Holtzmann's law.[7]
Epenthesis
An epenthetic vowel became popular by 1200 in Old Danish, 1250 in Old Swedish and Old Norwegian, and 1300 in Old Icelandic.[34] An unstressed vowel was used which varied by dialect. Old Norwegian exhibited all three: /u/ was used in West Norwegian south of Bergen, as in aftur, aftor (older aptr); North of Bergen, /i/ appeared in aftir, after; and East Norwegian used /a/, after, aftær.[21]
Grammar
Old Norse was a moderately inflected language with high levels of nominal and verbal inflection. Most of the fused morphemes are retained in modern Icelandic, especially in regard to noun case declensions, whereas modern Norwegian in comparison has moved towards more analytical word structures.
Gender
Old Norse had three grammatical genders – masculine, feminine, and neuter. Adjectives or pronouns referring to a noun must mirror the gender of that noun, so that one says, "heill maðr!" but, "heilt barn!". As in other languages, the grammatical gender of an impersonal noun is generally unrelated to an expected natural gender of that noun. While indeed karl, "man" is masculine, kona, "woman", is feminine, and hús, "house", is neuter, so also are hrafn and kráka, for "raven" and "crow", masculine and feminine respectively, even in reference to a female raven or a male crow.
All neuter words have identical nominative and accusative forms,[35] and all feminine words have identical nominative and accusative plurals.[36]
The gender of some words' plurals does not agree with that of their singulars, such as lim and mund.[cv 5] Some words, such as hungr, have multiple genders, evidenced by their determiners being declined in different genders within a given sentence.[37][38]
Morphology
Nouns, adjectives, and pronouns were declined in four grammatical cases – nominative, accusative, genitive, and dative – in singular and plural numbers. Adjectives and pronouns were additionally declined in three grammatical genders. Some pronouns (first and second person) could have dual number in addition to singular and plural. The genitive was used partitively and in compounds and kennings (e.g., Urðarbrunnr, the well of Urðr; Lokasenna, the gibing of Loki).
There were several classes of nouns within each gender. The following is an example of the "strong" inflectional paradigms:
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | armr | armar |
| Accusative | arm | arma |
| Genitive | arms | |
| Dative | armi | ǫrmum/armum |
| Old West Norse | Old East Norse | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative- Accusative |
Singular | hǫll | hall |
| Plural | hallir | hallar | |
| Genitive | Singular | hallar | |
| Plural | halla | ||
| Dative | Singular | hǫllu | hallu |
| Plural | hǫllum | hallum | |
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative-Accusative | troll | |
| Genitive | trolls | trolla |
| Dative | trolli | trollum |
The numerous "weak" noun paradigms had a much higher degree of syncretism between the different cases; i.e. they had fewer forms than the "strong" nouns.
A definite article was realised as a suffix that retained an independent declension; e.g., troll (a troll) – trollit (the troll), hǫll (a hall) – hǫllin (the hall), armr (an arm) – armrinn (the arm). This definite article, however, was a separate word and did not become attached to the noun before later stages of the Old Norse period.
Texts
The earliest inscriptions in Old Norse are runic, from the 8th century. Runes continued to be commonly used until the 15th century and have been recorded to be in use in some form as late as the 19th century in some parts of Sweden. With the conversion to Christianity in the 11th century came the Latin alphabet. The oldest preserved texts in Old Norse in the Latin alphabet date from the middle of the 12th century. Subsequently, Old Norse became the vehicle of a large and varied body of vernacular literature. Most of the surviving literature was written in Iceland. Best known are the Norse sagas, the Icelanders' sagas and the mythological literature, but there also survives a large body of religious literature, translations into Old Norse of courtly romances, classical mythology, and the Old Testament, as well as instructional material, grammatical treatises and a large body of letters and official documents.[39]
Dialects
Most of the innovations that appeared in Old Norse spread evenly through the Old Norse area. As a result, the dialects were very similar and considered to be the same language, a language that they sometimes called the Danish tongue (Dǫnsk tunga), sometimes Norse language (Norrœnt mál), as evidenced in the following two quotes from Heimskringla by Snorri Sturluson:
Móðir Dyggva var Drótt, dóttir Danps konungs, sonar Rígs er fyrstr var konungr kallaðr á danska tungu. |
Dyggvi's mother was Drott, the daughter of king Danp, Ríg's son, who was the first to be called king in the Danish tongue. |
| —Heimskringla, Ynglinga saga § 20. Dauði Dyggva |
...stirt var honum norrœnt mál, ok kylfdi mᴊǫk til orðanna, ok hǫfðu margir menn þat mᴊǫk at spotti. |
...the Norse language was hard for him, and he often fumbled for words, which amused people greatly. |
| —Heimskringla, Saga Sigurðar Jórsalafara, Eysteins ok Ólafs § 35(34). Frá veðjan Haralds ok Magnús |
However, some changes were geographically limited and so created a dialectal difference between Old West Norse and Old East Norse.
As Proto-Norse evolved into Old Norse, in the 8th century, the effects of the umlauts seem to have been very much the same over the whole Old Norse area. But in later dialects of the language a split occurred mainly between west and east as the use of umlauts began to vary. The typical umlauts (for example fylla from fullijan) were better preserved in the West due to later generalizations in the east where many instances of umlaut were removed (many archaic Eastern texts as well as eastern runic inscriptions however portray the same extent of umlauts as in later Western Old Norse).
All the while, the changes resulting in breaking (for example hiarta from *hertō) were more influential in the East probably once again due to generalizations within the inflectional system. This difference was one of the greatest reasons behind the dialectalization that took place in the 9th and 10th centuries, shaping an Old West Norse dialect in Norway and the Atlantic settlements and an Old East Norse dialect in Denmark and Sweden.
Old West Norse and Old Gutnish did not take part in the monophthongization which changed æi (ei) into ē, øy (ey) and au into ø̄, nor did certain peripheral dialects of Swedish, as seen in modern Ostrobothnian dialects.[40] Another difference was that Old West Norse lost certain combinations of consonants. The combinations -mp-, -nt-, and -nk- were assimilated into -pp-, -tt- and -kk- in Old West Norse, but this phenomenon was limited in Old East Norse.
Here is a comparison between the two dialects as well as Old Gutnish. It is a transcription from one of the Funbo Runestones in Sweden (U 990) from the eleventh century:
Veðr
Weðr
Weðr
ok
ok
ok
Þegn
Þegn
Þegn
ok
ok
ok
Gunnarr
Gunnarr
Gunnarr
reistu
ræistu
raistu
stein
stæin
stain
þenna
þenna
þenna
at
at
at
Haursa,
Haursa,
Haursa,
fǫður
faður
faður
sinn.
sinn.
sinn.
