Basics of case report form designing in clinical research
| Full article title | Basics of case report form designing in clinical research |
|---|---|
| Journal | Perspectives in Clinical Research |
| Author(s) | Bellary, Shantala; Krishnankutty, Binny; Latha, M.S. |
| Author affiliation(s) | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd., Hyderabad, India; USV Limited, Mumbai, India |
| Primary contact | Email: lathasu@gmail.com |
| Year published | 2014 |
| Volume and issue | 5 (4) |
| Page(s) | 159–166 |
| DOI | 10.4103/2229-3485.140555 |
| ISSN | 2229-3485 |
| Distribution license | Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported |
| Website | http://www.picronline.org |
| Download | http://www.picronline.org/temp/PerspectClinRes54159-5195597_142555.pdf (PDF) |
Abstract
Case report form (CRF) is a specialized document in clinical research. It should be study protocol driven, robust in content and have material to collect the study specific data. Though paper CRFs are still used largely, use of electronic CRFs (eCRFs) are gaining popularity due to the advantages they offer such as improved data quality, online discrepancy management and faster database lock etc. Main objectives behind CRF development are preserving and maintaining quality and integrity of data. CRF design should be standardized to address the needs of all users such as investigator, site coordinator, study monitor, data entry personnel, medical coder and statistician. Data should be organized in a format that facilitates and simplifies data analysis. Collection of large amount of data will result in wasted resources in collecting and processing it and in many circumstances, will not be utilized for analysis. Apart from that, standard guidelines should be followed while designing the CRF. CRF completion manual should be provided to the site personnel to promote accurate data entry by them. These measures will result in reduced query generations and improved data integrity. It is recommended to establish and maintain a library of templates of standard CRF modules as they are time saving and cost-effective. This article is an attempt to describe the methods of CRF designing in clinical research and discusses the challenges encountered in this process.
Keywords: Case report form, completion guidelines, case report form design, electronic case report form, standard templates
Introduction
A case report form (CRF) is designed to collect the patient data in a clinical trial; its development represents a significant part of the clinical trial and can affect study success.[1] Site personnel capture the subject's data on the CRF, which is collected during their participation in a clinical trial. The International Conference on Harmonization Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice define the CRF as: A printed, optical or electronic document designed to record all of the protocol - required information to be reported to the sponsor on each trial subject.[2]
Case report form designing requires enormous planning and attention to minute detail. Designing a CRF is crucial in a clinical trial as it will aid in assessing the safety and efficacy of the medicinal product accurately. CRF should be designed for optimal collection of data in accordance with the study protocol compliance, regulatory requirements and shall enable the researcher test the hypothesis or answer the trial related questions.
A well-designed CRF should represent the essential contents of the study protocol and in an ideal situation, CRF is designed once the study protocol is finalized. It can be prepared either concurrently along with the protocol development, but may result in many versions, and hence needs to be version controlled. Timing of the design process will also play an important role as both the approaches have pros and cons.
It is increasingly recognized that the design of the CRF (paper form/electronic form) is a key quality step in ensuring the data required by the protocol, regulatory compliance and/or safety needs/comments, study-specific hypothesis attributes, site work flow, and cross-checking of data items within a form or across different forms are addressed.[3] The CRF used in clinical research reduces messy clinical realities to round integers and categorical answers.[4]
This article is an attempt to describe the methods of CRF designing in clinical research, discusses the challenges encountered and measures to be taken to prevent the occurrence of issues in its development.
Paper case report form versus electronic case report form
There are two types of CRFs used in clinical research, that is, traditional paper CRF and improvised electronic CRF (eCRF). Paper CRF is the traditional way of data capture and a better option if studies are small or vary in design, whereas eCRFs are considered if studies are large with similar designs.[5]
In the current global scenario, eCRFs are preferred over paper CRFs as they are less time-consuming, and also encourage the sponsor/pharmaceutical company to carry out large multicentric studies at the same time due to the ease of administration. It is designed in such a way that data entry can be done with zero/minimal errors. Moreover, the regulatory authorities are readily accepting submissions in which validated electronic data capture (EDC) systems are used.[6]
While designing an eCRF, repetitive data such as protocol ID, site code, subject ID, and patient initials will be generated by the system automatically from the first page to all others, thus ensuring no duplication of CRF pages.
