Type a search term to find related articles by LIMS subject matter experts gathered from the most trusted and dynamic collaboration tools in the laboratory informatics industry.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Fenoglide, Lipofen, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601052 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | 20 h |
| Excretion | urine (60%), feces (25%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.051.234 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
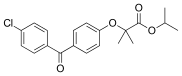
| Formula | C20H21ClO4 |
| Molar mass | 360.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 80 to 81 °C (176 to 178 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Fenofibrate (sold under the brand name Tricor among others), is an oral medication of the fibrate class used to treat abnormal blood lipid levels.[3] It is less commonly used compared than statins because it treats a different type of cholesterol abnormality to statins. While statins have strong evidence for reducing heart disease and death, there is evidence to suggest that fenofibrate also reduces the risk of heart disease and death. However, this seems only to apply to specific populations of people with elevated triglyceride levels and reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.[3][4][5] Its use is recommended together with dietary changes.[3]
Common side effects include liver problems, breathing problems, abdominal pain, muscle problems, and nausea.[3] Serious side effects may include toxic epidermal necrolysis, rhabdomyolysis, gallstones, and pancreatitis.[3] Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended.[6][7] It works by multiple mechanisms.[3]
It was patented in 1969, and came into medical use in 1975.[8] It is available as a generic medication.[6] In 2022, it was the 88th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 7 million prescriptions.[9][10]
Fenofibrate is mainly used for primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia. Fenofibrate may slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy and the need for invasive treatment such as laser therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes with pre-existing retinopathy.[11][12][13] It was initially indicated for diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic retinopathy in Australia.[14] The large scale, international FIELD and ACCORD-Eye trials found that fenofibrate therapy reduced required laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy by 1.5% over 5 years, as well as reducing progression by 3.7% over 4 years. [11][12][13][15] Further studies looking at the role of fenofibrate in the progression of diabetic retinopathy as the primary outcome is warranted to understand its role in this condition. Although no statistically significant cardiovascular risk benefits were identified in these trials, benefits may accrue to add on therapy to patients with high triglyceride dyslipidaemia currently taking statin medications.[16][17]
Fenofibrate appears to reduce the risk of below ankle amputations in patients with Type 2 diabetes without microvascular disease.[18] The FIELD study reported that fenofibrate at doses of 200 mg daily, reduced the risk for any amputation by 37% independent of glycaemic control, presence or absence of dyslipidaemia and its lipid-lowering mechanism of action.[18][19] However, the cohort of participants who underwent amputations were more likely to have had previous cardiovascular disease (e.g. angina, myocardial infarction), longer duration of diabetes and had baseline neuropathy.[18][19]
Fenofibrate has an off-label use as an added therapy of high blood uric acid levels in people who have gout.[20]
It is used in addition to diet to reduce elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), total cholesterol, triglycerides (TG), and apolipoprotein B (apo B), and to increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) in adults with primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia.[21]
It is used in tandem with diet for treatment of adults with severe hypertriglyceridemia. Improving glycemic control in diabetics showing fasting chylomicronemia usually reduces the need for pharmacologic intervention.[21]
Statins remain the first line for treatment of blood cholesterol. AHA guidelines from 2013 did not find evidence for routine use of additional medications.[22]
Additionally, in 2016, the FDA filed "Withdrawal of Approval of Indications Related to the Coadministration With Statins in Applications for Niacin Extended-Release Tablets and Fenofibric Acid Delayed Release Capsules" noting "the Agency has concluded that the totality of the scientific evidence no longer supports the conclusion that a drug-induced reduction in triglyceride levels and/or increase in HDL cholesterol levels in statin-treated patients results in a reduction in the risk of cardiovascular events. Consistent with this conclusion, FDA has determined that the benefits of niacin ER tablets and fenofibric acid DR capsules for coadministration with statins no longer outweigh the risks, and the approvals for this indication should be withdrawn."[23]
Fenofibrate is contraindicated in:[21]
The most common adverse events (>3% of patients with coadministered statins) are[24]
When fenofibrate and a statin are given as combination therapy, it is recommended that fenofibrate be given in the morning and the statin at night, so that the peak dosages do not overlap.[25]
Musculoskeletal
Hepatotoxicity
Nephrotoxicity
Biliary
Coagulation/Bleeding
"There is no specific treatment for overdose with fenofibric acid delayed-release capsules. General supportive care is indicated, including monitoring of vital signs and observation of clinical status". Additionally, hemodialysis should not be considered as an overdose treatment option because fenofibrate heavily binds to plasma proteins and does not dialyze well.[24]
These drug interactions with fenofibrate are considered major and may need therapy modifications:
"In summary, enhanced catabolism of triglyceride-rich particles and reduced secretion of VLDL underlie the hypotriglyceridemic effect of fibrates, whereas their effect on HDL metabolism is associated with changes in HDL apolipoprotein expression."[29]
Fenofibrate is a fibrate derivative, a prodrug comprising fenofibric acid linked to an isopropyl ester. It lowers lipid levels by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα). PPARα activates lipoprotein lipase and reduces apoprotein CIII, which increases lipolysis and elimination of triglyceride-rich particles from plasma.[29]
PPARα also increases apoproteins AI and AII, reduces VLDL- and LDL-containing apoprotein B, and increases HDL-containing apoprotein AI and AII.
Fenofibrate is available in several formulations and is sold under several brand names, including:
The formulations may differ in terms of pharmacokinetic properties, particularly bioavailability; some must be taken with meals, whereas others may be taken without regard to food.[30]
The choline salt of fenofibrate is available in the United States, sold as Trilipix, and may be taken without regard to meals.[24][31]
Fenofibric acid was one of the 12 compounds identified in sludge samples taken from 12 wastewater treatment plants in California that were associated with estrogenic activity in in vitro.[32]
Fenofibrate was first synthesized in 1974, as a derivative of clofibrate, and was initially offered in France. It was initially known as procetofen, and was later renamed fenofibrate to comply with World Health Organization International Nonproprietary Name guidelines.[33]
Fenofibrate was developed by Groupe Fournier SA of France.
In the United States, Tricor was reformulated in 2005. This reformulation was controversial, seen as an attempt to stifle competition from generic equivalents,[34] and was the subject of antitrust litigation by Teva.[34]
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link)
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link)