Guð
Guð
Guð
hjalpi
hialpi
hialpi
ǫnd
and
and
hans.
hans
hans
(Old West Norse)
(Old East Norse)
(Old Gutnish)
translation: 'Veðr and Thegn and Gunnar raised this stone after Haursi, their father. God help his spirit'
The OEN original text above is transliterated according to traditional scholarly methods, wherein u-umlaut is not regarded in runic Old East Norse. Modern studies[citation needed] have shown that the positions where it applies are the same as for runic Old West Norse. An alternative and probably more accurate transliteration would therefore render the text in OEN as such:
Some past participles and other words underwent i-umlaut in Old West Norse but not in Old East Norse dialects. Examples of that are Icelandic slegið/sleginn and tekið/tekinn, which in Swedish are slagit/slagen and tagit/tagen. This can also be seen in the Icelandic and Norwegian words sterkur and sterk ("strong"), which in Swedish is stark as in Old Swedish.[41] These differences can also be seen in comparison between Norwegian and Swedish.
Old West Norse
Old West Norse is by far the best attested variety of Old Norse.[42] The term Old Norse is often used to refer to Old West Norse specifically, in which case the broader subject receives another name, such as Old Scandinavian.[4] Another designation is Old West Nordic.
The combinations -mp-, -nt-, and -nk- mostly merged to -pp-, -tt- and -kk- in Old West Norse around the 7th century, marking the first distinction between the Eastern and Western dialects.[43] The following table illustrates this:
| English | Old West Norse | Old East Norse | Proto-Norse |
|---|---|---|---|
| mushroom | s(v)ǫppr | swampʀ | *swampuz |
| steep | brattr | brantʀ | *brantaz |
| widow | ekkja | ænkija | *ain(a)kjōn |
| to shrink | kreppa | krimpa | *krimpan |
| to sprint | spretta | sprinta | *sprintan |
| to sink | søkkva | sænkwa | *sankwijan |
An early difference between Old West Norse and the other dialects was that Old West Norse had the forms bú, "dwelling", kú, "cow" (accusative) and trú, "faith", whereas Old East Norse bó, kó and tró. Old West Norse was also characterized by the preservation of u-umlaut, which meant that, for example, Proto-Norse *tanþu, "tooth", became tǫnn and not tann as in post-runic Old East Norse; OWN gǫ́s and runic OEN gǫ́s, while post-runic OEN gás "goose".
The earliest body of text appears in runic inscriptions and in poems composed c. 900 by Þjóðólfr of Hvinir (although the poems are not preserved in contemporary sources, but only in much later manuscripts). The earliest manuscripts are from the period 1150–1200 and concern legal, religious and historical matters. During the 12th and 13th centuries, Trøndelag and Western Norway were the most important areas of the Norwegian kingdom and they shaped Old West Norse as an archaic language with a rich set of declensions. In the body of text that has survived into the modern day from until c. 1300, Old West Norse had little dialect variation, and Old Icelandic does not diverge much more than the Old Norwegian dialects do from each other.[citation needed]
Old Norwegian differentiated early from Old Icelandic by the loss of the consonant h in initial position before l, n and r; thus whereas Old Icelandic manuscripts might use the form hnefi, "fist", Old Norwegian manuscripts might use nefi.
From the late 13th century, Old Icelandic and Old Norwegian started to diverge more. After c. 1350, the Black Death and following social upheavals seem to have accelerated language changes in Norway. From the late 14th century, the language used in Norway is generally referred to as Middle Norwegian.[citation needed]
Old West Norse underwent a lengthening of initial vowels at some point, especially in Norwegian, so that OWN eta became éta, ONW akr > ákr, OIC ek > ék.[44]
Old Icelandic
In Iceland, initial /w/ before /ɾ/ was lost:[cv 6] compare Icelandic rangur with Danish vrang, OEN wrangʀ. The change is shared with Old Gutnish.[34]
A specifically Icelandic sound, the long, u-umlauted A, spelled ⟨Ǫ́ ⟩ and pronounced /ɔː/, developed around the early 11th century.[cv 1] It was short-lived, being marked in the Grammatical Treatises and remaining until the end of the 12th century.[cv 1] It then merged back into /aː/; as a result, long A is not affected by u-umlaut in Modern Icelandic.
/w/ merged with /v/ during the 12th century,[7] which caused /v/ to become an independent phoneme from /f/ and the written distinction of ⟨v⟩ for /v/ from medial and final ⟨f⟩ to become merely etymological.
Around the 13th century, Œ/Ǿ (/øː/, which had probably already lowered to /œː/) merged to Æ (/ɛː/).[cv 7] Thus, pre-13th-century grœnn (with ⟨œ⟩) 'green' became spelled as in modern Icelandic grænn (with ⟨æ⟩). The 12th-century Gray Goose Laws manuscripts distinguish the vowels, and so does the Codex Regius copy.[cv 7] However, the 13th-century Codex Regius copy of the Poetic Edda probably relied on newer or poorer quality sources, or both. Demonstrating either difficulty with or total lack of natural distinction, the manuscripts show separation of the two phonemes in some places, but they frequently confuse the letters chosen to distinguish them in others.[cv 7][45]
Towards the end of the 13th century, Ę (/ɛ/) merged to E (/e/).[cv 8]
Old Norwegian
Around the 11th century, Old Norwegian ⟨hl⟩, ⟨hn⟩, and ⟨hr⟩ became ⟨l⟩, ⟨n⟩ and ⟨r⟩.[46][failed verification] It is debatable whether the ⟨hC⟩ sequences represented a consonant cluster (/hC/) or devoicing (/C̥/).
Orthographic evidence suggests that in a confined dialect of Old Norwegian, /ɔ/ may have been unrounded before /u/ and that u-umlaut was reversed unless the u had been eliminated: ǫll, ǫllum > ǫll, allum.[47]
Greenlandic Norse
This dialect of Old West Norse was spoken by Icelandic colonies in Greenland. When the colonies died out around the 15th century, the dialect went with it. The phoneme /θ/ and some instances of /ð/ merged to /t/ and so Old Icelandic Þórðr became Tortr.
Text example
The following text is from Alexanders saga, an Alexander romance. The manuscript, AM 519 a 4to, is dated c. 1280. The facsimile demonstrates the sigla used by scribes to write Old Norse. Many of them were borrowed from Latin. Without familiarity with these abbreviations, the facsimile will be unreadable to many. In addition, reading the manuscript itself requires familiarity with the letterforms of the native script. The abbreviations are expanded in a version with normalized spelling like that of the standard normalization system. Compared to the spelling of the same text in Modern Icelandic, pronunciation has changed greatly, but spelling has changed little since Icelandic orthography was intentionally modelled after Old Norse in the 19th century.