In eCRF, linking the data between two related pages of CRFs becomes easy and quick. They have built-in edit checks tagged to each data field as well as to the CRF as a whole. Therefore, majority of data cleaning activities will take place during the completion of the eCRFs, thus reducing the time and effort required by data management personnel. Instant query resolution reduces the time spent on obtaining the clarification from the site/investigator and hence, clean data is obtained much quickly, resulting in timely database lock, faster regulatory submission, and subsequent approval.
Standard case report form design
Designing a paper CRF is a tedious job that could result in data errors and wrong conclusions, requiring meticulous attention to minimize duplication of CRF pages. Chances of error during data transfer from the source document to paper CRF are common. Moreover, for studies with large sample size if traditional method of data collection through paper CRFs is opted, then manual data cleaning may be a major concern. However, this method may not require user training and system validation as in the case of EDC systems, where such things are essential before implementing it. Despite their many advantages, eCRFs have not been accepted widely. Main reasons behind this are lack of available on-site technology, investigators' lack of motivation, complexity of installation, and maintenance of the software and high investment cost.
Designing a CRF is an art that should to be based on scientific practices and the design should be implemented keeping the end-user (the one who enters data in the CRF) in mind. While designing, all important sections of the CRF should be included with care; always it is worth to remember that insufficient/inaccurate data collection would prove expensive during analysis. Hence, it is advisable to have a standard operating procedure for CRF preparation and to follow best practices of CRF designing.
Primary objective of CRF designing is to gather complete and accurate data by avoiding duplication and facilitating transcription of data from source documents onto the CRF. CRF should be designed with the primary safety and efficacy endpoints as the main goal of data collection.[6] Ideally, it should be well-structured, easy to complete without much assistance and should collect data of the highest quality. Always minimum amount of data needed to answer the study hypotheses should be collected avoiding collection of elaborate, unimportant information. For ordinal data, to ensure uniformity and clarity among raters, adequate explanation should be provided adjacent to the CRF fields. Capturing the same piece of data in more than one place (duplication) on the CRF should also be avoided. In other words, CRF should collect data in sufficient detail without ambiguity and at the same time, should avoid redundancy and avoid capture of unwanted details. Hence, striking the perfect chords to ensure balance between effective data collection and structuring the CRF to support accurate data entry is essential. Collecting the data in the coded form whenever possible is ideal as it facilitates data entry (at CRF and at the database levels) and helps the statistician in data interpretation and analysis.
Important part of the CRF is an informative header and footer, which can be customized.[7]
In general, the header includes protocol ID, site code, subject ID, and patient initials. Whereas, the footer includes investigator's signature, date of signature, version number, and page number.
In order to enhance easy reading/understanding and accurate data entry, an uncrowded CRF layout should be preferred. Placing too many details on the same page, makes the CRF look cluttered and makes data entry difficult, which eventually leads to increase in data discrepancies.
Case report form design should be standardized to address the needs of all those who handle the data such as investigator, data manager, biostatistician, clinical research monitor/coordinator, database developer/programmer and data entry personnel etc. An effective CRF design would always be user friendly. Moreover, it should capture legible, consistent and valid data, thereby, reducing query generations.[7] While designing the CRFs, design standards should be adhered to for improving the quality of data collected. Hence, data should be organized in a format that facilitates data analysis and makes it simplified.
