Effects of the storage conditions on the stability of natural and synthetic cannabis in biological matrices for forensic toxicology analysis: An update from the literature
Contents
No edit summary |
InternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs) Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.5.3) |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* {{SUNYAnatomyLabs|15|st|04|01}} |
* {{SUNYAnatomyLabs|15|st|04|01}} |
||
* [http://www.ptcentral.com/muscles/musclelegs.html#extensor%20digitorum%20longus PTCentral] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20100715211225/http://www.ptcentral.com/muscles/musclelegs.html#extensor%20digitorum%20longus PTCentral] |
||
{{Muscles_of_lower_limb}} |
{{Muscles_of_lower_limb}} |
||
Revision as of 12:03, 26 September 2017
| Extensor digitorum longus muscle | |
|---|---|
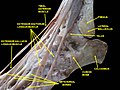
 The mucous sheaths of the tendons around the ankle. Lateral aspect. (Extensor dig. longus labeled at upper right.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Anterior lateral condyle of tibia, anterior shaft of fibula and superior 3⁄4 of interosseous membrane |
| Insertion | Dorsal surface; middle and distal phalanges of lateral four digits |
| Artery | anterior tibial artery |
| Nerve | deep fibular nerve |
| Actions | extension of toes and dorsiflexion of ankle |
| Antagonist | Flexor digitorum longus, Flexor digitorum brevis |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus extensor digitorum longus |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.038 |
| TA2 | 2645 |
| FMA | 22534 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The extensor digitorum longus is a pennate muscle, situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg.
Origin and insertion
It arises from the lateral condyle of the tibia; from the upper three-fourths of the anterior surface of the body of the fibula; from the upper part of the interosseous membrane; from the deep surface of the fascia; and from the intermuscular septa between it and the tibialis anterior on the medial, and the fibularis muscles on the lateral side. Between it and the tibialis anterior are the upper portions of the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve.
The muscle passes under the superior and inferior extensor retinaculum of foot in company with the fibularis tertius, and divides into four slips, which run forward on the dorsum of the foot, and are inserted into the second and third phalanges of the four lesser toes.
The tendons to the second, third, and fourth toes are each joined, opposite the metatarsophalangeal articulations, on the lateral side by a tendon of the extensor digitorum brevis. The tendons are inserted in the following manner: each receives a fibrous expansion from the interossei and lumbricals, and then spreads out into a broad aponeurosis, which covers the dorsal surface of the first phalanx: this aponeurosis, at the articulation of the first with the second phalanx, divides into three slips—an intermediate, which is inserted into the base of the second phalanx; and two collateral slips, which, after uniting on the dorsal surface of the second phalanx, are continued onward, to be inserted into the base of the third phalanx.
Variations
This muscle varies considerably in the modes of origin and the arrangement of its various tendons.
The tendons to the second and fifth toes may be found doubled, or extra slips are given off from one or more tendons to their corresponding metatarsal bones, or to the short extensor, or to one of the interosseous muscles.
A slip to the great toe from the innermost tendon has been found.
See also
Additional Images
-
Dorsum of Foot. Deep dissection.
-
Dorsum of Foot. Deep dissection.
-
Ankle joint. Deep dissection. Lateral view.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 481 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 481 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:15:st-0401 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- PTCentral