| Digital facsimile of the manuscript text[48] | The same text with normalized spelling[48] | The same text with Modern Icelandic spelling |
|---|---|---|
|
[...] ſem oꝩın͛ h̅ſ brıgzloðo h̅o̅ epꞇ͛ þͥ ſe̅ ſıðaʀ mon ſagꞇ verða. Þeſſı ſveın̅ aͬ.* ꝩar ıſcola ſeꞇꞇr ſem ſıðꝩenıa e͛ ꞇıl rıkra man̅a vꞇan-lanꝺz aꞇ laꞇa g͛a vıð boꝛn̅ ſíıƞ́ Meıſꞇarı ꝩar h̅o̅ ꝼengın̅ ſa e͛ arıſꞇoꞇıleſ heꞇ. h̅ ꝩar harðla goðꝛ clercr ⁊ en̅ meſꞇı ſpekıngr aꞇ ꝩıꞇı. ⁊ er h̅ ꝩͬ.xíí. veꞇᷓ gamall aꞇ allꝺrı nalıga alroſcın̅ aꞇ ꝩıꞇı. en ſꞇoꝛhvgaðꝛ u̅ ꝼᷓm alla ſına ıaꝼnallꝺꝛa. |
[...] sem óvinir hans brigzluðu honum eftir því, sem síðarr man sagt verða. þessi sveinn Alexander var í skóla settr, sem siðvenja er til ríkra manna útanlands at láta gera við bǫrn sín. meistari var honum fenginn sá, er Aristoteles hét. hann var harðla góðr klerkr ok inn mesti spekingr at viti. ok er hann var tólv vetra gamall at aldri, náliga alroskinn at viti, en stórhugaðr umfram alla sína jafnaldra, [...] |
[...] sem óvinir hans brigsluðu honum eftir því, sem síðar mun sagt verða. Þessi sveinn Alexander var í skóla settur, sem siðvenja er til ríkra manna utanlands að láta gera við börn sín. Meistari var honum fenginn sá, er Aristóteles hét. Hann var harla góður klerkur og hinn mesti spekingur að viti og er hann var tólf vetra gamall að aldri, nálega alroskinn að viti, en stórhugaður umfram alla sína jafnaldra, [...] |
* a printed in uncial. Uncials not encoded separately in Unicode as of this section's writing.
Old East Norse

Old East Norse or Old East Nordic between 800 and 1100 is called Runic Swedish in Sweden and Runic Danish in Denmark, but for geographical rather than linguistic reasons. Any differences between the two were minute at best during the more ancient stages of this dialect group. Changes had a tendency to occur earlier in the Danish region. Even today many Old Danish changes have still not taken place in modern Swedish. Swedish is therefore the more conservative of the two in both the ancient and the modern languages, sometimes by a profound margin. The language is called "runic" because the body of text appears in runes.
Runic Old East Norse is characteristically conservative in form, especially Swedish (which is still true for modern Swedish compared to Danish). In essence it matches or surpasses the conservatism of post-runic Old West Norse, which in turn is generally more conservative than post-runic Old East Norse. While typically "Eastern" in structure, many later post-runic changes and trademarks of OEN had yet to happen.
The phoneme ʀ, which evolved during the Proto-Norse period from z, was still clearly separated from r in most positions, even when being geminated, while in OWN it had already merged with r.
The Proto-Germanic phoneme /w/ was preserved in initial sounds in Old East Norse (w-), unlike in West Norse where it developed into /v/. It survived in rural Swedish dialects in the provinces of Westro- and North Bothnia, Skåne, Blekinge, Småland, Halland, Västergötland and south of Bohuslän into the 18th, 19th and 20th century. It is still preserved in the Dalecarlian dialects in the province of Dalarna, Sweden, and in Jutlandic dialects in Denmark. The /w/-phoneme did also occur after consonants (kw-, tw-, sw- etc.) in Old East Norse and did so into modern times in said Swedish dialects and in a number of others. Generally, the initial w-sound developed into [v] in dialects earlier than after consonants where it survived much longer.
In summation, the /w/-sound survived in the East Nordic tongues almost a millennium longer than in the West Norse counterparts, and does still subsist at the present.
Monophthongization of æi > ē and øy, au > ø̄ started in mid-10th-century Denmark.[21] Compare runic OEN: fæigʀ, gæiʀʀ, haugʀ, møydōmʀ, diūʀ; with Post-runic OEN: fēgher, gēr, hø̄gher, mø̄dōmber, diūr; OWN: feigr, geirr, haugr, meydómr, dýr; from PN *faigijaz, *gaizaz, *haugaz, *mawi- + dōmaz 'maidendom; virginity', *diuza '(wild) animal'.
Feminine o-stems often preserve the plural ending -aʀ, while in OWN they more often merge with the feminine i-stems: (runic OEN) *sōlaʀ, *hafnaʀ, *hamnaʀ, *wāgaʀ versus OWN sólir, hafnir and vágir (modern Swedish solar, hamnar, vågar ("suns, havens, scales"); Danish has mainly lost the distinction between the two stems, with both endings now being rendered as -er or -e alternatively for the o-stems).
Vice versa, masculine i-stems with the root ending in either g or k tended to shift the plural ending to that of the ja-stems while OEN kept the original: drængiaʀ, *ælgiaʀ and *bænkiaʀ versus OWN drengir, elgir ("elks") and bekkir (modern Danish drenge, elge, bænke, modern Swedish drängar, älgar, bänkar).
The plural ending of ja-stems were mostly preserved while those of OWN often acquired that of the i-stems: *bæðiaʀ, *bækkiaʀ, *wæfiaʀ versus OWN beðir ("beds"), bekkir, vefir (modern Swedish bäddar, bäckar, vävar).
Old Danish
Until the early 12th century, Old East Norse was very much a uniform dialect. It was in Denmark that the first innovations appeared that would differentiate Old Danish from Old Swedish (Bandle 2005, Old East Nordic, pp. 1856, 1859) as these innovations spread north unevenly (unlike the earlier changes that spread more evenly over the East Norse area), creating a series of isoglosses going from Zealand to Svealand.
In Old Danish, /hɾ/ merged with /ɾ/ during the 9th century.[49] From the 11th to 14th centuries, the unstressed vowels -a, -o and -e (standard normalization -a, -u and -i) started to merge into -ə, represented with the letter ⟨e⟩. This vowel came to be epenthetic, particularly before -ʀ endings.[34] At the same time, the voiceless stop consonants p, t and k became voiced plosives and even fricative consonants. Resulting from these innovations, Danish has kage (cake), tunger (tongues) and gæster (guests) whereas (Standard) Swedish has retained older forms, kaka, tungor and gäster (OEN kaka, tungur, gæstir).
Moreover, the Danish pitch accent shared with Norwegian and Swedish changed into stød around this time.[citation needed]
Old Swedish
At the end of the 10th and early 11th century initial h- before l, n and r was still preserved in the middle and northern parts of Sweden, and is sporadically still preserved in some northern dialects as g-, e.g. gly (lukewarm), from hlýʀ. The Dalecarlian dialects developed independently from Old Swedish[50] and as such can be considered separate languages from Swedish.
Text example
This is an extract from Västgötalagen, the Westrogothic law. It is the oldest text written as a manuscript found in Sweden and from the 13th century. It is contemporaneous with most of the Icelandic literature. The text marks the beginning of Old Swedish as a distinct dialect.