The following points are to be borne in mind while designing a CRF:
- Use of consistent formats, font style and font sizes throughout the CRF booklet
- Selection of portrait versus landscape versus combination layouts
- Use of clear and concise questions, prompts, and instructions
- Visual cues, such as boxes that clearly indicate place and format of data to be recorded should be provided to the person recording the data as much as possible
- Using the option of "circling of answers" should be limited as it's hard to interpret; instead check boxes would be appropriate
- Clear guidance about skip patterns like what to skip and what not to skip should be mentioned at appropriate places
- Skips (are instructions provided in the CRF page to maintain the connectivity between pages) should be kept to a minimum by the placement of questions to avoid confusions
- Provide boxes or separate lines to hold the answers. This indirectly informs the data recorder where to write/enter the response and helps to differentiate it visually from the entry fields for other questions
- Separate the columns with thick lines
- Provide bold and italicized instructions
- Minimize free text responses
- Position only specified density of questions on each page
- Page numbering if necessary, should be consistent throughout
- Avoid using "check all that apply" as it forces assumptions about the clinical data
- Specify the unit of measurement
- Indicate the number of decimal places to be recorded
- Use standard data format (e.g., dd/mm/yyyy) throughout the CRF
- Use precoded answer sets such as yes/no, male/female, method of administration of medicine, and severity of adverse event (AE) (mild/moderate/severe) wherever possible
- Not to split modules/sections (a set of one or more related groups of questions that pertain to a single clinical study visit) like, for example, AE section should not be split and laid across pages such that information related to a single AE will have to be collected from different pages
- Use "no carbon required (NCR)" copies to ensure exact replica of CRF
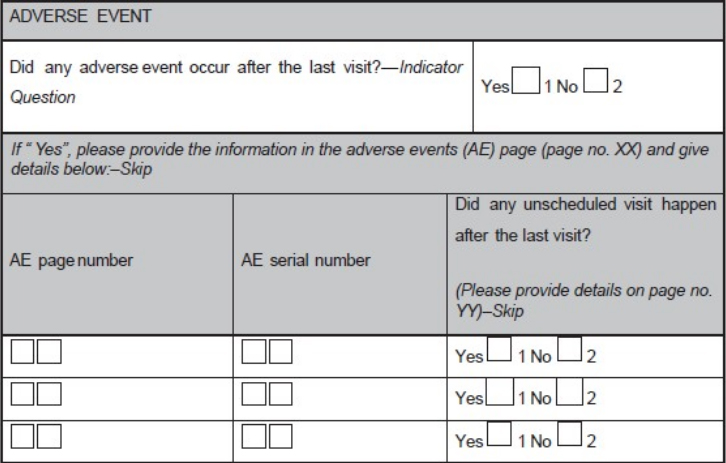
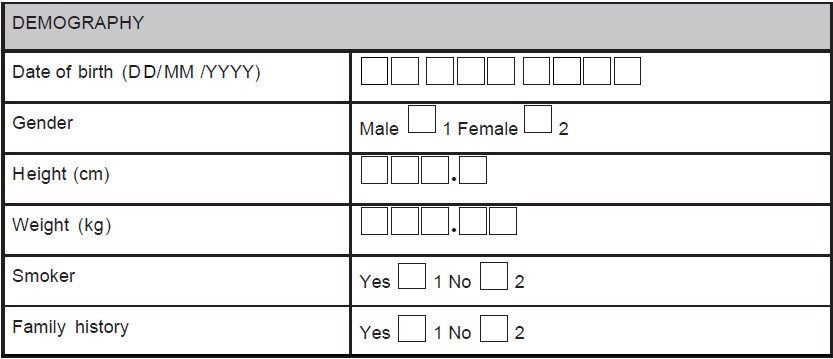
- Use instructions including page numbers where data has to be entered (e.g., during a follow-up visit, the investigator is supposed to record whether any AE has occurred and if occurred, details of the AE has to be recorded in the AE module. Hence, the field corresponding to this question on the module for the particular visit would be having the options "yes" or "no". There should be an instruction "If 'yes', please provide the information in the AEs page (page no. XX)" as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. A sample case report form (CRF) page. An adverse event page
of CRF is depicted showing codes, and skips questions
Well designed case report form versus poorly designed case report form
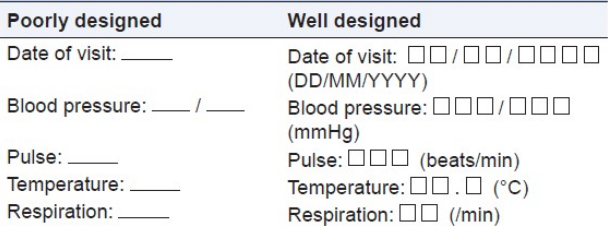
Table 1 provides the comparison between well-designed and poorly designed CRF. In case of poorly designed CRF, by placing a single line for required response results in variations in the investigator's responses from site to site. On the other hand, separate lines and boxes are provided in the well-designed form, which gives the visual cues about what is expected as a response and thereby, reduces the unnecessary queries. Usually, boxes are used for entering dates and the date format (i.e., dd/mm/yyyy ) should be consistent on all pages of CRF. Units and decimal points should be displayed for vital sign records, which clarify the user about the expected values and also facilitates the data interpretation and reduces manipulation during analysis procedures. Figure 2 and Figure 3 are examples of poorly designed CRFs. Poor CRF design results in frequent database modification thus affecting the study timelines. Data need to be collected in a way that does not introduce bias or errors. Collection of a large amount of data will result in wasted resources in collecting and processing it. Questions in the CRF should be clear and unambiguous to avoid unnecessary confusions.[8]
Table 1. Illustrating a well-designed and poorly designed data fields imparting
the significance of visual cues to help the site personnel to understand the format
Figure 2. Example of a poorly designed case report form
Figure 3. Illustrating the missing indicator question
In some circumstances, data can be obtained using derivation procedures; collection of derived data again on the CRF should be avoided to minimize calculation errors. For example, age can be calculated using date of birth. Body mass index can be calculated using height and weight of the subject, only the latter two should be captured.
