Effects of the storage conditions on the stability of natural and synthetic cannabis in biological matrices for forensic toxicology analysis: An update from the literature
Contents
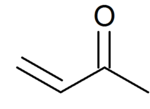
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
But-3-en-2-one | |
| Other names
MVK
Methylene acetone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.055 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O | |
| Molar mass | 70.09 g/mol |
| Density | 0.8407 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −7 °C (19 °F; 266 K) |
| Boiling point | 81.4 °C (178.5 °F; 354.5 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
    
| |
| Danger | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | −7 °C (19 °F; 266 K) |
| 370 °C (698 °F; 643 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 2.1% v/v (lower), 15.6% v/v (higher) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Fisher Scientific |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Methyl vinyl ketone (MVK, IUPAC name: butenone) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH=CH2. It is a reactive compound classified as an enone, in fact the simplest example thereof. It is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic liquid with a pungent odor. It is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a useful intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds.[2]
Production
MVK has been prepared industrially by the condensation of acetone and formaldehyde, followed by dehydration. Similarly it is prepared by the Mannich reaction involving diethylammonium chloride and acetone, which produces the Mannich adduct:[2][3]
- CH3C(O)CH3 + CH2O + [H2NEt2]Cl → [CH3C(O)CH2CH2N(H)Et2]Cl + H2O
Heating this ammonium salt releases the ammonium chloride and the MVK:[3]
- [CH3C(O)CH2CH2N(H)Et2]Cl → CH3C(O)CH=CH2 + [H2NEt2]Cl
Reactivity and applications
MVK can act as an alkylating agent because it is an effective Michael acceptor. It gained early attention for its use in the Robinson annulation, a method useful in the preparation of steroids:
Its alkylating ability is both the source of its high toxicity and the feature that makes it a useful intermediate in organic synthesis. MVK will polymerize spontaneously. The compound is typically stored with hydroquinone, which inhibits polymerization.

Vinclozolin is a commercial fungicide prepared using MVK.
As an electrophilic alkene, it forms an adduct with cyclopentadiene. The resulting norbornene derivative is an intermediate in the synthesis of the anticholinergic drug biperiden. Via its cyanohydrin is also a precursor to vinclozolin. It is also a precursor to synthetic vitamin A.[2]
MVK is an intermediate in the synthesis of some pharmaceutical drugs including etorphine, buprenorphine, tolquinzole, butaclamol, and etretinate.[citation needed]
MVK is used in the synthesis of Wieland–Miescher ketone.
Safety
MVK is extremely hazardous upon inhalation causing coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath even at low concentrations. It will also readily cause irritation of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 6052.
- ^ a b c Siegel, H.; Eggersdorfer, M. "Ketones". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_077. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ a b L. Wilds, Alfred; Nowak, Robert M.; McCaleb, Kirtland E. (1957). "1-Diethylamino-3-butanone". Organic Syntheses. 37: 18. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.037.0018.



