Dræpær maþar svænskan man eller smalenskæn, innan konongsrikis man, eigh væstgøskan, bøte firi atta ørtogher ok þrettan markær ok ænga ætar bot. [...] Dræpar maþær danskan man allæ noræn man, bøte niv markum. Dræpær maþær vtlænskan man, eigh ma frid flyia or landi sinu oc j æth hans. Dræpær maþær vtlænskæn prest, bøte sva mykit firi sum hærlænskan man. Præstær skal i bondalaghum væræ. Varþær suþærman dræpin ællær ænskær maþær, ta skal bøta firi marchum fiurum þem sakinæ søkir, ok tvar marchar konongi. |
If someone slays a Swede or a Smålander, a man from the kingdom, but not a West Geat, he will pay eight örtugar and thirteen marks, but no weregild. [...] If someone slays a Dane or a Norwegian, he will pay nine marks. If someone slays a foreigner, he shall not be banished and have to flee to his clan. If someone slays a foreign priest, he will pay as much as for a fellow countryman. A priest counts as a freeman. If a Southerner is slain or an Englishman, he shall pay four marks to the plaintiff and two marks to the king. |
| —Västgötalagen |
Old Gutnish
Due to Gotland's early isolation from the mainland, many features of Old Norse did not spread from or to the island, and Old Gutnish developed as an entirely separate branch from Old East and West Norse. For example, the diphthong ai in aigu, þair and waita was not subject to anticipatory assimilation to ei as in e.g. Old Icelandic eigu, þeir and veita. Gutnish also shows dropping of /w/ in initial /wɾ/, which it shares with the Old West Norse dialects (except Old East Norwegian[51]), but which is otherwise abnormal. Breaking was also particularly active in Old Gutnish, leading to e.g. biera versus mainland bera.[34]
Text example
The Guta lag 'law of the Gutes' is the longest text surviving from Old Gutnish. Appended to it is a short texting dealing with the history of the Gotlanders. This part relates to the agreement that the Gotlanders had with the Swedish king sometime before the 9th century:
So gingu gutar sielfs wiliandi vndir suia kunung þy at þair mattin frir Oc frelsir sykia suiariki j huerium staþ. vtan tull oc allar utgiftir. So aigu oc suiar sykia gutland firir vtan cornband ellar annur forbuþ. hegnan oc hielp sculdi kunungur gutum at waita. En þair wiþr þorftin. oc kallaþin. sendimen al oc kunungr oc ierl samulaiþ a gutnal þing senda. Oc latta þar taka scatt sinn. þair sendibuþar aighu friþ lysa gutum alla steþi til sykia yfir haf sum upsala kunungi til hoyrir. Oc so þair sum þan wegin aigu hinget sykia. |
So, by their own will, the Gotlanders became the subjects of the Swedish king, so that they could travel freely and without risk to any location in the Swedish kingdom without toll and other fees. Likewise, the Swedes had the right to go to Gotland without corn restrictions or other prohibitions. The king was to provide protection and help, when they needed it and asked for it. The king and the jarl shall in return send emissaries to the Gutnish All-thing to receive the taxes. These emissaries shall declare free passage for the Gotlanders to all ports across the sea which belong to the king at Uppsala and likewise for everyone who want to travel to Gotland. |
| —Gutasaga, § Inträdet i Sverige |
Relationship to other languages
Relationship to English
Old English and Old Norse were related languages. It is therefore not surprising that many words in Old Norse look familiar to English speakers; e.g., armr (arm), fótr (foot), land (land), fullr (full), hanga (to hang), standa (to stand). This is because both English and Old Norse stem from a Proto-Germanic mother language. In addition, numerous common, everyday Old Norse words were adopted into the Old English language during the Viking Age. A few examples of Old Norse loanwords in modern English are (English/Viking Age Old East Norse), in some cases even displacing their Old English cognates:[citation needed]
- Nouns – anger (angr), bag (baggi), bait (bæit, bæita, bæiti), band (band), bark (bǫrkʀ, stem bark-), birth (byrðr), dirt (drit), dregs (dræggiaʀ), egg (ægg, related to OE. cognate æg which became Middle English eye/eai), fellow (félagi), gap (gap), husband (húsbóndi), cake (kaka), keel (kiǫlʀ, stem also kial-, kil-), kid (kið), knife (knífʀ), law (lǫg, stem lag-), leg (læggʀ), link (hlænkʀ), loan (lán, related to OE. cognate læn, cf. lend), race (rǫs, stem rás-), root (rót, related to OE. cognate wyrt, cf. wort), sale (sala), scrap (skrap), seat (sæti), sister (systir, related to OE. cognate sweostor), skill (skial/skil), skin (skinn), skirt (skyrta vs. the native English shirt of the same root), sky (ský), slaughter (slátr), snare (snara), steak (stæik), thrift (þrift), tidings (tíðindi), trust (traust), window (vindauga), wing (væ(i)ngʀ)
- Verbs – are (er, displacing OE sind), blend (blanda), call (kalla), cast (kasta), clip (klippa), crawl (krafla), cut (possibly from ON kuta), die (døyia), gasp (gæispa), get (geta), give (gifa/gefa, related to OE. cognate giefan), glitter (glitra), hit (hitta), lift (lyfta), raise (ræisa), ransack (rannsaka), rid (ryðia), run (rinna, stem rinn-/rann-/runn-, related to OE. cognate rinnan), scare (skirra), scrape (skrapa), seem (søma), sprint (sprinta), take (taka), thrive (þrífa(s)), thrust (þrysta), want (vanta)