In conditions where same parameters are to be recorded at multiple visits, it is recommended to use the same CRF module for each visit to reduce the number of query generation. For example, vital Signs and body systems in the physical examination (PE) module can be collected in the same order each time.
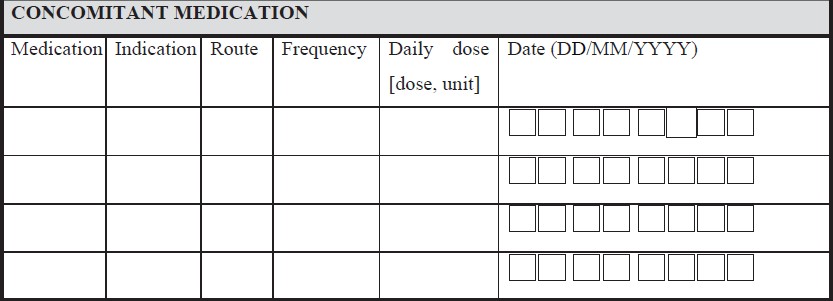
In some places, answers are coded in order to simplify the data collection. When codes are used to obtain an answer for a question, consistency in codes should be maintained throughout the CRF booklet and there should not be any variation in the answer for the same question.
For example, yes/no answers are coded as 1 = yes and 2 = no (preferred coding) as shown in Figure 4. If the codes are assigned in this order, the same order should be practiced throughout the CRF. Nowhere in the same CRF "1" should be coded for "no" and "2" should be coded for "yes".
Figure 4. Coding on the case report form module
Even the location of these codes on the CRF should be consistent; same is shown in Figure 4. Clear instructions should be provided to the user where ever necessary; otherwise, it will have a significant impact on the data management activities like database designing, data cleaning, data validation, and data extraction due to poor understanding of the site personnel about the expected responses. It is advisable to use indicator questions wherever needed to avoid assumptions about the data. Use indicator questions in connection to a set of other questions, and the response to the indicator question would decide on whether the associated set of questions needs to be answered or not. For example, in an AE question group, an indicator question could be, "Did any AE occur after the last visit?"
If the response is "yes", the remaining questions pertaining to the details of the AE(s) (such as severity, seriousness, causality, date of onset, date of resolution, and action taken) require responses. If the response is "no", the rest of the question group is not answered. Incorporation of an indicator question and skips are shown in Figure 1. Ideally, CRF booklet should have a chart reflecting the expected list of assessments as per schedule specified in the protocol.
Standard case report form templates
Some of the data requirements such as demography, PE, AEs are same across studies, so standard CRF templates should be developed which can be customized accordingly. These templates are of great help while conducting multiple studies in the same research area. These templates will have the same design principles that help the user to enter data with ease since the design is familiar to them; there is no need for special training on these modules of CRFs.
A "library" of standard templates should be established and maintained by the sponsor/contract research organizations, pharmaceutical companies in order to maintain uniformity in the CRF design and to save time. Most commonly used standard CRF templates are inclusion criteria, exclusion criteria, demography, medical history, PE, AE, concomitant medication and study outcome modules, whereas, the modules which captures efficacy data are not unique. Their design varies from study to study depending on the protocol specifications.
Case report form connectivity/Well referenced case report forms
Linking of CRF (paper CRF and eCRF) pages wherever necessary is known as CRF connectivity. Each CRF booklet is assigned with unique subject ID and it is the duty of site personnel to make sure that same ID is entered on all pages of CRF booklet. Consistently entered subject ID will help in tracking the missing CRF pages. The fields such as protocol ID, site code, subject ID, and patient initials make database designing easier and helps linking CRF pages to the study database. The fields like protocol ID and visit labels are informative features as they provide brief descriptions of the study and the schedule of assessments, respectively. The CRF version number is a critical field that prevents an incorrect CRF page being used. All pages of the CRF booklet should be numbered in sequential order, which will help in identifying queries through data validation procedures and manual reviews. Page numbering not only provides the site personnel with a quick reference to specific pages, but also helps to design the database in a structured manner. Especially, in case of eCRF, retrieving of CRFs becomes challenging if proper programming is not carried out. CRF connectivity is crucial when statistical analysis plan (SAP) is complex and these fields will be of help in statistical analysis.
Challenges in case report form designing
Commonly encountered challenges in CRF designing are consistency in the design, collection of precise data and user-friendliness. These challenges can be overcome by proper planning by a team of data management personnel, biostatisticians, clinicians, and medical writers. Objectives should be defined clearly before designing. Consistent design is a crucial aspect as it reduces the number of mistakes in data entry. It is of great advantage when using them across various studies. Maintaining standard CRF templates would resolve this issue. Collection of extraneous data is another issue and measures should be taken to avoid it, as processing this becomes tedious. In such instances, ensuring accuracy and quality become major challenges. Attention should be paid to avoid duplication. Design the CRF to avoid referential and redundant data collection. For example, collecting calculated fields/derivable data should be avoided and to ensure that data collection is cost-effective. Designing user-friendly CRF to reduce data entry errors is again a challenge. Simple/standard designs should be incorporated wherever possible.
User feedback mechanism should be built into the CRF design and maintenance process. Best practices should be applied to improve the data quality and save time with CRF design. Providing CRF completion guideline aids in minimizing the challenges in data capture and data entry.
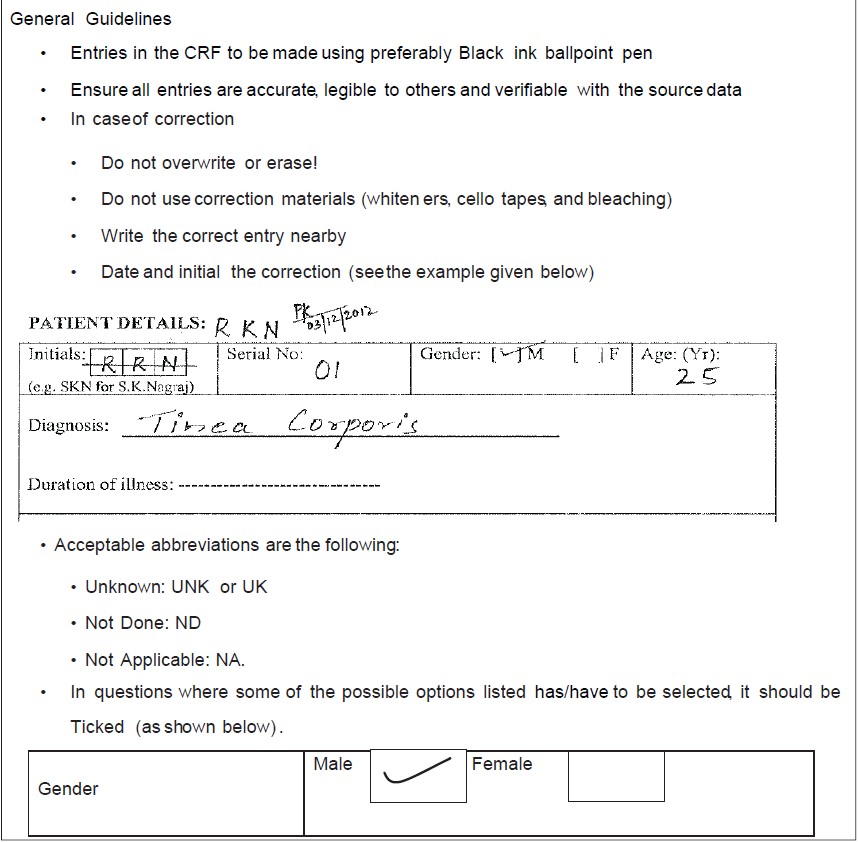
Case report form completion guidelines
A CRF completion guideline is a document to assist the investigator to complete the CRF in a step by step manner and is drafted concurrently in line with the CRF and protocol. Figure 5 shows sample page of CRF completion guideline. There is no standard template for CRF completion guidelines as it is study specific. It should be prepared in such a way that it enables the site personnel to complete the CRFs with ease and legibility. CRF completion manual should provide clear instructions to site personnel for accurate completion of CRFs along with clear expectations including proper instructions on handling unknown data. For example, if exact date is unknown, then use a preferred notation in the place of missing value (i.e., UK/UNK/2012). The language used should be simple with clear instructions, concise, and easy to understand.