- Adjectives – flat (flatr), happy (happ), ill (illr), likely (líklígʀ), loose (lauss), low (lágʀ), meek (miúkʀ), odd (odda), rotten (rotinn/rutinn), scant (skamt), sly (sløgʀ), weak (væikʀ), wrong (vrangʀ)
- Adverbs – thwart/athwart (þvert)
- Prepositions – till (til), fro (frá)
- Conjunction – though/tho (þó)
- Interjection – hail (hæill), wassail (ves hæill)
- Personal pronoun – they (þæiʀ), their (þæiʀa), them (þæim) (for which the Anglo-Saxons said híe,[52][53] hiera, him)
- Prenominal adjectives – same (sam)
In a simple sentence like "They are both weak", the extent of the Old Norse loanwords becomes quite clear (Old East Norse with archaic pronunciation: Þæiʀ eʀu báðiʀ wæikiʀ while Old English híe syndon bégen (þá) wáce). The words "they" and "weak" are both borrowed from Old Norse, and the word "both" might also be a borrowing, though this is disputed (cf. German beide).[who?] While the number of loanwords adopted from the Norse was not as numerous as that of Norman French or Latin, their depth and everyday nature make them a substantial and very important part of everyday English speech as they are part of the very core of the modern English vocabulary.[citation needed]
Tracing the origins of words like "bull" and "Thursday" is more difficult.[citation needed] "Bull" may derive from either Old English bula or Old Norse buli,[citation needed] while "Thursday" may be a borrowing or simply derive from the Old English Þunresdæg, which could have been influenced by the Old Norse cognate.[citation needed] The word "are" is from Old English earun/aron, which stems back to Proto-Germanic as well as the Old Norse cognates.[citation needed]
Relationship to modern Scandinavian languages
| Old Norse | Modern Icelandic |
Modern Faroese |
Modern Swedish[54] |
Modern Danish[54] |
Examples[n 1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a ⟨a⟩ | a(ː)[n 2] | a/ɛaː;[n 2] ɛ ⟨a⟩ (+ng,nk) |
a/ɑː[n 2] ⟨a⟩; ɔ/oː ⟨å⟩ (+ld,rd,ng) |
⟨a⟩; ɔ/ɔː ⟨å⟩ (+rd) |
ON land "land": Ic/Fa/Sw/Da/No land; ON dagr "day": Ic/Fa dagur, Sw/Da/No dag; ON harðr "hard": Ic/Fa harður, Sw/Da hård, No hard; ON langr "long": Ic/Fa langur, Sw lång, Da/No lang |
| ja ⟨ja⟩ | ja(ː) | ja/jɛaː | (j)ɛ(ː) ⟨(j)ä⟩ | jɛ: ⟨jæ⟩; jæ: ⟨je⟩ (+r) |
ON hjalpa "to help": Ic/Fa hjálpa, Sw hjälpa, Da hjælpe, No hjelpe, NN hjelpa; ON hjarta "heart": Ic/Fa hjarta, Sw hjärta, Da/NB hjerte, NN hjarta/hjarte |
| aː ⟨á⟩ | au(ː) | ɔ/ɔaː | ɔ/oː ⟨å⟩ | ɔ/ɒ: ⟨å⟩ | ON láta "to let": Ic/Fa láta, Sw låta, Da lade, No la |
| ɛː ⟨æ⟩ | ai(ː) | a/ɛaː | ɛ(ː) ⟨ä⟩ | ON mæla "to speak": Ic/Fa/NN mæla, Sw mäla, No mæle; ON sæll "happy": Ic sæll, Fa sælur, Sw säll, Da/No sæl | |
| e ⟨e⟩ | ɛ(ː) | ɛ/eː | ON menn "men": Ic/Fa menn, Sw män, Da mænd, No menn; ON bera "to bear": Ic/Fa bera, Sw bära, Da/NB bære, NN bera/bere; ON vegr "way": Ic/Fa vegur, Sw väg, Da vej, No veg/vei | ||
| eː ⟨é⟩ | jɛ(ː) | a/ɛaː ⟨æ⟩ | ON kné "knee": Ic hné, Fa/Da knæ, Sw knä, No kne | ||
| i ⟨i⟩ | ɪ(ː) | ɪ/iː | ɪ/iː ⟨i⟩ | e ⟨i⟩/ eː ⟨e⟩ |
ON kinn "cheek": Ic/Fa/No kinn, Sw/Da kind |
| iː ⟨í⟩ | i(ː) | ʊɪ(ː) ʊt͡ʃː ⟨íggj⟩[n 3] |
⟨i⟩ | ON tíð "time": Ic/Fa tíð, Sw/Da/No tid | |
| ɔ ⟨ǫ⟩ | ø > œ(ː) ⟨ö⟩ | œ/øː ⟨ø⟩ ɔ/oː ⟨o⟩ [n 4] |
⟨a⟩; ⟨o⟩;[n 5] ⟨ø⟩ (+r);[n 5] ⟨å⟩ (+ld,rd,ng) |
ON hǫnd "hand": Ic hönd, Fa hond, Sw/NN hand, Da/NB hånd; ON nǫs "nose": Ic nös, Fa nøs, Sw/NN nos, Da næse, NB nese, NN nase; ON ǫrn "eagle": Ic/Sw örn, Fa/Da/No ørn; ON sǫngr "song": Ic söngur, Fa songur, Sw sång, Da/NB sang, NN song | |
| jɔ ⟨jǫ⟩ | jø > jœ(ː) ⟨jö⟩ | jœ/jøː ⟨jø⟩ | (j)œ/(j)øː ⟨(j)ö⟩ | ON skjǫldr "shield": Ic skjöldur, Fa skjøldur, Sw sköld, Da/No skjold; ON bjǫrn "bear": Ic/Sw björn, Fa/Da/NN bjørn | |
| ɔː ⟨ǫ́⟩ | aː > au(ː) ⟨á⟩ | ɔ/ɔaː ⟨á⟩, œ/ɔuː ⟨ó⟩ | ɔ/oː ⟨å⟩ | ⟨å⟩ | ON tá (*tǫ́) "toe": Ic/Fa tá, Sw/Da/No tå |
| o ⟨o⟩ | ɔ(ː) | ɔ/oː | ɔ/oː ⟨o⟩ | ON morginn/morgunn "morning": Ic morgunn, Fa morgun, Sw/NN morgon, Da/NB morgen | |
| oː ⟨ó⟩ | ou(ː) | œ/ɔuː ɛkv ⟨ógv⟩[n 3] |
ʊ/uː ⟨o⟩ | ⟨o⟩ | ON bók "book": Ic/Fa bók, Sw/No bok, Da bog |
| u ⟨u⟩ | ʏ(ː) | ʊ/uː | ɵ/ʉː ⟨u⟩ | ON fullr "full": Ic/Fa fullur, Sw/Da/No full | |
| uː ⟨ú⟩ | u(ː) | ʏ/ʉuː ɪkv ⟨úgv⟩[n 3] |
⟨u⟩ | ON hús "house": Ic/Fa hús, Sw/Da/No hus | |
| joː ⟨jó⟩ | jou(ː) | jœ/jɔuː (j)ɛkv ⟨(j)ógv⟩[n 3] |
jɵ/jʉː ⟨ju⟩ | ⟨y⟩ | ON bjóða "to offer, command": Ic/Fa bjóða, Sw bjuda, Da/No byde, NN byda, No by |
| juː ⟨jú⟩ | ju(ː) | jʏ/jʉuː (j)ɪkv ⟨(j)úgv⟩[n 3] |
ON djúpr "deep": Ic/Fa djúpur, Sw/No djup, Da dyb, NB dyp | ||
| ø ⟨ø⟩ | ø > œ(ː) ⟨ö⟩ | œ/øː ⟨ø⟩ | œ/øː ⟨ö⟩ | ON gøra "to prepare": Sw göra | |
| øː ⟨œ⟩ | ɛː > ai(ː) ⟨æ⟩ | ⟨ø⟩ | ON grœnn "green": Ic grænn, Fa grønur, Sw grön, Da/NN grøn, No grønn | ||
| y ⟨y⟩ | ɪ(ː) | ɪ/iː | ⟨ö⟩; ⟨y⟩[n 6] |
ON dyrr "door": Ic/Fa dyr, Sw dörr, Da/No dør ON fylla "to fill": Ic/Fa/NN/Sw fylla, Da fylde, No fylle | |
| yː ⟨ý⟩ | i(ː) | ʊɪ(ː) ʊt͡ʃː ⟨ýggj⟩[n 3] |
ʏ/yː ⟨y⟩ | ⟨y⟩ | ON dýrr "dear": Ic dýr, Fa dýrur, Sw/Da/No dyr |
| ɛi ⟨ei⟩ | ei(ː) | aɪ(ː) at͡ʃː ⟨eiggj⟩[n 3] |
e(ː) ⟨e⟩ | ⟨e⟩ | ON steinn "stone": Ic steinn, Fa steinur, Sw/Da/NB sten, No stein |
| œy[21] ⟨ey⟩ | ei(ː) | ɔɪ(ː) ⟨oy⟩ ɔt͡ʃː ⟨oyggj⟩[n 3] |
œ/øː ⟨ö⟩ | ⟨ø⟩ | ON ey "island": Ic ey, Fa oyggj, Sw ö, Da ø, No øy |
| ɔu ⟨au⟩ | øy(ː) | ɛ/ɛɪː ⟨ey⟩ ɛt͡ʃː ⟨eyggj⟩[n 3] |
ON draumr "dream": Ic draumur, Fa dreymur, Sw dröm, Da/NB drøm, NN draum |
- ^ Bokmål Norwegian – Norwegianization of written Danish; Nynorsk Norwegian – Standardised written Norwegian based on Norwegian dialects; No = same in both forms of Norwegian.