Figure 5. Sample page of case report form completion guideline
Case report form completion guidelines document, while bridging the gap between the study protocol and the data collection process, explains the activities involved in CRF completion, correction, signing, and data handling.[7] It provides unambiguous instructions on CRF completion in all practical scenarios. For example, if data were wrongly entered and the site personnel wants to correct it, the instruction provided would be to strike-through the incorrect data with a single line, put the initials (of the person who makes the change) with date and to write the correct entry in the margin against the corresponding line. Similarly, instructions will be provided for each data entry field on each page in the CRF booklet. This helps to ensure completion of all required data fields and enhances the data flow.[7] CRF completion guidelines could be a separate document or could be a part of the CRF booklet giving page by page instructions. If it is included as part of the CRF, it is advisable to print instructions on the page facing the CRF page (back side of the previous page) as the investigator can easily take instructions and simultaneously fill the CRF page. CRF completion guidelines document should have version control and amendments should be done as and when required.
Conclusion
Case report form design is the initial step in translating the protocol into standard questionnaires and is paramount to a successful clinical trial. Standard CRF should be designed in such a way that it helps the collection of consistent and valid data, ultimately resulting in submission of data to regulatory authorities and its acceptance. Regardless of the time and effort spent conducting the trial, the correct data points (response to a CRF question/data is entered) must be collected; otherwise, a meaningful analysis may not be possible. Therefore, a sound SAP should be used as a tool to develop and judge the adequacy of the CRF, which should be available to guide on what data points need to be captured on the CRF. To avoid future amendments, it is important to have design principles in mind well in advance before CRF designing is initiated. These standard guidelines will contribute in preparing a well-designed CRF for data acquisition.
Acknowledgement
We would like to acknowledge the technical support offered by Mr. Vinoth T. and Mr. Sagi Subbaraju that has helped us during the preparation of this article.
References
- ↑ Nahm, M.; Shepherd, J.; Buzenberg, A.; Rostami, R.; Corcoran, A.; McCall, J. et al. (2011). "Design and implementation of an institutional case report form library". Clinical Trials 8 (1): 94–102. doi:10.1177/1740774510391916. PMC PMC3494996. PMID 21163853. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3494996.
- ↑ ICH Steering Committee (1996). "Guidance for Industry - E6 Good Clinical Practice: Consolidated Guidance" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/ucm073122.pdf. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- ↑ Lu, Z.; Su, J. (June 2010). "Design and implementation of an institutional case report form library". Open Access Journal of Clinical Trials 2010 (2): 93—105. doi:10.2147/OAJCT.S8172.
- ↑ Latimer, P. (May 2008). "Case report form insanity" (PDF). Journal of Clinical Research Best Practices 4 (5). http://www.firstclinical.com/journal/2008/0805_Insanity.pdf. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ↑ Stark, N.J. (October 2011). "Data management in device studies" (PDF). Journal of Clinical Research Best Practices 7 (10). http://www.firstclinical.com/journal/2011/1110_Data_Management.pdf. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Good Clinical Data Management Practices" (PDF). Society for Clinical Data Management. October 2009. http://www.swaggerinfosolutions.pro/sridevi/New%20Folder/ICRI/GCDMP_complete_OCT2009.pdf. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Moon, K.K. (Fall 2006). "Techniques for designing case report forms in clinical trials: Considerations for efficient data management and statistical analysis" (PDF). ScianNews 9 (1). Archived from the original on 12 May 2013. https://web.archive.org/web/20130512162105/http://www.mycro.ca/media/1533/sciannews91b.pdf.
- ↑ CDISC CDASH Core and Domain Teams (1 October 2008). "Clinical Data Acquisition Standards Harmonization (CDASH)" (PDF). CDISC, Inc. http://www.cdisc.org/system/files/all/standard/application/pdf/cdash_std_1_0_2008_10_01.pdf. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
Notes
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation. In most of the article's references DOIs and PubMed IDs were not given; they've been added to make the references more useful. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added.