- ^ a b c Vowel length in the modern Scandinavian languages does not stem from Old Norse vowel length. In all of the modern languages, Old Norse vowel length was lost, and vowel length became allophonically determined by syllable structure, with long vowels occurring when followed by zero or one consonants (and some clusters, e.g. in Icelandic, most clusters of obstruent to obstruent + [r], [j] or [v], such as [pr], [tj], [kv] etc.); short vowels occurred when followed by most consonant clusters, including double consonants. Often, pairs of short and long vowels became differentiated in quality before the loss of vowel length and thus did not end up merging; e.g. Old Norse /a aː i iː/ became Icelandic /a au ɪ i/, all of which can occur allophonically short or long. In the mainland Scandinavian languages, double consonants were reduced to single consonants, making the new vowel length phonemic.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i When not followed by a consonant.
- ^ When followed by a nasal consonant.
- ^ a b ⟨o⟩ or (before /r/) ⟨ø⟩ in some isolated words, but the tendency was to restore ⟨a⟩.
- ^ When un-umlauted */u/ is still present elsewhere in the paradigm.
| Spelling | Old Norse | Modern Icelandic |
Modern Faroese |
Modern Swedish |
Modern Norwegian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ⟨a⟩ | a | a(ː) | a/ɛaː | a/ɑː | ɑ(ː) |
| ⟨á⟩ | aː | au(ː) | ɔ/ɔaː | – | |
| ⟨ä⟩ | – | ɛ/ɛː | – | ||
| ⟨å⟩ | ɔ/oː | ||||
| ⟨æ⟩ | ɛː | ai(ː) | a/ɛaː | – | æ(ː), ɛ/eː |
| ⟨e⟩ | e | ɛ(ː) | ɛ/eː | e/eː | ɛ/eː, ə, æ(ː) |
| ⟨é⟩ | eː | jɛ(ː) | – | ||
| ⟨i⟩ | i | ɪ(ː) | ɪ/iː | ||
| ⟨í⟩ | iː | i(ː) | ʊɪ(ː) | – | |
| ⟨o⟩ | o | ɔ(ː) | ɔ/oː | ʊ/uː, ɔ/oː | uː, ɔ/oː |
| ⟨ó⟩ | oː | ou(ː) | œ/ɔuː | – | |
| ⟨ǫ⟩ | ɔ | – | |||
| ⟨ǫ́⟩ | ɔː | ||||
| ⟨ö⟩ | – | ø > œ(ː) | – | œ/øː | – |
| ⟨ø⟩ | ø | – | œ/øː | – | œ/øː |
| ⟨œ⟩ | øː | – | |||
| ⟨u⟩ | u | ʏ(ː) | ʊ/uː | ɵ/ʉː | ʉ(ː) |
| ⟨ú⟩ | uː | u(ː) | ʏ/ʉuː | – | |
| ⟨y⟩ | y | ɪ(ː) | ɪ/iː | ʏ/yː | |
| ⟨ý⟩ | yː | i(ː) | ʊɪ(ː) | – | |
| ⟨ei⟩ | ɛi | ei(ː) | aɪ(ː) | – | æɪ |
| ⟨ey⟩ | œy[21] | ei(ː) | ɛ/ɛɪː | – | |
| ⟨oy⟩ | – | ɔɪ(ː) | – | ||
| ⟨øy⟩ | – | œʏ | |||
| ⟨au⟩ | ɔu | øy(ː) | – | æʉ | |
See also
- Germanic a-mutation
- An Introduction to Old Norse – A common textbook on the language
- List of English words of Old Norse origin
- List of Old Norse exonyms – Names that speakers of Old Norse assigned to foreign places and peoples.
- Old Norse morphology – The grammar of the language.
- Old Norse orthography – The spelling of the language
- Old Norse poetry
- Proto-Norse language – The Scandinavian dialect of Proto-Germanic that developed into Old Norse
Dialectal information
Citations
General citations
- ^ Josephson, Folke; Söhrman, Ingmar (29 August 2008). Interdependence of Diachronic and Synchronic Analyses. John Benjamins. ISBN 9789027290359. Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 7 January 2021.
- ^ König, Ekkehard; van der Auwera, Johan, eds. (2002). The Germanic Languages. Routledge. p. 38. ISBN 978-0415280792.
- ^ Torp & Vikør 1993.
- ^ a b König, Ekkehard; van der Auwera, Johan, eds. (2002). The Germanic Languages. Routledge. p. 38. ISBN 978-0415280792.
- ^ "Old Norse language". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- ^ Sanders, Ruth H. (2021). The Languages of Scandinavia: Seven Sisters of the North. University of Chicago Press. pp. 63–64. ISBN 978-0-226-75975-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g Adams 1899, "Scandinavian Languages", pp. 336–338
- ^ a b "Nordiska språk", Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish), § Historia, §§ Omkring 800–1100, 1994
- ^ van der Auwera & König 1994, "Faroese" (Barnes & Weyhe), p. 217.
- ^ Moberg et al. 2007.
- ^ See, e.g., Harbert 2007, pp. 7–10
- ^ Farren, Robert (2014), Old Norse loanwords in modern Irish (thesis), Lund University, archived from the original on 16 August 2017, retrieved 5 September 2018
- ^ Borkent, Aukje (2014), Norse loanwords in Old and Middle Irish (thesis), Utrecht University, hdl:1874/296646
- ^ "Some Irish words with Norse Origins", irisharchaeology.ie, 21 November 2013, archived from the original on 5 September 2018, retrieved 5 September 2018
- ^ Greene, D. (1973), Almqvist, Bo; Greene, David (eds.), "The influence of Scandinavian on Irish", Proceedings of the Seventh Viking Congress, Dundalgan Press, Dundalk, pp. 75–82
- ^ Stewart, Thomas W. (Jr.) (2004), "Lexical imposition: Old Norse vocabulary in Scottish Gaelic", Diachronica, 21 (2): 393–420, doi:10.1075/dia.21.2.06ste
- ^ Medievalists.net (13 April 2014). "Old Norse Influence in Modern English: The Effect of the Viking Invasion". Medievalists.net. Archived from the original on 29 November 2020. Retrieved 5 August 2020.
- ^ Henderson, George (1910), The Norse influence on Celtic Scotland, Glasgow : J. Maclehose and Sons, pp. 108–204
- ^ Bandle 2005, Ch. XVII §202 "The typological development of the Nordic languages I: Phonology" (H. Sandøy) : Old East Nordic, pp. 1856, 1859.
- ^ Bandle 2005, Ch. XVII §202 "The typological development of the Nordic languages I: Phonology" (H. Sandøy) : Old West Nordic, p. 1859.
- ^ a b c d e f Bandle 2005, Ch.XIII §122 "Phonological developments from Old Nordic to Early Modern Nordic I: West Scandinavian." (M. Schulte). pp. 1081–1096; Monophthongization: p.1082; /øy/: p. 1082; Reduced vowels: p. 1085
- ^ Haugen 1950, pp. 4–64.
- ^ Robinson, Orrin W. (1993), Old English and Its Closest Relatives, p. 83
- ^ Sweet 1895, p. 5
- ^ Bandle 2005, Ch. XVII §202 "The typological development of the Nordic languages I: Phonology" (H. Sandøy) : Common Nordic, p.1855.
- ^ Schalin, Johan (2018). "Preliterary Scandinavian Sound Change Viewed From the East". Nordica Helsingiensia. 54: 146–147.
- ^ Vigfússon & Powell 1879, Ch. 1
- ^ Benediktsson, H. (1963), "Some Aspects of Nordic Umlaut and Breaking", Language, 39 (3): 409–431, doi:10.2307/411124, JSTOR 411124
- ^ a b Iversen 1961, pp. 24-
- ^ Bandle 2005, Ch. XVII §202 "The typological development of the Nordic languages I: Phonology" (H. Sandøy) : Proto-Nordic, p.1853.
- ^ Old Norse for Beginners, Lesson 5.
- ^ Noreen, Adolf. Altnordische Grammatik I: Altisländische und altnorwegische Grammatik. pp. 200–202, 207 (§ 277, § 283). Archived from the original on 2 June 2017. Retrieved 17 September 2018.
- ^ Noreen, A. G., Abriss Der Altnordischen (Altisländischen) Grammatik (in German), p. 12
- ^ a b c d Bandle 2005
- ^ Old Norse for Beginners, Neuter nouns.
- ^ Old Norse for Beginners, Feminine nouns.
- ^ The Menota handbook, Ch. 8 §3.2.1 "Gender".
- ^ Zoëga 1910, H: hungr.
- ^ O'Donoghue 2004, p. 22–102.
- ^ "The Old Norse dialect areas", aveneca.com, 2009, archived from the original on 7 July 2011
- ^ Hellquist, Elof, ed. (1922), "stark", Svensk etymologisk ordbok [Swedish etymological dictionary] (in Swedish), p. 862, archived from the original on 8 March 2012, retrieved 1 March 2012
- ^ König, Ekkehard; van der Auwera, Johan, eds. (2002). The Germanic Languages. Routledge. p. 38. ISBN 978-0415280792. "Old Norse is by far the best attested variety of Old Scandinavian."
- ^ Bandle 2005, Ch. XVII §202 "The typological development of the Nordic languages I: Phonology" (H. Sandøy) : Old East Nordic, pp. 1856, 1859.
- ^ Sturtevant, Albert Morey (1953), "Further Old Norse Secondary Formations", Language, 29 (4): 457–462, doi:10.2307/409955, JSTOR 409955
- ^ See Codex Regius
- ^ "Introduction – History of Norwegian up to 1349". Archived from the original on 31 January 2023. Retrieved 21 May 2023.
- ^ Hock, Hans Henrich (1986), Principles of Historical Linguistics, p. 149
- ^ a b van Weenen, Andrea de Leeuw (ed.), "(Manuscript AM 519 a 4to) "Alexanders saga"", Medieval Nordic Text Archive www.menota.org, fol. 1v, lines 10–14, archived from the original on 5 September 2018, retrieved 4 September 2018
- ^ Wills, Tarrin (2006), The Anonymous Verse in the Third Grammatical Treatise, The Centre for Medieval and Renaissance Studies, Durham University, archived from the original on 4 September 2018, retrieved 4 September 2018
- ^ Kroonen, Guus, "On the origins of the Elfdalian nasal vowels from the perspective of diachronic dialectology and Germanic etymology" (PDF), inss.ku.dk (Presentation), archived (PDF) from the original on 6 February 2016, retrieved 27 January 2016,
(Slide 26) §7.2 quote: "In many aspects, Elfdalian, takes up a middle position between East and West Nordic. However, it shares some innovations with West Nordic, but none with East Nordic. This invalidates the claim that Elfdalian split off from Old Swedish."
- ^ Noreen, Adolf. Altnordische Grammatik I: Altisländische und altnorwegische Grammatik. p. 211 (§ 288, note 1). Archived from the original on 2 June 2017. Retrieved 17 September 2018.
- ^ O'Donoghue 2004, pp. 190–201.
- ^ Lass 1993, pp. 187–188.
- ^ a b Helfenstein, James (1870). A Comparative Grammar of the Teutonic Languages: Being at the Same Time a Historical Grammar of the English Language. London: MacMillan and Co.
Cleasby-Vigfússon citations
- ^ a b c d e Cleasby & Vigfússon 1874, p.1, "A"
- ^ Cleasby & Vigfússon 1874, pp. 761–762 (Introduction to Letter Ö (Ø))
- ^ Cleasby & Vigfússon 1874, pp. xxix–xxx "Formation of Words" : Vowel Changes
- ^ Cleasby & Vigfússon 1874, p. xvi "Strong Nouns" – Masculine – Remarks on the 1st Strong Masculine Declension, 3.a
- ^ Cleasby & Vigfússon 1874, p. 389 col.1, "LIM"; p. 437, col.1 "MUND"
- ^ Cleasby & Vigfússon 1874, p. 481 "R"
- ^ a b c Cleasby & Vigfússon 1874, p. 757 "Æ"
- ^ Cleasby & Vigfússon 1874, pp. 113–114 "E"
Sources
General sources
- Harbert, Wayne (2007), "The Germanic Languages", Cambridge Language Surveys, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Haugan, Jens (1998), "Right Dislocated 'Subjects' in Old Norse", Working Papers in Scandinavian Syntax, no. 62, pp. 37–60
- Haugen, Einar (1950), "First Grammatical Treatise. The Earliest Germanic Phonology", Language, 26 (4): 4–64, doi:10.2307/522272, JSTOR 522272
- Haugen, Odd Einar, ed. (2008) [2004], The Menota handbook: Guidelines for the electronic encoding of Medieval Nordic primary sources (Version 2.0 ed.), Bergen: Medieval Nordic Text Archive, ISBN 978-82-8088-400-8, archived from the original on 24 May 2020, retrieved 4 September 2018 , "The Menota handbook 2.0"
- Lass, Roger (1993), Old English: A Historical Linguistic Companion, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Adams, Charles Kendall, ed. (1899) [1876], Johnson's Universal Cyclopedia: A New Edition, vol. 7 (Raleigh-Tananarivo), D. Appleton, A. J. Johnson
- van der Auwera, J.; König, E., eds. (1994), The Germanic Languages
- Moberg, J.; Gooskens, C.; Nerbonne, J.; Vaillette, N. (2007), "4. Conditional Entropy Measures Intelligibility among Related Languages", Proceedings of the 17th Meeting of Computational Linguistics in the Netherlands, vol. 7 (LOT Occasional series), pp. 51–66, hdl:1874/296747
- Bandle, Oskar; Braunmüller, Kurt; Jahr, Ernst Hakon; Karker, Allan; Naumann, Hans-Peter; Teleman, Ulf; Elmevik, Lennart; Widmark, Gun, eds. (2002), The Nordic Languages, An International Handbook on the History of the North Germanic Languages, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin
- Volume 2, 2005
- O'Donoghue, Heather (2004), Old Norse-Icelandic Literature: A Short Introduction, Blackwell Introductions to Literature, Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
- Torp, Arne; Vikør, Lars S (2014) [1993], Hovuddrag i norsk språkhistorie [The main features of Norwegian language history] (in Norwegian) (4th ed.), Gyldendal Norsk Forlag, ISBN 978-8205464025
Dictionaries
- Cleasby, Richard; Vigfússon, Guðbrandur (1874), An Icelandic-English Dictionary, Oxford: Clarendon Press
- e-text Archived 20 July 2021 at the Wayback Machine via the Germanic Lexicon Project (germanic-lexicon-project.org)
- e-text Archived 17 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine adapted from the Germanic Lexicon Project version to work better with mobile devices and with an improved search (old-norse.net)
- Zoëga, G. T. (1896), Íslenzk-Ensk orðabók, S. Kristjánsson
- Íslenzk-Ensk orðabók, Reykjavík, Kostnaarmaur: Sigurdur Kristjánsson, 1922
- Zoëga, G. T. (1910), A Concise Dictionary of Old Icelandic
- scanned document Archived 11 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine via "Germanic Lexicon Project" (lexicon.ff.cuni.cz)
- e-text Archived 1 January 2022 at the Wayback Machine via norroen.info
- ONP: Dictionary of Old Norse Prose (in Danish and English), University of Copenhagen, archived from the original on 18 December 2019, retrieved 6 August 2021
- de Vries, Jan (1977) [1961], Altnordisches Etymologisches Wörterbuch
- Egilsson, Sveinbjorn, ed. (1854), Lexicon poeticum antiquæ linguæ septentrionalis (in Danish and Latin), Hafniæ, typis J. D. Qvist & comp
- Egilsson, Sveinbjorn; Jónsson, Finnur, eds. (1931) [1913–1916], Lexicon poeticum antiquæ linguæ septentrionalis (2nd ed.)
- First and Second editions Archived 19 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine via www.septentrionalia.net
Grammars
- Bayldon, George (1870), An Elementary Grammar of the Old Norse or Icelandic Language, London: Williams and Norgate
- Vigfússon, Gudbrand; Powell, F. York (1879), An Icelandic Prose Reader: with Notes, Grammar, and Glossary, Oxford Clarendon Press
- Noreen, Adolf (1923), Altnordische grammatik I. Altisländische und altnorwegische grammatik (laut- und flexionslehre) (4th ed.), Halle (Saale): Max Niemeyer, archived from the original on 24 October 2021, retrieved 9 June 2020 (Old West Norse)
- Noreen, Adolf (1904), Altnordische grammatik II. Altschwedische grammatik mit einschluss des altgutnischen, Halle: Max Niemeyer (Old Swedish and Old Gutnish)
- Brøndum-Nielsen, Johannes (1928–1974), Gammeldansk Grammatik i sproghistorisk Fremstilling (8 volumes), København: J. H. Schultz (Old Danish)
- Iversen, Ragnvald (1972). Norrøn grammatikk (7th ed.). Oslo: Aschehoug. (Old West Norse)
- Faarlund, Jan Terje (2004), The Syntax of Old Norse, New York: Oxford University Press (Old Norse in the narrow sense, i.e. Old West Norse)
- Haugen, Odd Einar (2006), Grunnbok i norrønt språk (3rd, revised printing of the 4th ed.), Gyldendal Akademisk (Old West Norse)
- Haugen, Odd Einar (2015), Norröne Grammatik im Überblick (2nd ed.), Universität Bergen, archived from the original on 24 October 2021, retrieved 10 June 2021 (Old West Norse)
Old Norse texts
- Aronsson, Lars, ed. (1997), "Gutasagan", Project Runeberg (in Old Norse), archived from the original on 12 November 2020, retrieved 16 May 2007
- Tunstall, Peter (ed.), Gutarnas Krönika eller Gutasagan [The History of the Gotlanders] (in Old Norse and English), archived from the original on 10 November 2011, retrieved 17 July 2011 , facing translation
Language learning resources
- Barnes, Michael; Faulkes, Anthony (2007–2011), A New Introduction to Old Norse. Part I - Grammar. Part II - Reader. Part III - Glossary. Viking Society for Northern Research. University College London. Available at the Viking Society for Northern Research homepage.
- Byock, Jesse (2013), Viking Language: Learn Old Norse, Runes, and Icelandic Sagas, Jules William Press, ISBN 978-1-4802-1644-0
- Gordon, Eric V.; Taylor, A. R. (1981), An Introduction to Old Norse, Oxford: Clarendon Press, ISBN 978-0-19-811184-9
- Sweet, Henry (1895), An Icelandic Primer, with Grammar, Notes, and Glossary (2nd ed.), Univerzita Karlova
- alt source Archived 24 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine via Germanic Lexicon Project (lexicon.ff.cuni.cz)
- e-ext Archived 26 October 2021 at the Wayback Machine via Project Gutenberg
- Þorgeirsson, Haukur; Guðlaugsson, Óskar, Old Norse for Beginners, archived from the original on 23 January 2017, retrieved 4 September 2018
- Valfells, Sigrid; Caithey, James E. (1982), Old Icelandic: An Introductory Course. Oxford University Press.
External links
- Heimskringla.no, an online collection of Old Norse source material
- Old Norse Online by Todd B. Krause and Jonathan Slocum, free online lessons at the Linguistics Research Center at the University of Texas at Austin
- Video: Old Norse text read with a reconstructed pronunciation and a Modern Icelandic pronunciation, for comparison. With subtitles
- Old Norse sound samples for early Old Norse and 13th century Norwegian Old Norse by Arne Torp
- Old Norse sound sample by Haukur Þorgeirsson (archived from the original)
- Old Norse loans in Old and Middle English, and their legacy in the dialects of England and modern standard English
- Old Norse basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical Database